Islam emphasizes monotheism and submission to Allah, while Hinduism embraces polytheism and a diverse range of spiritual practices. Explore the nuanced perspectives on relationships in Islam and Hinduism in this article.
Table of Comparison
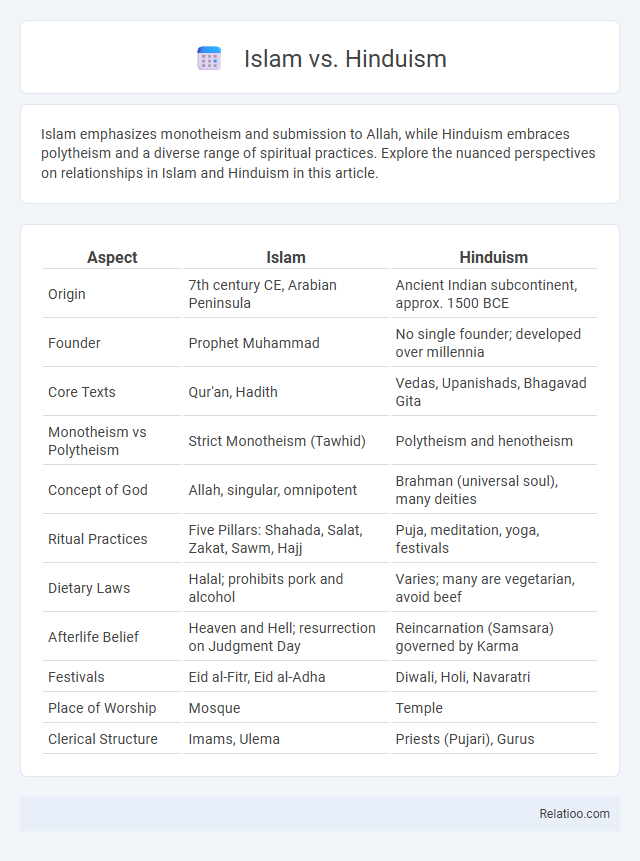
| Aspect | Islam | Hinduism |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | 7th century CE, Arabian Peninsula | Ancient Indian subcontinent, approx. 1500 BCE |
| Founder | Prophet Muhammad | No single founder; developed over millennia |
| Core Texts | Qur'an, Hadith | Vedas, Upanishads, Bhagavad Gita |
| Monotheism vs Polytheism | Strict Monotheism (Tawhid) | Polytheism and henotheism |
| Concept of God | Allah, singular, omnipotent | Brahman (universal soul), many deities |
| Ritual Practices | Five Pillars: Shahada, Salat, Zakat, Sawm, Hajj | Puja, meditation, yoga, festivals |
| Dietary Laws | Halal; prohibits pork and alcohol | Varies; many are vegetarian, avoid beef |
| Afterlife Belief | Heaven and Hell; resurrection on Judgment Day | Reincarnation (Samsara) governed by Karma |
| Festivals | Eid al-Fitr, Eid al-Adha | Diwali, Holi, Navaratri |
| Place of Worship | Mosque | Temple |
| Clerical Structure | Imams, Ulema | Priests (Pujari), Gurus |
Introduction to Islam and Hinduism
Islam is a monotheistic Abrahamic faith founded in the 7th century CE by Prophet Muhammad, emphasizing submission to Allah and following the Quran as its holy scripture. Hinduism, one of the world's oldest religions, is a diverse and polytheistic tradition rooted in Vedic texts, featuring a vast array of gods, rituals, and philosophical teachings centered on dharma and karma. Both religions shape the cultural and spiritual lives of millions, differing fundamentally in theology, practices, and worldview.
Core Beliefs and Doctrines
Islam centers on the belief in one God (Allah), the prophethood of Muhammad, and the Quran as the ultimate revelation guiding all aspects of life. Hinduism embraces a diverse range of beliefs, including the concepts of karma, dharma, reincarnation, and the worship of multiple deities representing various aspects of the divine. Your understanding of these religious doctrines highlights contrasting monotheistic and polytheistic frameworks, as well as differing views on salvation, morality, and the nature of existence.
Concept of God: Monotheism vs Polytheism
Islam is strictly monotheistic, emphasizing the belief in one, indivisible God (Allah) who is all-powerful and merciful, central to the faith's creed (Tawhid). Hinduism encompasses a diverse range of theological views, including monotheism, polytheism, and pantheism, often worshiping multiple deities representing various aspects of the supreme reality (Brahman). Religious belief across cultures varies widely, with monotheistic systems focusing on a singular divine entity, while polytheistic traditions celebrate multiple gods and goddesses, each with distinct attributes and roles.
Foundational Texts: Quran and Vedas
The Quran, central to Islam, is a revealed scripture believed to be the literal word of God, providing guidance on theology, law, and morality. The Vedas, foundational to Hinduism, consist of ancient hymns, rituals, and philosophical teachings, compiled over centuries by sages and serving as the basis for Hindu spiritual knowledge. Both texts shape distinct religious beliefs, rituals, and worldviews, deeply influencing followers' practices and cultural identities.
Prophets and Avatars
Islam emphasizes the role of prophets as direct messengers of Allah, with Muhammad regarded as the final prophet delivering the Quran. Hinduism centers around avatars, divine incarnations of gods like Vishnu, who descend to restore dharma and guide humanity. While Islamic prophets convey revealed scripture and monotheism, Hindu avatars embody complex theological concepts within a polytheistic framework, highlighting fundamental differences in religious belief and divine interaction.
Religious Practices and Rituals
Islamic religious practices center on the Five Pillars, including daily prayers (Salah), fasting during Ramadan, and pilgrimage to Mecca (Hajj), emphasizing submission to Allah. Hinduism emphasizes diverse rituals such as puja (worship), yoga, and various festivals like Diwali, reflecting devotion to multiple deities. Religious beliefs shape distinct ritualistic observances in both faiths, underscoring contrasts in monotheism versus polytheism and the significance of prescribed rites in spiritual life.
Afterlife and Salvation
Islam emphasizes belief in one God, with the afterlife involving judgment leading to Paradise or Hell based on one's faith and deeds. Hinduism presents diverse views on afterlife and salvation, including reincarnation and liberation (moksha) from the cycle of birth and death through spiritual knowledge and righteous living. Your understanding of afterlife and salvation will vary significantly depending on the religious framework you embrace.
Social Structure and Caste System
Islam emphasizes egalitarian social principles, promoting equality among believers without endorsement of caste divisions, whereas Hinduism's social structure is deeply rooted in the caste system, delineating rigid hereditary classes known as varnas and jatis. Your understanding of religious belief highlights that Islamic teachings seek to eliminate social stratification based on birth, fostering unity through the ummah concept, in contrast to Hinduism's caste-based hierarchy which governs social interaction, occupation, and marital norms. The interplay between these religious doctrines profoundly influences societal roles, mobility, and community identity in regions where both faiths coexist.
Festivals and Sacred Observances
Islam and Hinduism feature distinct festivals that highlight their spiritual and cultural identities, with Ramadan and Eid al-Fitr central to Islamic practice, emphasizing fasting and communal prayers. Hinduism celebrates a diverse range of festivals such as Diwali and Holi, rooted in mythological significance and seasonal cycles, illustrating rich symbolism and rituals. Your understanding of these Sacred Observances enriches appreciation for their role in reinforcing faith, community, and tradition across both religions.
Mutual Influence and Historical Interactions
Islam and Hinduism have shaped each other's religious practices and cultural expressions through centuries of coexistence, especially in the Indian subcontinent. Sufi traditions influenced Bhakti movements by emphasizing devotion and personal connection to the divine, while Hindu customs affected Islamic art and architecture, evident in Mughal-era monuments. Historical interactions such as trade, conquests, and intellectual exchanges fostered a syncretic environment that enriched theological discourses and societal norms in both religions.
Infographic: Islam vs Hinduism
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com