Parental nurturance involves providing emotional support, guidance, and care during childhood, which forms the foundation for healthy development, while self-nurturance refers to the adult practice of self-care and emotional regulation to maintain well-being. Explore the differences and impacts of parental nurturance versus self-nurturance in this article.
Table of Comparison
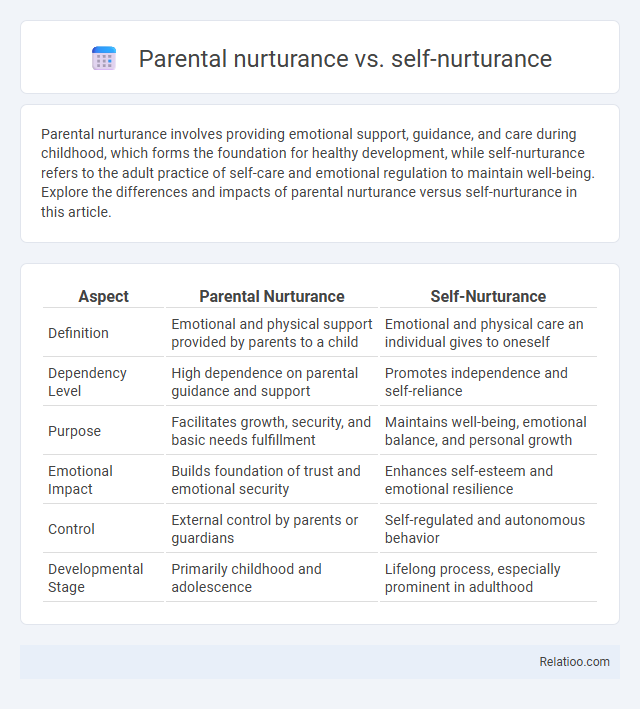
| Aspect | Parental Nurturance | Self-Nurturance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional and physical support provided by parents to a child | Emotional and physical care an individual gives to oneself |
| Dependency Level | High dependence on parental guidance and support | Promotes independence and self-reliance |
| Purpose | Facilitates growth, security, and basic needs fulfillment | Maintains well-being, emotional balance, and personal growth |
| Emotional Impact | Builds foundation of trust and emotional security | Enhances self-esteem and emotional resilience |
| Control | External control by parents or guardians | Self-regulated and autonomous behavior |
| Developmental Stage | Primarily childhood and adolescence | Lifelong process, especially prominent in adulthood |
Understanding Parental Nurturance
Parental nurturance involves responsive caregiving that fosters a child's emotional security, cognitive development, and social competence through consistent warmth and support. Understanding parental nurturance requires recognizing its impact on attachment formation and long-term psychological well-being, distinguishing it from self-nurturance, which emphasizes self-care and emotional regulation. Effective parental nurturance creates a foundation for healthy development by meeting the child's physical and emotional needs, essential for resilience and adaptive functioning.
Defining Self-Nurturance
Self-nurturance refers to the deliberate actions and attitudes you adopt to care for your own emotional, physical, and psychological well-being. Unlike parental nurturance, which centers on the support and care provided to children, self-nurturance emphasizes self-compassion, self-care routines, and setting healthy boundaries to maintain personal balance. Understanding self-nurturance is key to fostering resilience and promoting overall mental health in your daily life.
Key Differences Between Parental and Self-Nurturance
Parental nurturance involves providing care, support, and protection to a child, fostering emotional and physical development through consistent guidance and affection. Self-nurturance, by contrast, centers on your ability to care for your own emotional, mental, and physical well-being, emphasizing self-compassion and self-care practices. The key difference lies in the direction of care: parental nurturance is outward-focused on another person's growth, while self-nurturance is inward-focused on maintaining and enhancing your personal health and resilience.
Psychological Impact of Parental Nurturance
Parental nurturance plays a crucial role in shaping your psychological development by fostering secure attachment, emotional regulation, and self-esteem from an early age. Unlike self-nurturance, which involves personal practices of self-care and self-compassion, parental nurturance directly influences your brain architecture, stress response, and social behaviors through consistent, responsive caregiving. Nurturance in general promotes emotional well-being, but the psychological impact of parental nurturance is foundational for resilience and mental health across the lifespan.
Benefits of Developing Self-Nurturance
Developing self-nurturance enhances emotional resilience, promoting mental well-being by fostering self-compassion and reducing dependence on external validation. Unlike parental nurturance, which forms the foundational sense of security from caregivers, self-nurturance empowers individuals to independently manage stress, regulate emotions, and maintain psychological balance. Cultivating self-nurturance ultimately supports healthier relationships and sustainable personal growth.
The Role of Childhood Experiences
Childhood experiences significantly impact the development of parental nurturance, self-nurturance, and general nurturance skills by shaping emotional bonding and self-awareness patterns. Your ability to provide warmth and support to others or yourself often originates from early interactions with caregivers who modeled affection, validation, and emotional regulation. Understanding these formative influences helps enhance nurturing behaviors crucial for healthy relationships and personal well-being.
Overcoming Lack of Parental Nurturance
Overcoming lack of parental nurturance involves cultivating self-nurturance practices that promote emotional resilience and self-compassion, addressing deficits in early caregiving experiences. Therapeutic interventions often focus on building secure attachment models within oneself through mindfulness, positive self-talk, and emotional regulation strategies. Effective nurturance integrates both internal self-care and external supportive relationships to compensate for early parental nurturing gaps and foster psychological well-being.
Tools and Strategies for Cultivating Self-Nurturance
Effective tools for cultivating self-nurturance include mindfulness practices, journaling, and setting healthy boundaries, which foster emotional awareness and self-compassion. Strategies such as regular self-reflection, engaging in hobbies that bring joy, and practicing positive self-talk help reinforce nurturing habits and resilience. Your commitment to these techniques can significantly enhance your emotional well-being and personal growth.
Balancing External and Internal Sources of Support
Balancing parental nurturance, self-nurturance, and general nurturance involves harmonizing external support from caregivers with internal self-care practices to enhance emotional well-being. Your ability to integrate parental nurturance, which provides foundational emotional security, with self-nurturance skills, such as self-compassion and mindfulness, strengthens resilience and personal growth. Effective nurturance occurs when external encouragement and internal self-support coexist, fostering balanced psychological health and adaptive coping mechanisms.
Fostering Lifelong Emotional Well-being
Parental nurturance involves providing consistent emotional support, security, and affection during childhood, which forms the foundation for healthy emotional development. Self-nurturance emphasizes the intentional practice of self-care, self-compassion, and emotional regulation to maintain psychological resilience throughout life. Cultivating both parental and self-nurturance enhances lifelong emotional well-being by fostering secure attachments, positive self-esteem, and adaptive coping strategies.
Infographic: Parental nurturance vs Self-nurturance
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com