Self-compassion enhances emotional resilience and personal growth, while compassion for others strengthens social bonds and empathy. Explore how balancing these qualities improves relationship dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
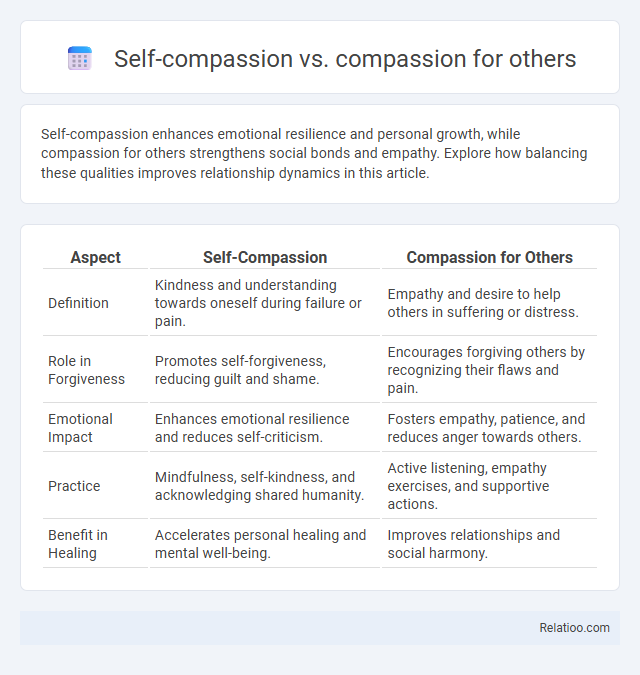
| Aspect | Self-Compassion | Compassion for Others |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Kindness and understanding towards oneself during failure or pain. | Empathy and desire to help others in suffering or distress. |
| Role in Forgiveness | Promotes self-forgiveness, reducing guilt and shame. | Encourages forgiving others by recognizing their flaws and pain. |
| Emotional Impact | Enhances emotional resilience and reduces self-criticism. | Fosters empathy, patience, and reduces anger towards others. |
| Practice | Mindfulness, self-kindness, and acknowledging shared humanity. | Active listening, empathy exercises, and supportive actions. |
| Benefit in Healing | Accelerates personal healing and mental well-being. | Improves relationships and social harmony. |
Understanding Self-Compassion: Definition and Importance
Self-compassion involves treating Yourself with kindness, recognizing your shared humanity, and maintaining mindfulness during difficult times, which promotes emotional resilience and reduces stress. Compassion for others focuses on empathy and a desire to alleviate another's suffering, fostering stronger social bonds and support networks. Understanding self-compassion enables You to balance caring for Yourself while maintaining healthy relationships through compassionate practices.
Defining Compassion for Others: Key Elements
Compassion for others involves recognizing their suffering, feeling empathy, and taking actionable steps to alleviate their pain or distress. It requires emotional resonance with others' experiences and a genuine desire to support and help without judgment. Understanding these key elements helps you cultivate meaningful connections and foster a more empathetic and caring environment.
Core Differences Between Self-Compassion and Compassion for Others
Self-compassion involves treating Your own suffering with kindness, recognizing personal imperfections, and maintaining a balanced perspective on one's failures, which fosters emotional resilience. Compassion for others centers on empathizing with others' pain and actively seeking to alleviate their distress, highlighting an outward focus on another's well-being. Core differences between self-compassion and compassion for others lie in the subject of care--self versus others--and the internal versus external application of empathy and kindness.
Psychological Benefits of Self-Compassion
Self-compassion provides significant psychological benefits by promoting emotional resilience, reducing anxiety, and enhancing overall well-being through self-kindness and mindfulness. While compassion for others fosters social connection and empathy, self-compassion directly improves your mental health by helping you overcome negative self-judgment and maintain a balanced perspective during challenging times. Prioritizing self-compassion creates a foundation for emotional healing, which ultimately supports healthier relationships and greater life satisfaction.
The Social Impact of Compassion for Others
Compassion for others significantly enhances social cohesion by fostering empathy, trust, and prosocial behavior within communities, which leads to stronger interpersonal relationships and collective well-being. This form of compassion activates neural circuits linked to social bonding and altruism, promoting cooperative interactions and reducing social conflicts. While self-compassion improves individual mental health, compassion for others drives social harmony and collective resilience, making it a crucial factor in building supportive, interconnected societies.
Common Misconceptions About Self-Compassion
Common misconceptions about self-compassion include the belief that it promotes selfishness or self-pity, when in fact, self-compassion involves treating oneself with the same kindness and understanding offered to others during times of suffering. Unlike compassion for others, which emphasizes empathy and support outwardly, self-compassion requires the internalization of this kindness to foster emotional resilience and mental well-being. Research shows that self-compassion enhances motivation and reduces anxiety, debunking the myth that it leads to complacency or indulgence.
Balancing Self-Care and Caring for Others
Balancing self-care and caring for others requires understanding the distinct roles of self-compassion and compassion for others; self-compassion nurtures your emotional resilience by promoting kindness toward yourself during personal struggles. Compassion for others fosters empathy and support, strengthening social bonds and enhancing collective well-being. Prioritizing both creates a sustainable cycle where caring for yourself rejuvenates your ability to care deeply for others without burnout.
Barriers to Practicing Compassion Towards Oneself and Others
Barriers to practicing compassion towards oneself often include harsh self-criticism, low self-worth, and fear of vulnerability, which hinder your ability to extend kindness inward. When it comes to compassion for others, obstacles such as judgment, emotional burnout, and social biases can prevent genuine empathetic connection. Overcoming these hurdles requires cultivating mindful awareness and embracing imperfections in both yourself and those around you.
Cultivating Self-Compassion: Practical Strategies
Cultivating self-compassion involves embracing mindfulness, self-kindness, and recognizing shared human experiences, which strengthens your emotional resilience and well-being. Practicing techniques such as guided meditations, journaling positive affirmations, and setting healthy boundaries enhances your ability to treat yourself with the same kindness you offer others. These strategies foster a balanced relationship between self-compassion and compassion for others, improving overall mental health and interpersonal connections.
Integrating Compassion for Others Into Daily Life
Integrating compassion for others into daily life enhances emotional resilience and strengthens social connections by fostering empathy and understanding. Practicing self-compassion alongside compassion for others creates a balanced mindset, promoting kindness towards oneself and preventing burnout. Daily acts such as active listening, mindful communication, and small altruistic gestures enrich relationships and cultivate a sustained compassionate environment.
Infographic: Self-compassion vs Compassion for others
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com