Grace offers unconditional forgiveness and healing in relationships, while justice emphasizes fairness and accountability. Explore how balancing grace and justice transforms connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
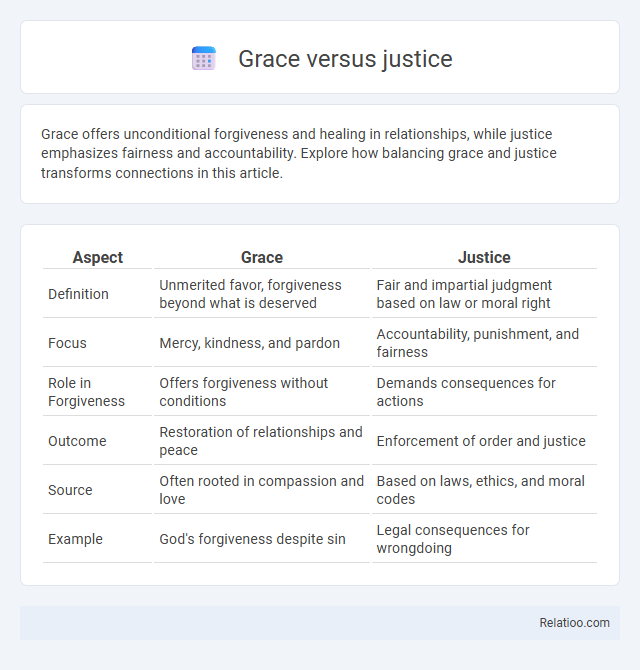
| Aspect | Grace | Justice |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unmerited favor, forgiveness beyond what is deserved | Fair and impartial judgment based on law or moral right |
| Focus | Mercy, kindness, and pardon | Accountability, punishment, and fairness |
| Role in Forgiveness | Offers forgiveness without conditions | Demands consequences for actions |
| Outcome | Restoration of relationships and peace | Enforcement of order and justice |
| Source | Often rooted in compassion and love | Based on laws, ethics, and moral codes |
| Example | God's forgiveness despite sin | Legal consequences for wrongdoing |
Understanding the Concepts: Grace and Justice
Grace embodies unmerited favor and forgiveness granted regardless of merit, while justice involves fair and impartial treatment based on law and moral rightness. Understanding these concepts helps you appreciate how grace offers mercy where justice demands accountability, highlighting the balance between compassion and righteousness. This distinction shapes ethical decision-making, legal frameworks, and personal conduct by integrating empathy without compromising fairness.
Historical Perspectives on Grace and Justice
Historical perspectives on grace and justice reveal evolving interpretations influenced by religious, legal, and philosophical contexts. Early Christian theology emphasized grace as unmerited divine favor contrasting with justice as strict adherence to moral law, shaping notions of salvation and mercy. Legal history reflects tension between justice as fair retribution and grace as altruistic leniency, influencing judicial reforms and societal values over centuries.
Philosophical Foundations: Comparing Grace and Justice
Grace embodies unconditional mercy that transcends strict legal or moral obligations, reflecting a philosophy of compassion and forgiveness beyond deservedness. Justice operates on principles of fairness, retribution, and accountability, emphasizing balance through proportional response to actions. Philosophically, grace challenges justice by introducing benevolence that surpasses transactional fairness, suggesting ethical frameworks grounded in love and mercy rather than solely on rights and duties.
Grace and Justice in Religious Teachings
Grace represents unmerited divine favor, emphasizing God's unconditional love and forgiveness, while Justice concerns the moral rightness and accountability for actions according to religious law. Your understanding deepens when recognizing that Grace offers redemption beyond the strict consequences of Justice, highlighting mercy over judgment. Religious teachings often balance these concepts to illustrate the coexistence of divine compassion with righteous order.
The Role of Grace in Legal Systems
Grace in legal systems serves as a compassionate override to strict justice, allowing judges or authorities to mitigate punishment or grant forgiveness despite established laws. Your understanding of grace highlights its function as a vital mechanism for mercy and humaneness, balancing retribution with empathy. This interplay between grace and justice ensures legal outcomes can reflect fairness beyond rigid rule enforcement.
Justice as a Pillar of Social Order
Justice serves as a fundamental pillar of social order, ensuring fairness and equity in the distribution of rights and responsibilities within a community. Your role in advocating for justice helps maintain balance and accountability, preventing societal chaos and fostering trust among members. While grace emphasizes mercy and forgiveness, justice upholds the structures that support stability and the rule of law.
Balancing Grace and Justice in Everyday Life
Balancing grace and justice in everyday life requires recognizing the value of empathy while maintaining accountability. Grace allows for forgiveness and understanding when mistakes occur, fostering personal growth and harmonious relationships. Justice ensures fairness and upholds boundaries, creating a stable foundation for trust and respect within communities.
Conflicts and Reconciliation Between Grace and Justice
Conflicts between grace and justice often arise when mercy appears to contradict fairness, challenging legal and ethical standards. Justice demands accountability and retribution, while grace emphasizes forgiveness and compassion, creating tension in judgments and decision-making. Your ability to reconcile grace and justice is essential for balanced resolutions that respect moral integrity and human dignity.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Grace vs Justice
Case studies reveal nuanced differences between grace and justice, as seen in the legal rulings of the South African Truth and Reconciliation Commission, which prioritized restorative justice and offered amnesty to promote healing. In educational settings, teachers who implement grace through flexible deadlines and understanding help students learn from mistakes, contrasting with strict justice that enforces uniform penalties. Corporate ethics often struggle to balance justice, ensuring accountability through policies, with grace, offering forgiveness to employees facing personal hardships.
The Future of Grace and Justice in Society
The future of grace and justice in society hinges on balancing compassionate understanding with equitable legal frameworks. Emerging social movements emphasize restorative justice, integrating grace to promote healing and reduce recidivism. Advances in policy-making and community engagement aim to foster environments where forgiveness and accountability coexist, shaping a more humane and fair future.
Infographic: Grace vs Justice
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com