Adoption and surrogacy are distinct paths to parenthood, with adoption involving legally assuming parenting rights of an existing child, while surrogacy entails a gestational carrier carrying a pregnancy for intended parents. Explore this article to uncover key differences, legal considerations, and emotional impacts between adoption and surrogacy.
Table of Comparison
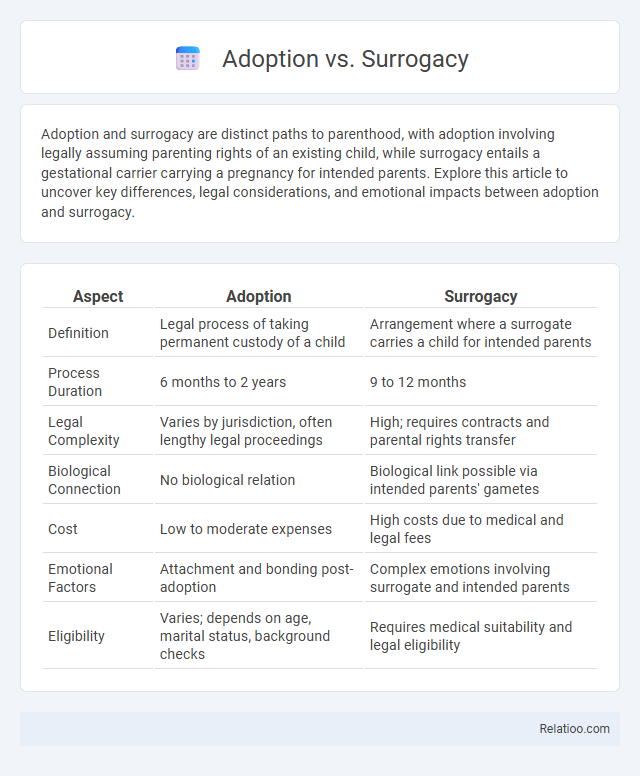
| Aspect | Adoption | Surrogacy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal process of taking permanent custody of a child | Arrangement where a surrogate carries a child for intended parents |
| Process Duration | 6 months to 2 years | 9 to 12 months |
| Legal Complexity | Varies by jurisdiction, often lengthy legal proceedings | High; requires contracts and parental rights transfer |
| Biological Connection | No biological relation | Biological link possible via intended parents' gametes |
| Cost | Low to moderate expenses | High costs due to medical and legal fees |
| Emotional Factors | Attachment and bonding post-adoption | Complex emotions involving surrogate and intended parents |
| Eligibility | Varies; depends on age, marital status, background checks | Requires medical suitability and legal eligibility |
Understanding Adoption: Definition and Process
Adoption is a legal process where parental rights and responsibilities are transferred from the birth parents to the adoptive parents, providing a permanent family for a child. You must navigate legal requirements such as background checks, home studies, and court approvals to complete the adoption process. Understanding the differences between adoption, surrogacy, and fertility treatments helps clarify the unique emotional and legal commitments involved in building your family.
Exploring Surrogacy: Types and Procedures
Surrogacy involves a woman carrying a pregnancy for intended parents and is divided into traditional and gestational types; traditional surrogacy uses the surrogate's egg fertilized by the intended father's sperm, while gestational surrogacy uses an embryo created via IVF with the intended parents' genetic material. The surrogacy process includes medical screening, legal agreements, IVF procedures, embryo transfer, pregnancy monitoring, and post-birth parental rights establishment. Understanding the distinctions and legal frameworks in various jurisdictions is crucial for intended parents navigating surrogacy options.
Legal Considerations in Adoption vs Surrogacy
Legal considerations in adoption versus surrogacy differ significantly, impacting parental rights and responsibilities. Adoption involves permanent transfer of parental rights through a court process, often requiring background checks and consent from birth parents, while surrogacy agreements necessitate detailed contracts that clarify custody and parental rights before birth. You should carefully review state laws and consult specialized legal counsel to navigate these complex regulations and ensure your parental status is legally recognized.
Emotional Journey: Adoption vs Surrogacy Experiences
Adoption and surrogacy both involve complex emotional journeys shaped by unique challenges and profound hopes for parenthood. Adoption often brings experiences of bonding with a child from a different background and managing feelings related to loss, identity, and connection, while surrogacy presents emotional dynamics around the biological link, trust with the surrogate, and navigating medical procedures. Fertility treatments add another layer of emotional resilience, as couples face cycles of hope and disappointment on their path to family building.
Costs Involved: Financial Comparison
Adoption costs typically range from $20,000 to $45,000, including agency fees, legal expenses, and travel, while surrogacy expenses average between $90,000 and $150,000 due to medical procedures, surrogate compensation, and legal fees. Fertility treatments such as IVF can cost $12,000 to $15,000 per cycle, with multiple cycles often required, significantly impacting total expenses. Comparing these options highlights that surrogacy generally incurs the highest financial commitment, followed by adoption, with fertility treatments varying widely depending on success rates and treatment cycles.
Eligibility Requirements for Prospective Parents
Eligibility requirements for adoption typically include age limits, stable financial status, and background checks to ensure a safe environment for the child. Surrogacy demands medical evaluations for both the surrogate and intended parents along with legal agreements confirming parental rights. Fertility treatments require comprehensive medical assessments, including hormone levels and reproductive health, to determine the best approach for prospective parents.
Impact on Family Dynamics
Adoption reshapes family dynamics by integrating a legally unrelated child, often requiring adjustments in identity and bonding processes. Surrogacy involves biological connections that can influence relationships with the surrogate and intended parents, affecting emotional and relational boundaries. Your choice among adoption, surrogacy, or fertility treatments profoundly impacts how family roles and attachments develop, necessitating careful consideration of long-term emotional implications.
Ethical Issues and Social Perspectives
Ethical issues in adoption revolve around the child's best interests, consent, and potential exploitation, while surrogacy raises concerns about commodification of the body, legal parental rights, and exploitation of surrogate mothers. Fertility treatments provoke debates over embryo rights, accessibility, and the impact on traditional family structures. Your decision intersects with complex social perspectives, including cultural acceptance, stigma, and the evolving definitions of family and parenthood.
Long-term Outcomes for Children
Long-term outcomes for children born through adoption, surrogacy, and fertility treatments reveal varied developmental and psychological profiles influenced by family dynamics and support systems. Research indicates children from adoption may face identity challenges but often benefit from stable, nurturing environments that promote resilience. Surrogacy and fertility-conceived children generally show comparable emotional and cognitive development to naturally conceived peers, emphasizing the role of early bonding and parental involvement.
Choosing What’s Right for Your Family
Choosing between adoption, surrogacy, and fertility treatments requires understanding each option's emotional, financial, and legal implications. Adoption offers the opportunity to provide a home for a child in need, often involving lengthy legal processes and potential wait times. Surrogacy and fertility treatments, including IVF, offer biological connections but may require significant medical intervention and associated costs, making personalized counseling and thorough research essential for family planning decisions.
Infographic: Adoption vs Surrogacy
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com