Self-regulation involves managing emotions and behaviors through awareness and adaptation, while self-control focuses on resisting immediate impulses to achieve long-term goals. Discover how mastering these skills can transform your relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
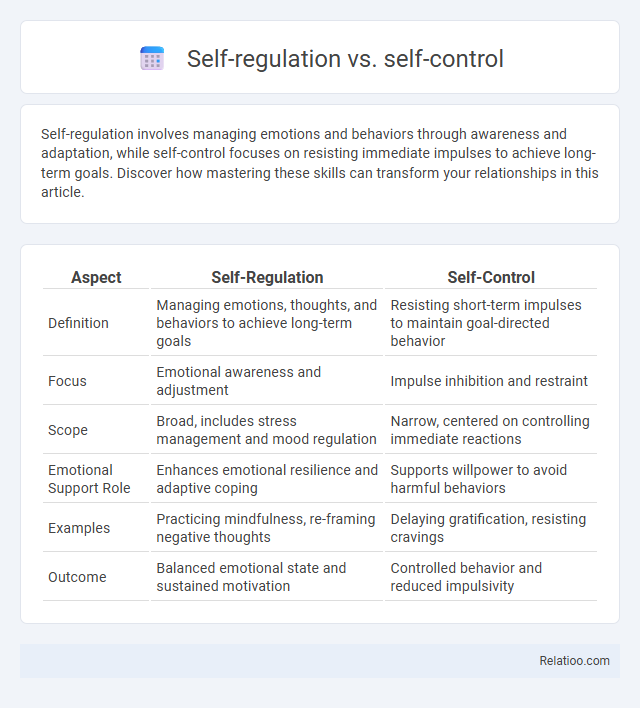
| Aspect | Self-Regulation | Self-Control |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Managing emotions, thoughts, and behaviors to achieve long-term goals | Resisting short-term impulses to maintain goal-directed behavior |
| Focus | Emotional awareness and adjustment | Impulse inhibition and restraint |
| Scope | Broad, includes stress management and mood regulation | Narrow, centered on controlling immediate reactions |
| Emotional Support Role | Enhances emotional resilience and adaptive coping | Supports willpower to avoid harmful behaviors |
| Examples | Practicing mindfulness, re-framing negative thoughts | Delaying gratification, resisting cravings |
| Outcome | Balanced emotional state and sustained motivation | Controlled behavior and reduced impulsivity |
Understanding Self-Regulation and Self-Control
Self-regulation involves managing emotions, thoughts, and behaviors to achieve long-term goals, while self-control refers specifically to resisting short-term impulses or temptations. Understanding self-regulation highlights its broader scope, including goal setting, monitoring progress, and adapting strategies, whereas self-control is a component focused on immediate impulse inhibition. Research in psychology indicates that developing strong self-regulation skills enhances overall well-being and success across various domains.
Key Differences Between Self-Regulation and Self-Control
Self-regulation involves managing your emotions, thoughts, and behaviors to achieve long-term goals, while self-control specifically refers to resisting short-term temptations or impulses. Unlike self-control, which is often situational and momentary, self-regulation encompasses a broader, ongoing process of adapting to changing circumstances and maintaining emotional balance. Understanding these key differences helps improve your ability to sustain motivation and make deliberate choices aligned with personal values.
The Science Behind Self-Regulation
The science behind self-regulation reveals it as a dynamic process involving your brain's ability to manage emotions, impulses, and behaviors to achieve long-term goals. Unlike self-control, which is often viewed as a momentary effort to resist temptation, self-regulation encompasses continuous monitoring and adjustment based on feedback. Neuroscientific studies highlight the prefrontal cortex's crucial role in sustaining self-regulation by integrating cognitive, emotional, and behavioral responses.
The Psychology of Self-Control
Self-control refers to the ability to resist short-term temptations and impulses to achieve long-term goals, while self-regulation encompasses the broader process of managing emotions, thoughts, and behaviors in alignment with personal standards. The psychology of self-control emphasizes mechanisms such as delay of gratification, executive function, and willpower as crucial for maintaining goal-directed behavior. Research highlights that effective self-regulation requires a dynamic balance between cognitive control and emotional modulation to sustain motivation and adaptive functioning.
Benefits of Practicing Self-Regulation
Practicing self-regulation enhances emotional stability by enabling individuals to manage impulses and adapt behaviors to long-term goals, fostering resilience and reducing stress-related disorders. This skill improves decision-making and interpersonal relationships through increased awareness and intentional responses, boosting productivity and mental well-being. Consistent self-regulation supports habit formation and goal achievement by aligning actions with core values and enhancing motivation.
Situations Where Self-Control Matters Most
Situations where self-control matters most include moments requiring delayed gratification, such as resisting impulsive spending or avoiding unhealthy foods, directly impacting your long-term goals. Self-regulation encompasses broader processes like managing emotions and adapting behavior to changing circumstances, while self-control specifically targets resisting immediate temptations or urges. Understanding these distinctions helps you develop strategies tailored to maintaining discipline in critical moments.
How Self-Regulation Impacts Emotional Wellbeing
Self-regulation involves managing emotions and behaviors through awareness and deliberate adjustment, whereas self-control primarily focuses on resisting impulses and delaying gratification. Effective self-regulation enhances emotional wellbeing by reducing stress, improving mood stability, and fostering resilience against negative emotional triggers. Research shows that individuals with strong self-regulatory skills experience lower anxiety levels and greater psychological flexibility, contributing to overall mental health.
Building Stronger Self-Control Habits
Building stronger self-control habits involves understanding the interplay between self-regulation, self-control, and emotional regulation. Self-regulation is the broader process encompassing goal setting, monitoring, and adjusting behaviors, while self-control specifically refers to resisting short-term temptations to achieve long-term goals. You can enhance your self-control by consistently practicing techniques like mindfulness, setting clear intentions, and creating supportive environments that reduce impulsive behavior.
Common Challenges in Developing Self-Regulation
Common challenges in developing self-regulation include managing impulsivity, maintaining emotional stability, and sustaining motivation in the face of setbacks. Unlike self-control, which often focuses on resisting specific temptations, self-regulation encompasses a broader ability to monitor and adjust behavior, emotions, and thoughts over time. Difficulties in consistent practice, external distractions, and lack of immediate rewards can hinder the development of effective self-regulation skills.
Self-Regulation vs Self-Control: Which Is More Effective?
Self-regulation and self-control both involve managing your behavior, but self-regulation encompasses long-term goal setting and emotional management, while self-control focuses on resisting immediate temptations. Research shows self-regulation is more effective for sustained success because it builds habits and adjusts your responses over time, whereas self-control relies heavily on willpower and can lead to burnout. Enhancing your self-regulation skills promotes resilience and consistent progress, making it a superior strategy for achieving lasting personal and professional growth.
Infographic: Self-regulation vs Self-control
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com