Overdependence in relationships can lead to emotional imbalance and hinder personal growth, while fostering independence promotes mutual respect and healthy boundaries. Discover effective strategies to balance reliance and autonomy in this article.
Table of Comparison
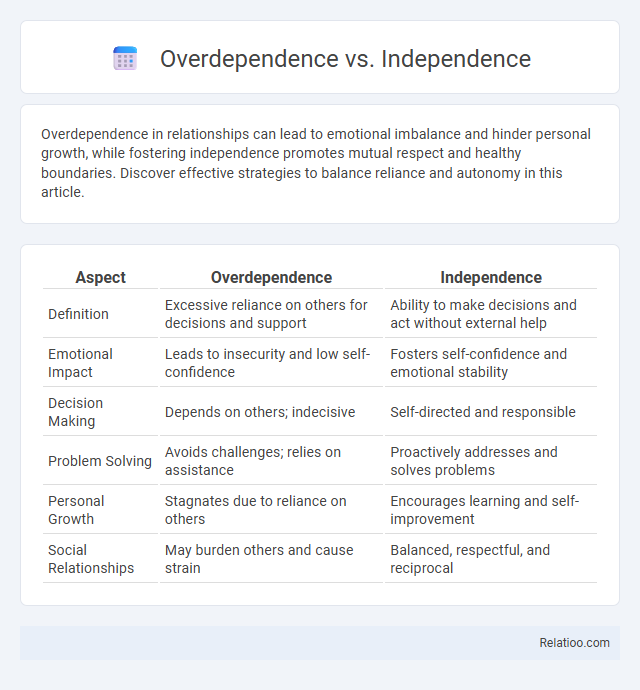
| Aspect | Overdependence | Independence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Excessive reliance on others for decisions and support | Ability to make decisions and act without external help |
| Emotional Impact | Leads to insecurity and low self-confidence | Fosters self-confidence and emotional stability |
| Decision Making | Depends on others; indecisive | Self-directed and responsible |
| Problem Solving | Avoids challenges; relies on assistance | Proactively addresses and solves problems |
| Personal Growth | Stagnates due to reliance on others | Encourages learning and self-improvement |
| Social Relationships | May burden others and cause strain | Balanced, respectful, and reciprocal |
Understanding Overdependence: Key Characteristics
Overdependence is characterized by excessive reliance on others for emotional support, decision-making, and validation, which often hinders personal growth and autonomy. Individuals exhibiting overdependence may struggle with low self-confidence, fear of abandonment, and difficulty in setting boundaries. Understanding these key traits is essential for addressing unhealthy relational patterns and fostering greater independence.
Defining Independence: Core Attributes
Independence is characterized by self-reliance, decision-making autonomy, and accountability for personal actions. Your ability to balance confidence with openness to feedback fosters growth without tipping into overdependence or isolation. Core attributes include emotional resilience, problem-solving skills, and the capacity to seek support when necessary while maintaining control over your choices.
Psychological Roots of Overdependence
Overdependence arises from unmet childhood needs and insecure attachment styles, causing individuals to rely excessively on others for validation and decision-making. Your psychological roots of overdependence often involve low self-esteem, fear of abandonment, and difficulties with emotional regulation. Building independence requires addressing these core issues through therapy and developing self-confidence and coping skills.
The Benefits of Fostering Independence
Fostering independence enhances decision-making skills, boosts self-confidence, and promotes personal growth, enabling individuals to navigate challenges effectively. Independence encourages problem-solving abilities and resilience, leading to greater adaptability in diverse situations. Balanced autonomy reduces the risks of overdependence, which can stifle creativity and limit potential.
Social and Cultural Influences on Dependency
Social and cultural influences significantly shape the balance between overdependence, independence, and interdependence in individuals. Traditional collectivist cultures often promote dependency through strong family ties and communal decision-making, while individualistic societies encourage personal autonomy and self-reliance. Your ability to navigate these influences affects not only personal growth but also social harmony and cultural identity.
Consequences of Excessive Overdependence
Excessive overdependence often leads to reduced personal autonomy and diminished problem-solving skills, impairing individual growth and resilience. It can foster unhealthy relational dynamics, creating imbalance and increasing vulnerability to manipulation or control. Long-term consequences include decreased self-confidence and hindered ability to adapt to new challenges independently.
Building Healthy Boundaries for Independence
Building healthy boundaries is essential for fostering true independence, as they allow individuals to maintain self-respect and personal autonomy while engaging in relationships. Overdependence compromises growth by creating excessive reliance on others, often leading to emotional burnout and diminished self-efficacy. Establishing clear limits supports emotional resilience and balanced interactions, promoting sustainable independence without swinging back into overdependence.
Balancing Support and Self-Sufficiency
Balancing support and self-sufficiency involves recognizing the risks of both overdependence and extreme independence, which can hinder growth and resilience. You achieve optimal personal development by fostering interdependent relationships where mutual support meets individual accountability. Cultivating this balance enhances your ability to adapt, ensuring emotional well-being and practical success in diverse situations.
Strategies to Transition from Overdependence to Independence
Building self-reliance requires setting clear personal goals and developing problem-solving skills to reduce reliance on others. Practicing decision-making in low-risk situations and gradually increasing responsibilities fosters confidence and autonomy. Seeking constructive feedback and engaging in supportive environments accelerates the transition from overdependence to functional independence.
Real-Life Examples: Success Stories of Gaining Independence
Overdependence often limits personal growth and decision-making, as seen in employees who rely heavily on management for direction, whereas independence empowers individuals to take initiative and innovate, exemplified by entrepreneurs like Elon Musk who transformed industries through self-reliance. Real-life success stories of gaining independence include Malala Yousafzai, who overcame cultural constraints to advocate for education, and J.K. Rowling, whose perseverance and self-belief led to the global success of the Harry Potter series. These examples demonstrate how shifting from overdependence to independence fosters resilience, confidence, and long-term achievement.
Infographic: Overdependence vs Independence
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com