Early marriage often leads to higher risks of health complications and limited educational opportunities, while late marriage is associated with greater financial stability and personal development. Discover detailed insights on the impacts of early versus late marriage in this article.
Table of Comparison
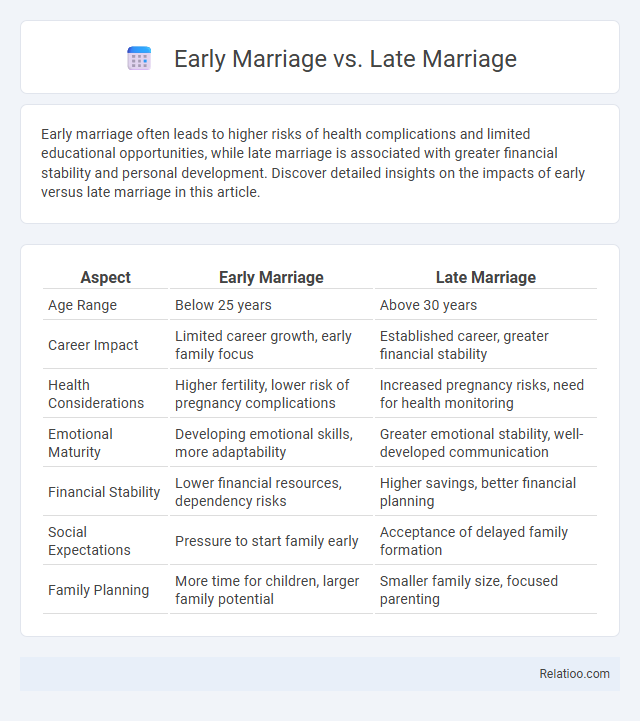
| Aspect | Early Marriage | Late Marriage |
|---|---|---|
| Age Range | Below 25 years | Above 30 years |
| Career Impact | Limited career growth, early family focus | Established career, greater financial stability |
| Health Considerations | Higher fertility, lower risk of pregnancy complications | Increased pregnancy risks, need for health monitoring |
| Emotional Maturity | Developing emotional skills, more adaptability | Greater emotional stability, well-developed communication |
| Financial Stability | Lower financial resources, dependency risks | Higher savings, better financial planning |
| Social Expectations | Pressure to start family early | Acceptance of delayed family formation |
| Family Planning | More time for children, larger family potential | Smaller family size, focused parenting |
Understanding Early Marriage: Definition and Trends
Early marriage, defined as the union of individuals typically under 18 years of age, remains prevalent in many regions due to cultural, economic, and social factors. Trends indicate a gradual decline globally, influenced by increased educational access, legal reforms, and awareness campaigns promoting delayed marriage. Understanding early marriage involves examining its impact on health, education, and economic opportunities, highlighting the benefits of postponing marriage for personal and societal development.
Exploring Late Marriage: Definition and Social Shifts
Late marriage typically refers to individuals marrying in their late 30s or beyond, a trend increasingly seen due to shifting social norms and career priorities. You may find that late marriage allows for greater emotional maturity and financial stability, contributing to stronger, more resilient relationships. This shift reflects broader societal changes, including higher education levels and delayed family planning, reshaping traditional expectations around romance and matrimony.
Emotional Maturity: A Comparison between Early and Late Marriages
Emotional maturity plays a crucial role in the success of both early and late marriages, influencing communication, conflict resolution, and long-term relationship satisfaction. Early marriages often face challenges due to limited life experience and underdeveloped emotional regulation, whereas late marriages benefit from greater self-awareness and stability gained through personal growth. Studies indicate that couples who marry later typically exhibit higher emotional intelligence, leading to stronger emotional bonds and reduced marital stress.
Financial Stability in Early vs Late Marriages
Financial stability plays a crucial role in the success of both early and late marriages, with late marriages often benefiting from greater economic security due to accumulated savings and established careers. Early marriages may face financial challenges as young couples typically have lower incomes, higher debt, and less experience managing joint expenses. Romantic relationships in both contexts require transparent communication about finances to ensure mutual understanding and long-term stability.
Impact on Career Development: Early Marriage vs Late Marriage
Early marriage often limits career development due to increased family responsibilities and reduced time for education or skill enhancement. Late marriage allows individuals to focus more on career growth, education, and professional opportunities before taking on marital commitments. The timing of marriage significantly influences career trajectory, with late marriage typically correlating with higher career advancement and financial stability.
Family Planning and Parenthood Timing
Early marriage often allows for a longer reproductive window, facilitating planned family growth and early parenthood, but may come with challenges of financial stability and emotional maturity. Late marriage typically correlates with greater career establishment and personal development, enabling more deliberate family planning and potentially fewer children due to biological constraints. Romance plays a critical role in both early and late marriages by influencing emotional bonds and decisions around timing for parenthood, impacting overall family dynamics and long-term satisfaction.
Social and Cultural Influences on Marriage Timing
Social and cultural influences significantly shape marriage timing, where early marriage often reflects traditional values and economic factors prevalent in rural or low-income communities. Late marriage is typically associated with urbanization, higher education, and career prioritization, reflecting shifting societal norms and increased individual autonomy. Romantic relationships increasingly influence marriage decisions, highlighting cultural shifts toward personal choice and emotional compatibility over arranged practices.
Health Outcomes Associated with Early and Late Marriages
Early marriage often correlates with increased health risks such as higher rates of maternal mortality, complications during childbirth, and limited access to reproductive health services, negatively impacting both young brides and their children. Late marriage is associated with improved health outcomes, including better access to healthcare, higher education levels, and delayed childbearing, which contribute to lower maternal and infant mortality rates. Your choice between early and late marriage can significantly influence physical and emotional health, highlighting the importance of informed decisions surrounding timing and relationship dynamics.
Divorce Rates and Marital Satisfaction Comparison
Early marriage often correlates with higher divorce rates due to factors like financial instability and emotional immaturity, while late marriage tends to show lower divorce rates and greater marital satisfaction linked to increased maturity and career stability. Romance plays a crucial role in both scenarios, as strong emotional connection and communication positively influence long-term relationship success regardless of marriage age. Your likelihood of marital satisfaction improves when prioritizing emotional compatibility and shared life goals over just the timing of the marriage.
Making the Right Choice: Factors to Consider When Deciding Marriage Timing
Choosing the right timing for marriage involves assessing emotional maturity, financial stability, and life goals to ensure a strong foundation. Early marriage can offer longer shared experiences but may face challenges related to personal growth and career establishment. Late marriage allows for greater self-discovery and financial security but requires balancing romance with realistic expectations about partnership.
Infographic: Early Marriage vs Late Marriage
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com