Revolutionary movements often seek rapid systemic change through forceful actions, while peaceful resistance relies on nonviolent methods to achieve social and political goals. Explore this article to understand the dynamics and effectiveness of both approaches in shaping history.
Table of Comparison
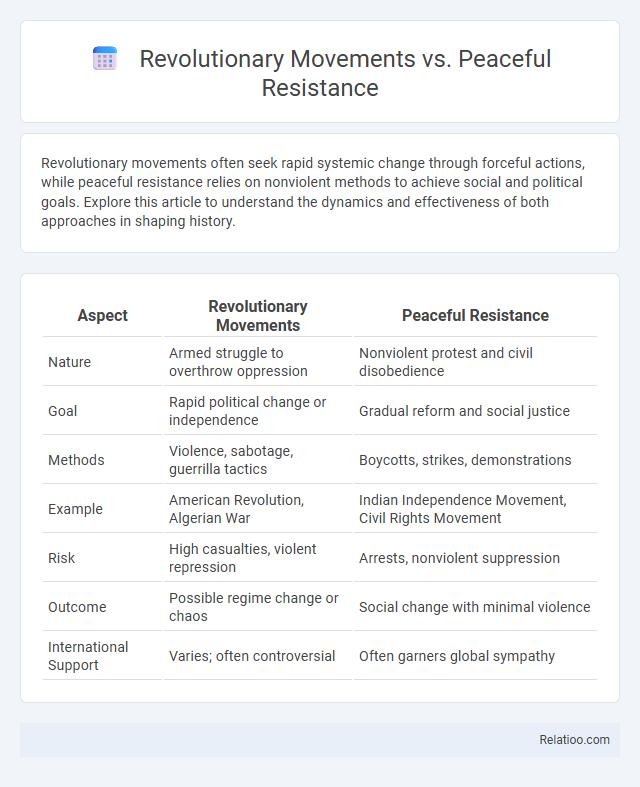
| Aspect | Revolutionary Movements | Peaceful Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Armed struggle to overthrow oppression | Nonviolent protest and civil disobedience |
| Goal | Rapid political change or independence | Gradual reform and social justice |
| Methods | Violence, sabotage, guerrilla tactics | Boycotts, strikes, demonstrations |
| Example | American Revolution, Algerian War | Indian Independence Movement, Civil Rights Movement |
| Risk | High casualties, violent repression | Arrests, nonviolent suppression |
| Outcome | Possible regime change or chaos | Social change with minimal violence |
| International Support | Varies; often controversial | Often garners global sympathy |
Defining Revolutionary Movements and Peaceful Resistance
Revolutionary movements involve radical actions aimed at overthrowing existing political systems through force or drastic change, often driven by deep social or economic grievances. Peaceful resistance, on the other hand, employs nonviolent methods such as protests, civil disobedience, and boycotts to achieve social or political goals without resorting to violence. Understanding the differences between these approaches helps you evaluate strategies in independence struggles and their impact on societal transformation.
Historical Origins of Revolutionary vs. Peaceful Change
Revolutionary movements often originate from deep social inequalities and the failure of existing political systems to address urgent demands, leading to radical upheavals aimed at systemic transformation. Peaceful resistance has its historical roots in nonviolent philosophies and civil disobedience tactics, exemplified by figures like Mahatma Gandhi and Martin Luther King Jr., emphasizing moral authority and mass participation to achieve reform. Your understanding of these origins highlights the distinct strategies where revolutionary movements seek rapid, forceful change, while peaceful resistance relies on sustained, nonviolent action to attain independence or social justice.
Philosophical Foundations: Violence vs. Nonviolence
Revolutionary movements often rest on the philosophical foundation that violence is a necessary means to overthrow oppressive systems, arguing that direct confrontation catalyzes social transformation. Peaceful resistance, rooted in nonviolence philosophies like those of Gandhi and Martin Luther King Jr., asserts that moral authority and mass civil disobedience can dismantle injustice without bloodshed. Your understanding of these strategies' underlying ideologies shapes the approach to independence struggles, highlighting the tension between forceful rebellion and ethical persistence.
Key Figures in Revolutionary Movements
Key figures in revolutionary movements include leaders like Che Guevara, whose guerrilla warfare tactics inspired global insurgencies, and Vladimir Lenin, who orchestrated the Bolshevik Revolution that radically transformed Russia. Other influential personalities such as Nelson Mandela, who initially supported armed struggle before embracing peaceful resistance, and Toussaint Louverture, the mastermind behind the Haitian Revolution, demonstrate the pivotal role of leadership in shaping the course of independence struggles. These leaders utilized ideology, strategy, and mass mobilization to challenge colonial or oppressive regimes, setting revolutionary movements apart from purely peaceful resistance efforts.
Influential Leaders of Peaceful Resistance
Mahatma Gandhi pioneered peaceful resistance through nonviolent civil disobedience, inspiring global movements for social change. Martin Luther King Jr. championed nonviolent protest during the American Civil Rights Movement, emphasizing equality and justice. Nelson Mandela combined peaceful resistance with strategic negotiations, ultimately leading South Africa out of apartheid toward democracy.
Case Studies: Successful Revolutions
The American Revolution exemplifies a successful revolutionary movement that combined armed conflict with widespread political mobilization, leading to independence from British colonial rule. India's independence struggle under Mahatma Gandhi highlighted the effectiveness of peaceful resistance through nonviolent civil disobedience, galvanizing mass participation and international support against British imperialism. The Cuban Revolution, led by Fidel Castro and Che Guevara, demonstrated a revolutionary movement where armed insurgency and popular support dismantled a dictatorship, establishing a socialist state.
Case Studies: Impactful Peaceful Movements
The Indian Independence Movement led by Mahatma Gandhi exemplifies the power of peaceful resistance, utilizing nonviolent civil disobedience to challenge British colonial rule and ultimately secure independence in 1947. Similarly, the American Civil Rights Movement, with figures like Martin Luther King Jr., effectively employed nonviolent protests to dismantle racial segregation and secure legislative reforms such as the Civil Rights Act of 1964. These case studies highlight how peaceful movements can achieve profound political and social change without resorting to revolutionary violence.
Social and Political Consequences
Revolutionary movements often result in profound social upheaval and political restructuring, frequently leading to the overthrow of existing regimes and the establishment of new governance systems. Peaceful resistance tends to foster social cohesion and international sympathy while promoting political reforms through non-violent means, often resulting in more stable and inclusive democratic institutions. Independence struggles can catalyze national identity formation and mobilize mass participation, but may also provoke prolonged conflicts and challenges in post-colonial state-building and governance.
Effectiveness: Measuring Lasting Change
Revolutionary movements often achieve rapid, radical change through force, but can struggle with long-term stability and governance. Peaceful resistance movements typically foster sustainable social and political transformation by mobilizing public support and international legitimacy. Independence struggles vary, yet those combining mass mobilization and strategic negotiation tend to secure lasting sovereignty and post-colonial development.
The Future of Activism: Revolution or Resistance?
Revolutionary movements demand radical change through forceful upheaval, often accelerating political transformation but risking instability. Peaceful resistance leverages nonviolent tactics like protests and civil disobedience to build broad-based support and sustainable reform. Your choice in activism shapes the future of social change, balancing urgency with ethical impact amid evolving global challenges.
Infographic: Revolutionary Movements vs Peaceful Resistance
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com