Parentification occurs when children assume adult responsibilities, impacting their emotional development, while enmeshment blurs boundaries, causing identity and autonomy challenges in relationships. Explore this article to understand the nuances and effects of parentification and enmeshment on family dynamics.
Table of Comparison
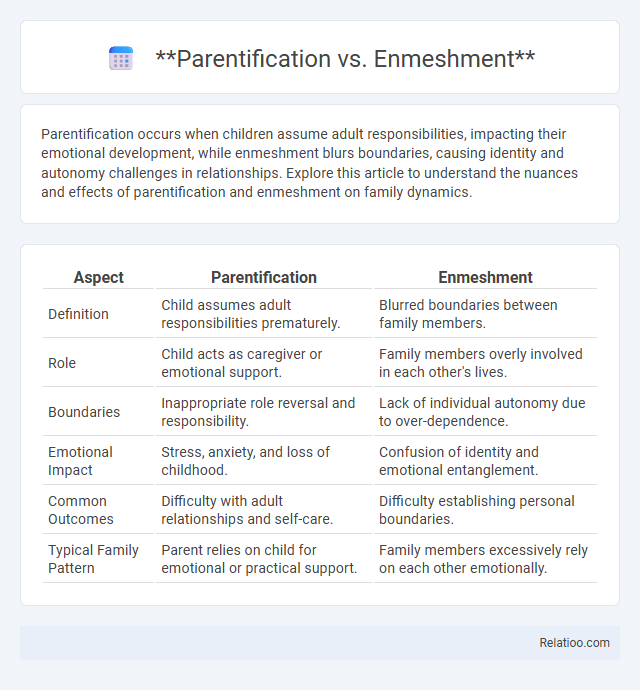
| Aspect | Parentification | Enmeshment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Child assumes adult responsibilities prematurely. | Blurred boundaries between family members. |
| Role | Child acts as caregiver or emotional support. | Family members overly involved in each other's lives. |
| Boundaries | Inappropriate role reversal and responsibility. | Lack of individual autonomy due to over-dependence. |
| Emotional Impact | Stress, anxiety, and loss of childhood. | Confusion of identity and emotional entanglement. |
| Common Outcomes | Difficulty with adult relationships and self-care. | Difficulty establishing personal boundaries. |
| Typical Family Pattern | Parent relies on child for emotional or practical support. | Family members excessively rely on each other emotionally. |
Defining Parentification and Enmeshment
Parentification occurs when a child is assigned adult responsibilities, such as caregiving or emotional support, disrupting their normal developmental role. Enmeshment describes a blurred boundary between parent and child, where individuality is compromised due to excessive emotional closeness or dependence. Understanding these dynamics helps you recognize unhealthy family patterns and their impact on emotional well-being.
Key Differences Between Parentification and Enmeshment
Parentification occurs when a child is given adult responsibilities prematurely, such as caregiving or emotional support, while enmeshment involves blurred boundaries where the child's sense of self becomes merged with the parent's identity. Key differences include that parentification imposes role reversal and burden on the child, whereas enmeshment limits the child's individuation and autonomy through excessive emotional dependence. Understanding these distinctions helps in identifying appropriate therapeutic interventions addressing boundary issues versus role confusion.
Types of Parentification
Parentification involves a child taking on adult responsibilities, categorized into emotional parentification, where the child meets the parent's emotional needs, and instrumental parentification, which includes practical tasks like caregiving or managing household duties. Enmeshment describes blurred boundaries between parent and child, leading to a lack of autonomy but differs as it doesn't necessarily assign adult roles to the child. Understanding these distinctions helps you recognize when your child is assuming excessive roles that may impact their development and well-being.
Signs and Symptoms of Enmeshment
Enmeshment is characterized by blurred boundaries between You and your family members, leading to excessive emotional involvement and loss of individuality. Signs and symptoms include difficulty making decisions independently, feeling responsible for others' emotions, and a lack of personal privacy. Unlike parentification, where a child takes on parental roles, enmeshment involves a fusion of identities that hinders healthy emotional separation.
Causes of Parentification in Families
Parentification in families often stems from role reversal where children take on adult responsibilities due to parental incapacity caused by factors like addiction, mental illness, or chronic stress. Enmeshment blurs boundaries by fostering excessive emotional dependence, whereas parentification imposes caregiving roles on children prematurely, impacting their development. Understanding these causes helps you recognize unhealthy family dynamics and seek appropriate support for healthier relationships.
Psychological Impacts of Enmeshment
Enmeshment blurs boundaries between family members, leading to role confusion and emotional dependency, which can hinder Your ability to develop a strong, independent identity. Unlike parentification, where a child assumes parental responsibilities, enmeshment traps individuals in overly close, intrusive relationships that limit autonomy and create long-term psychological stress. The emotional impact often includes anxiety, low self-esteem, and difficulty establishing healthy adult relationships.
Long-Term Effects on Children
Parentification involves children assuming adult responsibilities prematurely, often leading to heightened stress, reduced self-esteem, and difficulty forming boundaries in adulthood. Enmeshment blurs emotional boundaries between parent and child, causing identity diffusion and impaired autonomy, which can result in dependency and relational challenges later in life. Long-term effects of both dynamics may include anxiety, depression, and challenges in establishing healthy adult relationships, with parentification emphasizing role reversal and enmeshment focusing on emotional entanglement.
How to Identify Unhealthy Family Boundaries
Unhealthy family boundaries can be identified by recognizing patterns of role reversal where children perform parental duties, a hallmark of parentification, often leading to emotional burden and stress. Enmeshment is characterized by blurred interpersonal boundaries, where family members are overly involved in each other's lives, inhibiting autonomy and fostering dependence. Signs like lack of privacy, emotional fusion, and children managing adult conflicts are key indicators distinguishing these dynamics and signaling the need for clearer, healthier family roles.
Strategies for Healing and Recovery
Healing from parentification and enmeshment requires setting clear boundaries and developing a strong sense of individual identity separate from family roles. Therapeutic approaches like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and family therapy help address underlying emotional wounds and improve communication dynamics. Building supportive relationships outside the family fosters resilience and promotes healthier patterns of attachment and self-care.
When to Seek Professional Help
Recognizing the signs of parentification, enmeshment, or role reversal in your family can be challenging, but seeking professional help is crucial when these patterns interfere with your emotional well-being or relationships. You should consider therapy if you experience persistent feelings of overwhelm, loss of identity, or difficulty setting boundaries due to caregiving responsibilities that are inappropriate for your age or role. Mental health professionals can provide strategies to restore healthy family dynamics and support your personal growth.
Infographic: Parentification vs Enmeshment
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com