Multiculturalism celebrates diverse cultural identities within a society, fostering inclusivity and mutual respect, while the melting pot concept encourages blending different cultures into a single, unified identity. Explore the nuances and impacts of these approaches on relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
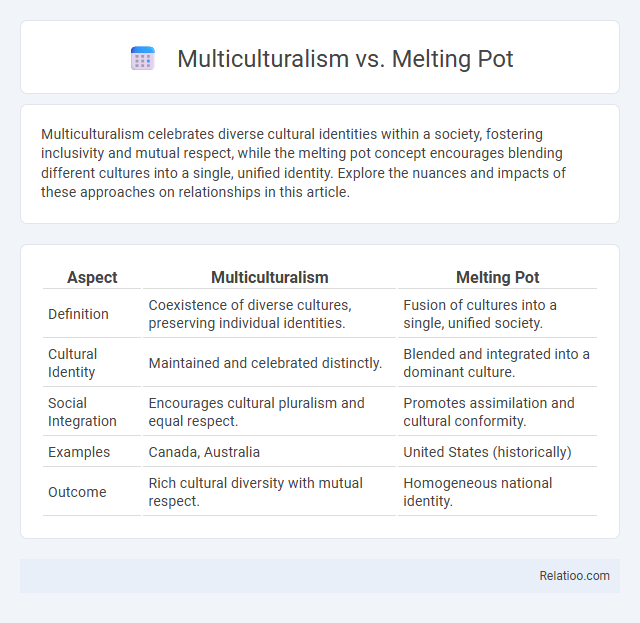
| Aspect | Multiculturalism | Melting Pot |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coexistence of diverse cultures, preserving individual identities. | Fusion of cultures into a single, unified society. |
| Cultural Identity | Maintained and celebrated distinctly. | Blended and integrated into a dominant culture. |
| Social Integration | Encourages cultural pluralism and equal respect. | Promotes assimilation and cultural conformity. |
| Examples | Canada, Australia | United States (historically) |
| Outcome | Rich cultural diversity with mutual respect. | Homogeneous national identity. |
Understanding Multiculturalism: Definition and Principles
Multiculturalism promotes the coexistence of diverse cultural identities within a society, emphasizing respect, inclusion, and equal recognition of all cultural groups. Unlike the melting pot concept, which encourages blending cultures into a single homogeneous identity, multiculturalism values preserving distinct cultural heritages while fostering social cohesion. Understanding multiculturalism helps you appreciate the principles of cultural pluralism and active intercultural dialogue essential for harmonious community living.
The Melting Pot Concept: Origins and Ideology
The Melting Pot concept originated in early 20th-century America, symbolizing the blending of diverse immigrant cultures into a single, unified national identity. Rooted in the ideology of assimilation, this approach emphasizes the absorption of individual cultural traits to create a cohesive society. Understanding this concept can help you navigate discussions about cultural integration and societal cohesion in multicultural contexts.
Historical Contexts: How Societies Embrace Diversity
Historical contexts reveal that multiculturalism promotes the coexistence of diverse cultures within a society, advocating for the preservation of distinct cultural identities. The melting pot metaphor, rooted in early 20th-century America, emphasizes assimilation and the blending of cultures to form a unified national identity. Acculturation involves the process whereby individuals or groups adopt elements of another culture while maintaining aspects of their original culture, often occurring in colonial or immigrant contexts where power dynamics influence cultural exchange.
Key Differences Between Multiculturalism and the Melting Pot
Multiculturalism promotes the coexistence of diverse cultural identities within a society, encouraging the preservation of distinct traditions and values, whereas the melting pot emphasizes the blending of different cultures into a unified, homogeneous culture. Multiculturalism values the recognition and celebration of cultural differences, while the melting pot seeks assimilation and integration into a single cultural norm. Understanding these differences helps Your perspective on social integration and cultural diversity in communities.
Social Integration vs. Cultural Preservation
Multiculturalism emphasizes social integration by encouraging diverse cultural groups to coexist while preserving their unique traditions, enriching Your community with multiple identities. The melting pot metaphor advocates for blending different cultures into a single, unified society, often prioritizing social cohesion over cultural preservation. Acculturation involves adapting to a dominant culture with possible changes in cultural practices, balancing integration efforts with the retention of core cultural elements.
Advantages of Multicultural Societies
Multicultural societies promote cultural diversity by allowing various ethnic groups to maintain their unique traditions and languages, fostering inclusivity and mutual respect. This environment enhances creativity and innovation as different perspectives and ideas come together, benefiting social and economic development. Your ability to engage with diverse cultures can improve social cohesion and global understanding, making multiculturalism a powerful advantage over assimilation approaches like the melting pot and acculturation.
Challenges and Criticisms of the Melting Pot Model
The Melting Pot model faces challenges such as the erosion of distinct cultural identities and the pressure on individuals to conform to a dominant culture, often leading to cultural homogenization. Critics argue that this approach overlooks the value of diversity and may perpetuate systemic inequalities by marginalizing minority cultures. Your quest for inclusive social integration requires recognizing these shortcomings and considering alternative models like multiculturalism that emphasize preserving cultural uniqueness.
Multiculturalism in Education and Media
Multiculturalism in education and media promotes the inclusion and representation of diverse cultural backgrounds, fostering an environment where You can appreciate and learn from different perspectives without losing individual cultural identities. Unlike the melting pot approach that encourages assimilation into a dominant culture, multiculturalism values cultural pluralism and encourages equal respect for all traditions within schools and media platforms. This approach enhances cultural awareness and critical thinking by providing varied narratives and inclusive content that reflect the breadth of global cultures.
Policy Implications: Laws and Government Approaches
Multiculturalism policies promote the preservation of diverse cultural identities through anti-discrimination laws and support for minority languages and traditions, fostering social inclusion and equality. The Melting Pot approach emphasizes assimilation, encouraging immigrants to adopt the dominant culture, often reflected in policies prioritizing a unified national identity and common language requirements. Acculturation policies balance cultural retention with integration, shaping government programs that facilitate cultural exchange while promoting civic participation and social cohesion.
The Future of Cultural Identity in Globalized Societies
The future of cultural identity in globalized societies hinges on balancing multiculturalism, melting pot integration, and acculturation processes. Multiculturalism promotes the coexistence and preservation of diverse cultural identities, while the melting pot ideal encourages blending distinct cultures into a unified national identity, leading to hybrid cultural forms. Acculturation facilitates exchange and adaptation between cultures, enabling individuals to navigate multiple identities and fostering dynamic, inclusive global communities.
Infographic: Multiculturalism vs Melting Pot
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com