Admission fosters trust and openness in relationships, allowing for authentic communication and deeper connection. Explore this article to understand how choosing admission over denial can strengthen your bonds.
Table of Comparison
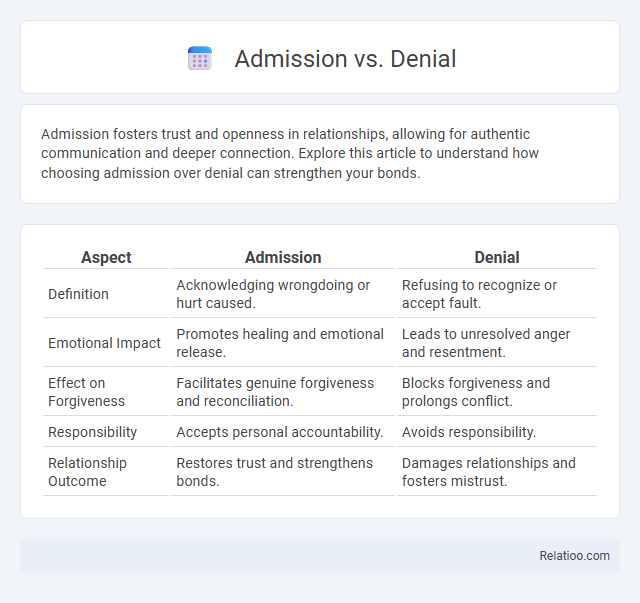
| Aspect | Admission | Denial |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Acknowledging wrongdoing or hurt caused. | Refusing to recognize or accept fault. |
| Emotional Impact | Promotes healing and emotional release. | Leads to unresolved anger and resentment. |
| Effect on Forgiveness | Facilitates genuine forgiveness and reconciliation. | Blocks forgiveness and prolongs conflict. |
| Responsibility | Accepts personal accountability. | Avoids responsibility. |
| Relationship Outcome | Restores trust and strengthens bonds. | Damages relationships and fosters mistrust. |
Understanding Admission and Denial: Core Concepts
Understanding admission and denial is crucial in mastering logical reasoning and decision-making processes. Admission involves accepting a statement or fact as true, forming the basis for further analysis or action, while denial rejects or disputes a statement, preventing acceptance of that information. Your ability to accurately distinguish between admission and denial ensures clearer communication, critical evaluation, and effective problem-solving in various contexts.
Psychological Foundations of Admission and Denial
Admission and denial play crucial roles in psychological processes, particularly in self-awareness and defense mechanisms. Admission involves acknowledging reality or emotions, promoting mental health congruence and reducing internal conflict, while denial acts as a protective barrier, shielding individuals from distress by rejecting uncomfortable truths. Understanding the dynamics between these mechanisms enhances insight into coping strategies and therapeutic interventions.
The Role of Truth in Admission and Denial
The role of truth in admission and denial is central to establishing credibility and transparency in legal and interpersonal contexts, as admission involves acknowledging facts or actions that are accurate and verifiable. Denial, contrastingly, serves as a defensive mechanism to reject false or unsubstantiated claims, emphasizing the necessity to differentiate between truthful and misleading statements. Balancing admission and denial requires a nuanced understanding of truth to ensure accountability and prevent misinformation.
Social Impacts: How Admission and Denial Affect Relationships
Admission fosters trust and open communication in relationships, strengthening emotional bonds and promoting mutual understanding. Denial often leads to misunderstandings, resentment, and weakened connections, as unacknowledged issues can fester over time. Your willingness to admit mistakes or feelings plays a crucial role in cultivating empathy and maintaining healthy social dynamics.
Legal Perspectives: Admission vs Denial in the Courtroom
In legal proceedings, admission refers to a party acknowledging the truth of a statement or fact, which can significantly impact the case's outcome by streamlining issues for the court. Denial involves disputing the accuracy or validity of an opposing party's assertion, requiring evidence to counter the claim and maintain your position. Understanding the strategic use of admission versus denial is crucial for effective courtroom advocacy and protecting your legal rights.
Strategies for Encouraging Admission
Encouraging admission in conflict resolution involves fostering an environment of trust and open communication, which increases the likelihood of acknowledging facts or mistakes. Strategies include active listening, asking open-ended questions, and providing evidence that gently challenges denial without triggering defensiveness. Utilizing empathy and creating a non-judgmental space can effectively shift denial towards acceptance and constructive admission.
Common Motivations Behind Denial
Denial often stems from emotional self-protection, where Your mind resists painful truths to avoid psychological discomfort. Common motivations include fear of vulnerability, desire to maintain control, and inability to accept change or failure. Understanding these drives can help you recognize when denial is obstructing personal growth and decision-making.
Consequences of Prolonged Denial
Prolonged denial can lead to significant emotional and psychological consequences, including increased anxiety, stress, and impaired mental health. Admitting your feelings or situation fosters self-awareness and promotes healing by allowing you to address underlying issues constructively. Choosing admission over denial ultimately supports healthier coping mechanisms and improves overall well-being.
Cultural Differences in Admission and Denial
Admission and denial processes are heavily influenced by cultural norms, which shape how individuals express acceptance or refusal. In some cultures, admission is conveyed through direct verbal affirmation, while others rely on nonverbal cues or indirect language to imply consent or denial. Understanding these cultural differences is crucial for accurate communication in international contexts, as misinterpretation of admission or denial can lead to misunderstandings.
Overcoming Denial: Steps Toward Acceptance
Overcoming denial involves recognizing and acknowledging the reality of a situation to move toward acceptance and healing. Key steps include practicing self-awareness, seeking support through therapy or support groups, and gradually confronting the emotions and facts previously avoided. Embracing acceptance can lead to personal growth, improved mental health, and the ability to make informed decisions moving forward.
Infographic: Admission vs Denial
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com