Balancing autonomy and dependency is essential for healthy relationships, as too much reliance can hinder personal growth while excessive independence may cause emotional distance. Discover strategies to navigate this dynamic effectively in this article.
Table of Comparison
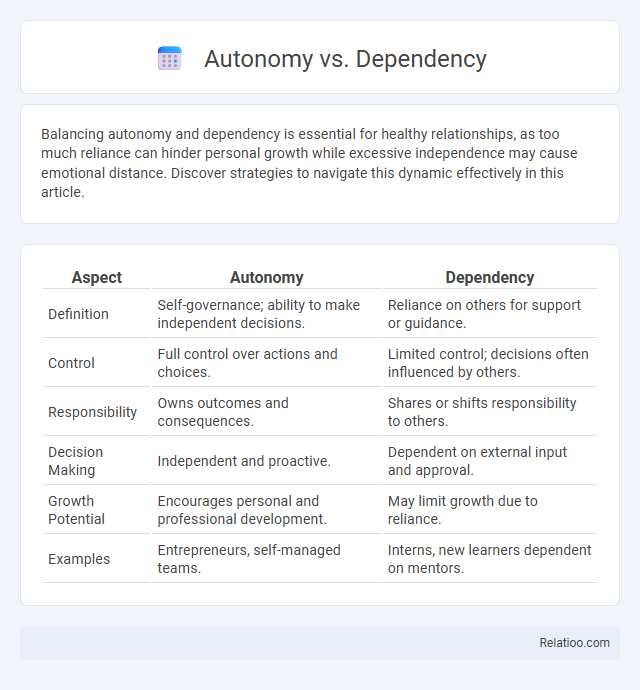
| Aspect | Autonomy | Dependency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Self-governance; ability to make independent decisions. | Reliance on others for support or guidance. |
| Control | Full control over actions and choices. | Limited control; decisions often influenced by others. |
| Responsibility | Owns outcomes and consequences. | Shares or shifts responsibility to others. |
| Decision Making | Independent and proactive. | Dependent on external input and approval. |
| Growth Potential | Encourages personal and professional development. | May limit growth due to reliance. |
| Examples | Entrepreneurs, self-managed teams. | Interns, new learners dependent on mentors. |
Understanding Autonomy: Definition and Importance
Autonomy refers to the capacity to make independent decisions and govern oneself without external control, which is essential for personal growth and empowerment. It fosters self-confidence and accountability, enabling individuals and organizations to adapt and thrive in dynamic environments. Understanding autonomy highlights its role in promoting psychological well-being, innovation, and sustainable development by balancing independence with responsible interdependence.
Dependency Explained: Concepts and Types
Dependency refers to a state where an individual or entity relies on external support or resources to meet their needs, often seen in psychological, economic, or social contexts. Types of dependency include emotional dependency, characterized by excessive reliance on others for validation; financial dependency, where one depends on others for monetary support; and physical dependency, involving reliance on others for daily living activities due to health or age. Understanding these concepts is crucial for addressing challenges in personal growth, relationships, and social policies aimed at promoting autonomy and self-sufficiency.
The Psychological Benefits of Autonomy
Autonomy promotes psychological well-being by enhancing your sense of control and personal freedom, which reduces stress and increases motivation. Studies in psychology reveal that individuals with higher autonomy experience greater life satisfaction and improved mental health. Developing autonomy fosters resilience and self-confidence, enabling you to make decisions aligned with your true values and goals.
Risks and Challenges of Excessive Dependency
Excessive dependency undermines your ability to develop critical problem-solving skills and can lead to increased vulnerability during crises or changes in circumstances. Relying heavily on external support or resources often results in reduced autonomy, limiting innovation and adaptability. This dependency poses significant risks to personal growth and long-term sustainability by creating obstacles to achieving true self-sufficiency.
Autonomy in Personal Relationships
Autonomy in personal relationships emphasizes maintaining your individual identity and decision-making power while engaging with others. It involves respecting each person's boundaries and fostering open communication to balance independence with emotional connection. Developing autonomy helps prevent unhealthy dependency and promotes mutual growth within close relationships.
Dependency in Professional Environments
Dependency in professional environments often leads to reduced innovation and slower decision-making processes, impacting overall productivity and team dynamics. Over-reliance on supervisors or colleagues can hinder your ability to develop critical problem-solving skills and adapt to changing work demands. Cultivating a balance between autonomy and collaboration is essential for fostering personal growth and achieving organizational success.
Striking a Healthy Balance: Autonomy and Support
Striking a healthy balance between autonomy and support fosters personal growth while ensuring essential assistance when needed. Emphasizing self-sufficiency encourages decision-making skills and resilience, whereas maintaining dependency relationships provides emotional and practical support during challenges. Optimal well-being arises when individuals navigate independence without isolation, integrating collaborative networks alongside autonomous capabilities.
Cultural Perspectives on Autonomy vs Dependency
Cultural perspectives on autonomy versus dependency reveal significant variations in values and social expectations across societies. In individualistic cultures, autonomy is esteemed as a sign of personal strength and independence, encouraging individuals to make decisions and take responsibility for their lives. Conversely, collectivist cultures often emphasize dependency and interdependence, viewing social connections and mutual support as essential to community well-being and Your identity.
Strategies to Foster Autonomy
Fostering autonomy involves empowering individuals to make informed decisions and take responsibility for their actions by providing them with access to relevant information, skills training, and opportunities for independent problem-solving. Encouraging a growth mindset and supportive feedback helps build confidence and resilience, reducing dependency on others. Your role includes creating an environment that balances guidance with freedom, enabling sustainable self-sufficiency and personal development.
Overcoming Unhealthy Dependency Patterns
Overcoming unhealthy dependency patterns requires cultivating self-awareness and establishing clear personal boundaries to promote autonomy. Developing self-sufficiency involves building practical life skills, emotional resilience, and decision-making confidence that reduce reliance on others. Psychological interventions like cognitive-behavioral therapy help individuals identify dependency triggers and replace maladaptive behaviors with healthy, independent coping strategies.
Infographic: Autonomy vs Dependency
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com