Nuclear families typically provide stable economic and emotional support, while single-parent families often face challenges balancing work and childcare, impacting children's development differently. Explore key differences and their effects on family dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
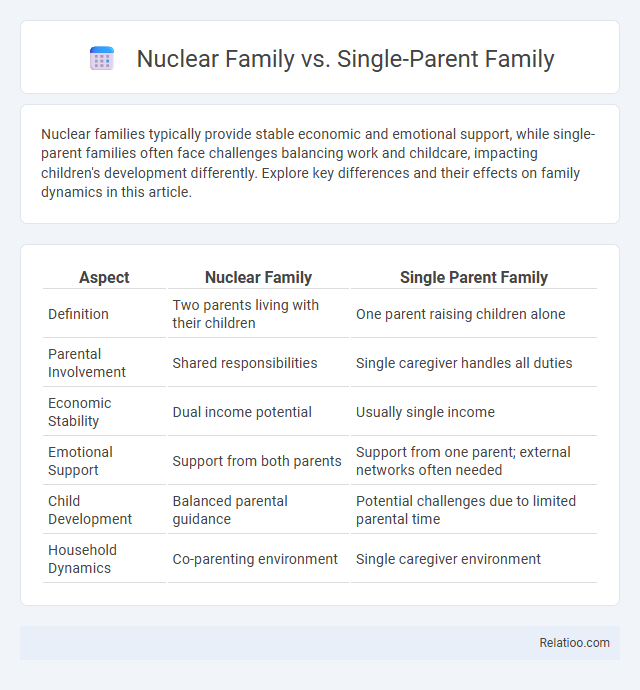
| Aspect | Nuclear Family | Single Parent Family |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Two parents living with their children | One parent raising children alone |
| Parental Involvement | Shared responsibilities | Single caregiver handles all duties |
| Economic Stability | Dual income potential | Usually single income |
| Emotional Support | Support from both parents | Support from one parent; external networks often needed |
| Child Development | Balanced parental guidance | Potential challenges due to limited parental time |
| Household Dynamics | Co-parenting environment | Single caregiver environment |
Introduction to Family Structures
Nuclear families consist of two parents and their children living together, forming a traditional household model with shared responsibilities and resources. Single parent families are headed by one adult, often balancing childcare and economic duties independently, which impacts family dynamics and resource allocation. Extended families include multiple generations or relatives under one roof, offering broader support networks but more complex relationships.
Defining Nuclear Family
A nuclear family consists of two parents and their children living together as a single unit, providing a stable and structured environment for child development. In contrast, a single parent family is headed by one adult responsible for raising the children, often facing unique economic and social challenges. Understanding the defining characteristics of your family type helps tailor support and resources effectively.
Understanding Single Parent Family
Single parent families consist of one guardian raising children, often facing unique financial and emotional challenges compared to nuclear families with two caregivers. Understanding single parent family dynamics involves recognizing the resilience and resourcefulness required to balance work, childcare, and personal well-being. Your support and awareness can enhance the well-being and development of children in single parent households.
Historical Evolution of Family Types
The historical evolution of family types shows that nuclear families, consisting of two parents and their children, became dominant during industrialization due to urbanization and economic shifts. Single parent families have increased significantly in recent decades, driven by social changes such as higher divorce rates and evolving gender roles. Extended families, once prevalent in agricultural societies, have declined as modernization favored smaller, more mobile household units.
Emotional Well-being: Nuclear vs Single Parent Families
Nuclear families often provide more stable emotional support due to shared parental responsibilities and consistent caregiving, fostering a secure environment for children's development. Single parent families face unique emotional challenges, including increased stress and limited social support, which can impact child well-being but can be mitigated by strong community ties and effective coping strategies. Emotional well-being in children depends on the quality of relationships and emotional responsiveness rather than family structure alone.
Financial Stability and Resources Comparison
Nuclear families typically enjoy greater financial stability due to dual incomes and shared expenses, which provide more resources for housing, education, and healthcare. Single parent families often face financial challenges as they rely on a single income, limiting access to resources and increasing vulnerability to economic stress. Extended families may offer supplementary financial support and pooled resources, enhancing stability and mitigating the limitations faced by single-parent households.
Impact on Child Development
Nuclear families provide children with consistent emotional support and stability, fostering healthy social and cognitive development. Single parent families may face challenges like limited resources and time constraints, but strong parental involvement can promote resilience and independence in children. Your child's development is influenced by the quality of relationships and support systems, regardless of family structure.
Social Support Networks and Community
In nuclear families, social support networks often include close relatives and neighbors, providing stability and shared responsibilities. Single parent families may rely more heavily on community resources, friends, and extended family for emotional and practical support due to limited household members. Your access to diverse social support networks is crucial in shaping the resilience and well-being of family members across different family structures.
Challenges Faced by Each Family Type
Nuclear families often face challenges balancing work-life responsibilities while maintaining effective communication and emotional support among members. Single parent families frequently encounter financial strain, limited time for child-rearing, and increased stress due to the sole caregiver role. Your ability to address these challenges depends on access to social support networks, resources, and adaptive coping strategies tailored to each family structure.
The Future of Family Dynamics
The future of family dynamics increasingly reflects diverse structures, with nuclear families, single parent families, and extended families each presenting unique strengths and challenges. Shifts in social norms, economic factors, and technological advancements influence how these family models function and adapt, impacting emotional support, financial stability, and child development. Your understanding of these evolving dynamics can help foster inclusive policies and community support systems that address the needs of all family types.
Infographic: Nuclear Family vs Single Parent Family
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com