Emotional support involves actively listening and validating feelings, fostering connection and healing, while sympathy often entails feeling pity without deep engagement. Discover how distinguishing between these responses can improve your relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
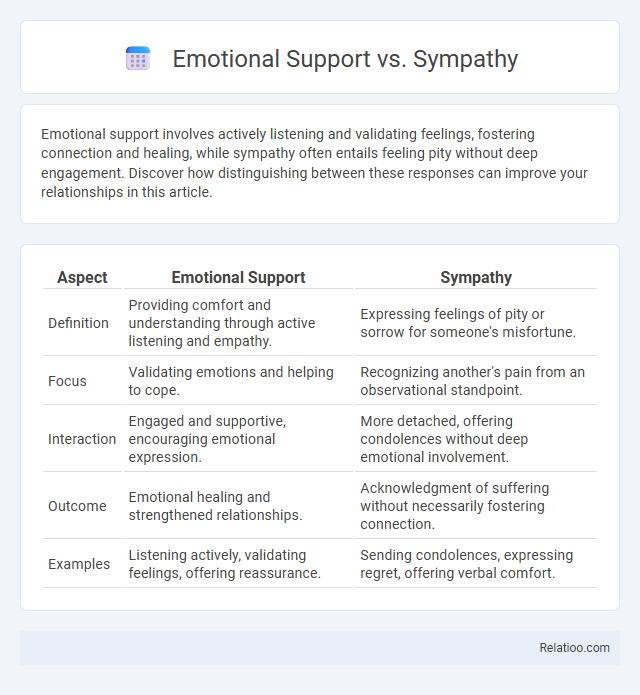
| Aspect | Emotional Support | Sympathy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Providing comfort and understanding through active listening and empathy. | Expressing feelings of pity or sorrow for someone's misfortune. |
| Focus | Validating emotions and helping to cope. | Recognizing another's pain from an observational standpoint. |
| Interaction | Engaged and supportive, encouraging emotional expression. | More detached, offering condolences without deep emotional involvement. |
| Outcome | Emotional healing and strengthened relationships. | Acknowledgment of suffering without necessarily fostering connection. |
| Examples | Listening actively, validating feelings, offering reassurance. | Sending condolences, expressing regret, offering verbal comfort. |
Understanding Emotional Support
Emotional support involves actively listening, validating feelings, and providing comfort to help someone cope with their emotions, distinguishing it from sympathy, which often centers on feeling pity or sorrow for another's situation without active engagement. Bridging, in the context of emotional connection, refers to the effort to close gaps in understanding or experience, fostering empathy through shared perspectives. Understanding emotional support means recognizing its role in promoting emotional resilience by offering genuine presence and encouragement rather than simply expressing concern or attempting to fix problems.
Defining Sympathy in Relationships
Sympathy in relationships involves recognizing and sharing another person's feelings of sorrow or distress, providing comfort without deeply engaging in their emotional experience. Unlike emotional support, which offers active assistance and understanding, sympathy often maintains a certain emotional distance. You can foster stronger connections by balancing sympathy with empathy and bridging strategies that encourage mutual understanding and healing.
Key Differences Between Emotional Support and Sympathy
Emotional support involves actively listening and validating Your feelings to foster connection and healing, while sympathy primarily consists of expressing pity or sorrow for someone's situation without deeper engagement. Emotional support encourages empathy and shared understanding, often accompanied by comforting actions, whereas sympathy may create a distance by highlighting the emotional gap. Bridging, on the other hand, seeks to connect people across differing emotional experiences, blending elements of both emotional support and sympathy to enhance relational trust.
The Psychological Impact of Emotional Support
Emotional support significantly enhances psychological well-being by fostering a sense of security and validation, which reduces stress and anxiety levels. Unlike sympathy, which may invoke pity or distance, emotional support actively engages empathy and understanding, promoting resilience and emotional regulation. Bridging social connections further amplifies this impact by creating networks that facilitate ongoing emotional exchanges and mental health stability.
How Sympathy Influences Interpersonal Connections
Sympathy involves recognizing and feeling concern for another person's suffering, which can foster trust and deepen interpersonal connections by showing empathy and understanding. This emotional response encourages supportive behaviors and validates the feelings of others, enhancing relationship quality. Unlike emotional support, which actively offers comfort and aid, sympathy primarily communicates acknowledgment of distress without necessarily providing direct assistance or solutions.
Benefits of Offering Emotional Support
Offering emotional support fosters deeper connections by validating your feelings and providing comfort during difficult times. Unlike sympathy, which may create distance by expressing pity, emotional support encourages active listening and empathy, enhancing trust and understanding. Bridging emotional gaps strengthens relationships by promoting open communication and emotional resilience, ultimately benefiting both you and those around you.
Potential Downsides of Sympathy
Sympathy can unintentionally create emotional distance by emphasizing differences rather than shared experiences, potentially making the recipient feel isolated or pitied. Unlike emotional support, which fosters connection and validation, sympathy may lead to misunderstanding or minimizing the recipient's feelings. Excessive sympathy risks reinforcing power imbalances and reducing the effectiveness of genuine support and empathy.
Building Skills for Effective Emotional Support
Building skills for effective emotional support involves understanding the subtle differences between emotional support, sympathy, and bridging. Emotional support requires active listening and validation of Your feelings, fostering a safe space for expressing vulnerability, while sympathy often focuses on pity rather than connection. Bridging enhances emotional support by creating a shared experience that strengthens empathy and deepens interpersonal bonds.
When to Offer Support vs. Sympathy
Offering emotional support involves actively listening and validating your loved one's feelings, fostering a safe space for expression during challenging times. Sympathy, on the other hand, is expressing empathy and concern without necessarily engaging in problem-solving or deep emotional connection. You should offer emotional support when someone needs comfort and understanding, while sympathy is appropriate for situations where acknowledging pain without intervention respects the person's boundaries.
Cultivating Empathy for Healthy Relationships
Emotional support involves actively listening and validating feelings without judgment, fostering deep trust and connection in relationships. Sympathy often entails feeling pity or sorrow for someone's situation, which may create emotional distance rather than closeness. Bridging builds empathy by encouraging open communication and shared experiences, promoting understanding and resilience essential for healthy, supportive bonds.
Infographic: Emotional Support vs Sympathy
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com