Power distance influences relationship dynamics by determining how much hierarchy and authority are accepted between partners, while equality fosters mutual respect and shared decision-making. Explore how these contrasting values shape interpersonal connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
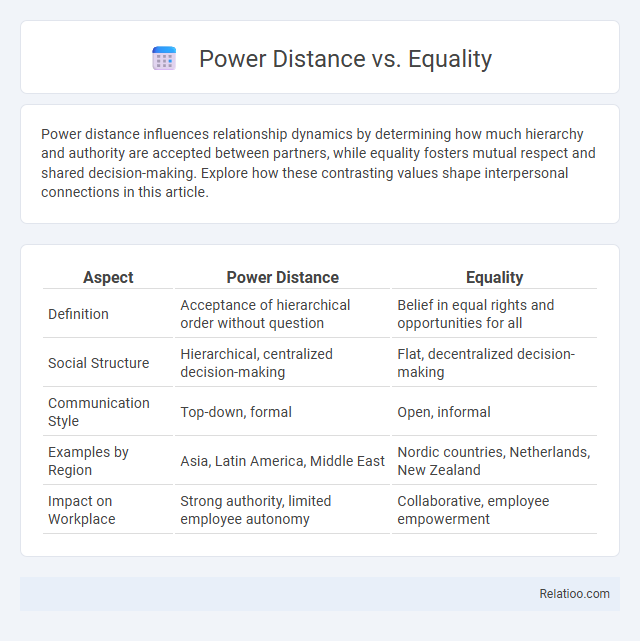
| Aspect | Power Distance | Equality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Acceptance of hierarchical order without question | Belief in equal rights and opportunities for all |
| Social Structure | Hierarchical, centralized decision-making | Flat, decentralized decision-making |
| Communication Style | Top-down, formal | Open, informal |
| Examples by Region | Asia, Latin America, Middle East | Nordic countries, Netherlands, New Zealand |
| Impact on Workplace | Strong authority, limited employee autonomy | Collaborative, employee empowerment |
Understanding Power Distance and Equality
Power distance refers to the extent to which less powerful members of a society accept and expect power to be distributed unequally, influencing organizational hierarchies and social interactions. In contrast, equality emphasizes minimizing power gaps to promote fairness and equal opportunities across individuals and groups. Understanding these concepts is crucial for analyzing cultural value systems that shape leadership styles, communication patterns, and conflict resolution strategies.
Historical Origins of Power Structures
Historical origins of power structures can be traced to the development of hierarchical societies where centralized authority governed resource distribution and social order. Power distance reflects these inherited inequalities, often rooted in feudalism, colonialism, or caste systems, which institutionalized dominance and deference as cultural norms. In contrast, value systems emphasizing equality emerged from Enlightenment ideals and revolutions advocating universal rights and social justice, challenging entrenched power disparities.
Defining Power Distance in Society
Power distance in society measures the extent to which less powerful members accept and expect unequal power distribution. High power distance cultures emphasize hierarchical structures and authority, while low power distance societies promote equality and participative decision-making. This value system profoundly influences social interactions, organizational behavior, and governance models within different communities.
Equality: Principles and Practices
Equality in social systems emphasizes equal access to resources, opportunities, and rights regardless of hierarchical status, supporting inclusive decision-making and merit-based advancement. This principle fosters collaboration by minimizing power distance, promoting transparency, and encouraging participatory governance that respects diverse perspectives. Effective equality practices include equitable policies, anti-discrimination measures, and ongoing education to challenge biases and sustain cultural respect across organizations and communities.
Power Distance Across Cultures
Power distance reflects the extent to which less powerful members of a society accept unequal power distribution, influencing organizational hierarchy and communication patterns. Cultures with high power distance, such as Malaysia and Mexico, emphasize authority and centralized decision-making, while low power distance cultures like Denmark and New Zealand prioritize egalitarianism and participative management. Understanding power distance is crucial for multinational companies to navigate value systems and foster effective cross-cultural collaboration.
Equality in the Workplace
Equality in the workplace promotes a value system where power distance is minimized, fostering collaboration and mutual respect among employees. Organizations that prioritize equality ensure fair treatment, equal opportunity, and inclusive policies, which enhance employee satisfaction and productivity. Your commitment to equality creates a balanced environment where diverse perspectives are valued and innovation thrives.
The Impact of Power Distance on Communication
Power distance significantly shapes communication styles, where high power distance cultures often exhibit hierarchical and formal interactions, limiting open dialogue between authority figures and subordinates. In contrast, low power distance societies encourage egalitarian communication, fostering directness, feedback, and collaborative decision-making. Understanding these dynamics is critical for global businesses and multicultural teams to navigate value systems effectively and enhance interpersonal and organizational communication.
Benefits and Drawbacks of High vs. Low Power Distance
High power distance cultures often provide clear hierarchical structures that can streamline decision-making and maintain order, but they may hinder open communication and innovation due to unequal power distribution. Low power distance environments encourage collaboration and egalitarian relationships, fostering creativity and employee empowerment, yet they can lead to ambiguity in authority and slower decision processes. Your choice between high and low power distance impacts organizational dynamics, affecting motivation, conflict resolution, and overall workplace culture.
Strategies to Promote Equality
Promoting equality in organizations with high power distance requires implementing transparent communication channels and fostering inclusive decision-making to reduce hierarchical barriers. Your strategy should include training programs that emphasize shared values, respect, and collaboration, ensuring all voices are heard irrespective of rank. Embedding a value system that prioritizes fairness and empowerment encourages equitable treatment and nurtures a culture where diversity thrives.
Future Trends: Bridging Power Distance and Achieving Equality
Future trends indicate a shift towards reducing power distance by fostering inclusive value systems that emphasize equality in leadership and decision-making processes. You can expect organizations to implement transparent communication channels and collaborative technologies to empower employees at all levels. Embracing these changes will drive cultural transformation and promote fairness in diverse global workplaces.
Infographic: Power distance vs Equality
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com