Self-compassion involves treating yourself with kindness during difficult times, while self-acceptance means embracing all aspects of yourself without judgment. Discover how cultivating both can transform your relationship with yourself and others in this article.
Table of Comparison
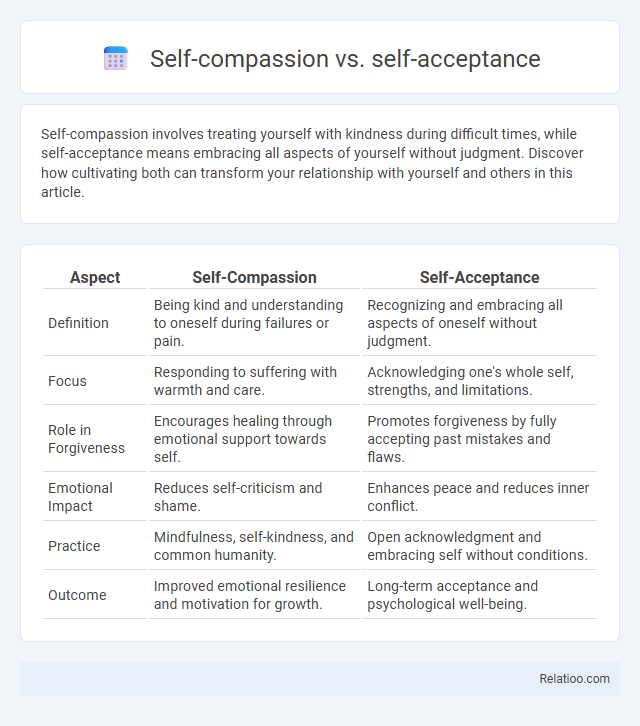
| Aspect | Self-Compassion | Self-Acceptance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Being kind and understanding to oneself during failures or pain. | Recognizing and embracing all aspects of oneself without judgment. |
| Focus | Responding to suffering with warmth and care. | Acknowledging one's whole self, strengths, and limitations. |
| Role in Forgiveness | Encourages healing through emotional support towards self. | Promotes forgiveness by fully accepting past mistakes and flaws. |
| Emotional Impact | Reduces self-criticism and shame. | Enhances peace and reduces inner conflict. |
| Practice | Mindfulness, self-kindness, and common humanity. | Open acknowledgment and embracing self without conditions. |
| Outcome | Improved emotional resilience and motivation for growth. | Long-term acceptance and psychological well-being. |
Understanding Self-Compassion
Understanding self-compassion involves recognizing and treating oneself with kindness during moments of failure or suffering, rather than harsh self-criticism. Differing from self-acceptance, which emphasizes embracing oneself unconditionally, self-compassion actively encourages supportive inner dialogue to foster emotional resilience. Compared to self-esteem, which relies on evaluating personal worth, self-compassion provides a stable foundation by promoting inherent kindness regardless of external achievements.
Defining Self-Acceptance
Self-acceptance involves recognizing and embracing all aspects of oneself, including strengths and weaknesses, without judgment or denial. It is a core component of psychological well-being that promotes resilience and reduces negative self-evaluation. Unlike self-compassion, which entails kindness toward oneself during suffering, and self-esteem, which relies on self-evaluation, self-acceptance is unconditional and fosters inner peace.
Key Differences Between Self-Compassion and Self-Acceptance
Self-compassion involves treating Yourself with kindness and understanding during moments of failure or suffering, emphasizing emotional resilience and reducing self-criticism. Self-acceptance focuses on embracing all aspects of Your identity and experiences without judgment, fostering a stable sense of self-worth regardless of circumstances. The key difference lies in self-compassion's active response to adversity, while self-acceptance represents a steady, unconditional embrace of who You are at any moment.
The Psychological Benefits of Self-Compassion
Self-compassion involves treating yourself with kindness and understanding during times of failure or suffering, which significantly reduces stress and promotes emotional resilience. Unlike self-acceptance, which focuses on acknowledging your traits without judgment, self-compassion actively encourages supportive internal dialogue that enhances mental well-being. You can experience lower anxiety, improved motivation, and better coping strategies by cultivating self-compassion in daily life.
The Impact of Self-Acceptance on Well-being
Self-acceptance significantly enhances well-being by fostering emotional resilience and reducing stress levels, as supported by numerous psychological studies. Unlike self-compassion, which involves treating oneself kindly during hardship, self-acceptance entails embracing all aspects of oneself, including flaws and limitations, promoting a stable and positive self-view. Research indicates that higher self-acceptance correlates with lower rates of depression and anxiety, contributing to overall mental health and life satisfaction.
Common Misconceptions About Self-Compassion
Self-compassion is often confused with self-acceptance and self-esteem, but it specifically involves treating yourself with kindness during moments of failure or suffering rather than simply accepting all aspects of yourself or feeling proud. Many people mistakenly believe self-compassion means being self-indulgent or complacent, when in fact, it promotes resilience and emotional well-being by encouraging mindful awareness and understanding. Your practice of self-compassion can transform how you respond to challenges by fostering a balanced, gentle approach that counteracts harsh self-criticism.
Myths and Truths of Self-Acceptance
Self-acceptance is often misunderstood as passive resignation or ignoring personal flaws, but it actually involves embracing all aspects of oneself without harsh judgment. Unlike the myth that self-acceptance leads to complacency, research shows it fosters resilience and motivation for growth by reducing self-criticism. Self-compassion complements self-acceptance by encouraging kindness towards oneself during failure, distinguishing it from the misconception that self-acceptance equates to a lack of personal accountability.
Cultivating Self-Compassion: Practical Strategies
Cultivating self-compassion involves recognizing your own suffering with kindness, rather than harsh judgment, and embracing your imperfections as part of being human. Practical strategies include mindful self-awareness, positive self-talk, and developing a nurturing inner voice to replace critical thoughts. These techniques foster emotional resilience and promote overall well-being by deepening your capacity for self-acceptance and authentic self-care.
Developing Genuine Self-Acceptance: Actionable Tips
Developing genuine self-acceptance involves recognizing your intrinsic worth without harsh judgment or unrealistic expectations, distinguishing it from self-compassion which emphasizes kindness during failure, and from self-esteem linked to achievements. Actionable tips include practicing mindfulness to observe thoughts non-judgmentally, journaling to identify and challenge negative self-beliefs, and setting realistic goals aligned with personal values to foster authentic self-acknowledgment. These strategies create a foundation for enduring self-acceptance that promotes emotional resilience and well-being.
Choosing Between Self-Compassion and Self-Acceptance for Personal Growth
Choosing between self-compassion and self-acceptance for personal growth involves understanding their distinct roles: self-compassion encourages kindness and understanding during setbacks, while self-acceptance promotes embracing all aspects of yourself without judgment. You benefit most by integrating self-compassion's nurturing support with self-acceptance's unconditional embrace, fostering resilience and motivation simultaneously. Research indicates that combining these practices enhances emotional well-being and accelerates progress toward your goals.
Infographic: Self-compassion vs Self-acceptance
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com