Self-forgiveness involves releasing guilt and accepting personal mistakes, while self-compassion emphasizes treating oneself with kindness and understanding during challenges. Discover how balancing self-forgiveness and self-compassion can transform your relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
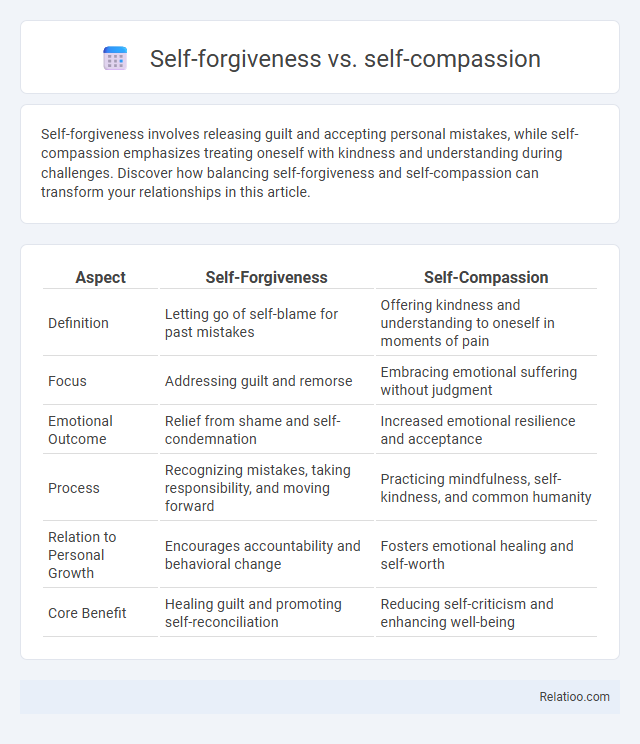
| Aspect | Self-Forgiveness | Self-Compassion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Letting go of self-blame for past mistakes | Offering kindness and understanding to oneself in moments of pain |
| Focus | Addressing guilt and remorse | Embracing emotional suffering without judgment |
| Emotional Outcome | Relief from shame and self-condemnation | Increased emotional resilience and acceptance |
| Process | Recognizing mistakes, taking responsibility, and moving forward | Practicing mindfulness, self-kindness, and common humanity |
| Relation to Personal Growth | Encourages accountability and behavioral change | Fosters emotional healing and self-worth |
| Core Benefit | Healing guilt and promoting self-reconciliation | Reducing self-criticism and enhancing well-being |
Understanding Self-Forgiveness
Understanding self-forgiveness involves recognizing personal mistakes without harsh judgment, allowing emotional healing and growth. Unlike self-compassion, which emphasizes kindness toward oneself in suffering, self-forgiveness specifically addresses releasing guilt and resentment related to past actions. Cultivating self-forgiveness promotes mental well-being by reducing shame and fostering accountability and self-acceptance.
Defining Self-Compassion
Self-compassion involves treating Yourself with kindness and understanding during times of failure or suffering, recognizing that imperfection is part of the shared human experience. Unlike self-forgiveness, which focuses on releasing guilt and accepting past mistakes, self-compassion emphasizes emotional support and mindfulness without harsh self-judgment. Embracing self-compassion fosters resilience by promoting a balanced, nurturing inner dialogue that encourages healing and growth.
Key Differences Between Self-Forgiveness and Self-Compassion
Self-forgiveness involves acknowledging personal mistakes and making amends, focusing on releasing guilt and self-punishment. Self-compassion emphasizes treating oneself with kindness and understanding during suffering or failure, promoting emotional resilience without necessarily addressing specific actions. The key difference lies in self-forgiveness targeting past wrongdoings, while self-compassion centers on emotional support regardless of context.
Psychological Benefits of Self-Forgiveness
Self-forgiveness offers profound psychological benefits by reducing feelings of guilt and shame, leading to improved emotional well-being and mental health. Unlike self-compassion, which emphasizes kindness towards oneself, self-forgiveness specifically addresses past mistakes and promotes acceptance, helping you release negative self-judgment and foster inner peace. This process enhances resilience, reduces anxiety and depression, and supports a healthier self-image essential for personal growth.
The Role of Self-Compassion in Emotional Well-being
Self-compassion plays a crucial role in emotional well-being by fostering a kind and understanding attitude towards oneself during times of failure or suffering, which helps reduce negative self-judgment and emotional distress. Unlike self-forgiveness, which focuses on releasing guilt for specific past actions, self-compassion encompasses broader acceptance and nurturance, promoting resilience and psychological healing. Studies show that higher levels of self-compassion are linked to lower rates of anxiety, depression, and stress, making it essential for maintaining mental health and emotional balance.
Self-Forgiveness and Guilt Resolution
Self-forgiveness involves acknowledging personal mistakes and releasing self-directed guilt, which plays a crucial role in emotional healing and guilt resolution. Unlike self-compassion, which emphasizes kindness and understanding toward oneself, self-forgiveness actively addresses feelings of shame and responsibility to overcome negative self-judgment. Effective guilt resolution through self-forgiveness promotes psychological well-being and reduces the risk of chronic self-punishment and associated mental health issues.
Self-Compassion as a Tool for Inner Healing
Self-compassion serves as a powerful tool for inner healing by fostering a non-judgmental awareness and kindness toward one's own suffering, which differs from self-forgiveness that specifically addresses letting go of guilt for past mistakes. Unlike self-forgiveness, which resolves personal accountability and regret, self-compassion promotes emotional resilience and reduces harsh self-criticism, creating a supportive internal environment for growth. Psychological studies highlight that cultivating self-compassion can lead to improved mental health outcomes, including reduced anxiety and depression, by encouraging acceptance and gentle self-care amid challenges.
Steps to Cultivate Self-Forgiveness
Cultivating self-forgiveness involves recognizing your mistakes without harsh judgment, understanding the context behind your actions, and committing to personal growth. Self-compassion supports this process by encouraging kindness toward yourself during moments of failure, while self-forgiveness specifically focuses on releasing guilt and self-blame. To foster self-forgiveness, you can practice mindfulness, write a letter of apology to yourself, and replace negative self-talk with affirming statements.
How to Practice Self-Compassion Daily
Practicing self-compassion daily involves treating your imperfections with kindness instead of harsh judgment, recognizing that everyone experiences suffering and setbacks as part of the human condition. Techniques include mindful awareness to observe negative thoughts without over-identifying, and self-soothing practices like positive affirmations or gentle physical touch to comfort yourself. Cultivating self-compassion enhances emotional resilience and promotes mental wellness more effectively than self-forgiveness alone, as it fosters consistent care rather than occasional absolution.
Integrating Self-Forgiveness and Self-Compassion for Personal Growth
Integrating self-forgiveness and self-compassion creates a powerful foundation for personal growth by helping you release guilt while nurturing kindness toward yourself. Self-forgiveness addresses past mistakes with accountability and release, whereas self-compassion offers emotional support through understanding and acceptance. Combining these approaches fosters resilience, improved mental health, and a balanced sense of self-worth essential for transformational change.
Infographic: Self-forgiveness vs Self-compassion
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com