Matriarchy is a social system where women hold primary power in roles of political leadership, moral authority, and control over property, while feminism advocates for gender equality and challenges patriarchal structures. Explore this article to understand the nuances and impacts of matriarchal societies versus feminist movements.
Table of Comparison
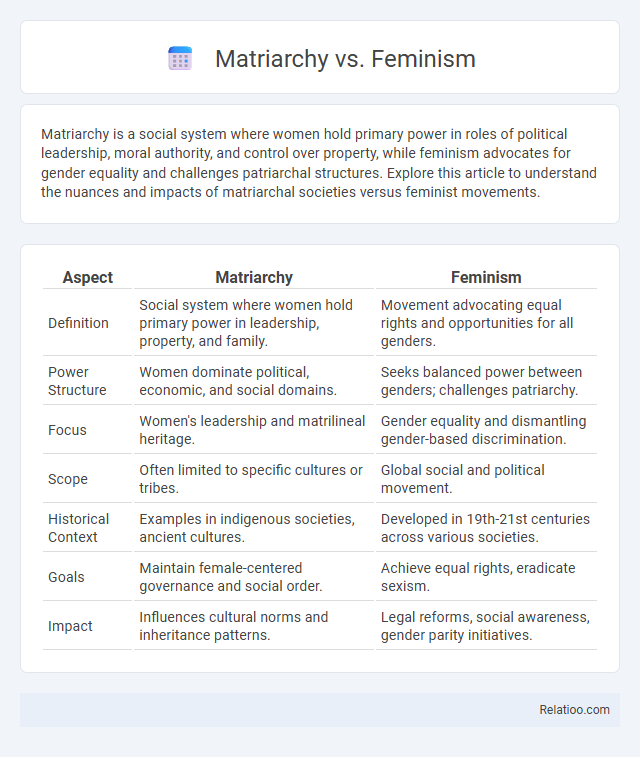
| Aspect | Matriarchy | Feminism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Social system where women hold primary power in leadership, property, and family. | Movement advocating equal rights and opportunities for all genders. |
| Power Structure | Women dominate political, economic, and social domains. | Seeks balanced power between genders; challenges patriarchy. |
| Focus | Women's leadership and matrilineal heritage. | Gender equality and dismantling gender-based discrimination. |
| Scope | Often limited to specific cultures or tribes. | Global social and political movement. |
| Historical Context | Examples in indigenous societies, ancient cultures. | Developed in 19th-21st centuries across various societies. |
| Goals | Maintain female-centered governance and social order. | Achieve equal rights, eradicate sexism. |
| Impact | Influences cultural norms and inheritance patterns. | Legal reforms, social awareness, gender parity initiatives. |
Understanding Matriarchy: Definition and Origins
Matriarchy refers to a social system where women, especially mothers, hold primary authority in roles of political leadership, moral authority, and control over property. Its origins trace back to early human societies where kinship and inheritance were matrilineal, emphasizing the centrality of women in communal life. Understanding matriarchy helps you distinguish it from feminism, which advocates for equality rather than exclusive female dominance.
Feminism Explained: Goals and Historical Context
Feminism, rooted in the 19th-century suffrage movements, seeks gender equality by challenging systemic patriarchy and advocating for women's rights in social, political, and economic spheres. Unlike matriarchy, which is a societal structure where women hold primary power, feminism promotes equal opportunities for all genders rather than dominance by one. Your understanding of feminism deepens by exploring its historical milestones, such as the Seneca Falls Convention and the rise of intersectional feminism.
Key Differences Between Matriarchy and Feminism
Matriarchy is a social system where women hold primary power in roles of political leadership, moral authority, and control over property, whereas feminism is a movement advocating for equal rights and opportunities regardless of gender. Your understanding of these concepts should highlight that matriarchy describes an existing or historical power structure dominated by women, while feminism seeks to dismantle gender-based inequalities across all systems. Key differences include matriarchy being a form of governance or societal organization and feminism being a broad ideological commitment to gender equality.
Power Dynamics: Matriarchy in Society
Matriarchy in society challenges traditional power dynamics by placing women in central roles of authority, contrasting with feminism which seeks equality within existing patriarchal frameworks. Matriarchal systems often emphasize communal decision-making and social cohesion, shifting power from hierarchical dominance to collaborative leadership. Understanding these differences can help you analyze how power structures influence gender roles and social organization.
Feminism’s Role in Gender Equality Movements
Feminism plays a pivotal role in gender equality movements by advocating for equal rights and opportunities regardless of gender, challenging both patriarchal and matriarchal systems that may perpetuate inequality. Your understanding of feminism highlights its commitment to dismantling systemic barriers and promoting social, political, and economic equality. Unlike matriarchy, which centers on female dominance, feminism seeks balance and inclusion in all spheres of society.
Common Misconceptions: Matriarchy vs Feminism
Matriarchy is often mistakenly seen as the direct opposite of patriarchy or equated with feminism, but it specifically refers to a societal structure where women hold primary power in political leadership, moral authority, and control of property, unlike feminism which advocates for gender equality and dismantling systemic gender biases. Common misconceptions arise when matriarchy is perceived as female dominance or the inverse patriarchy, whereas feminism challenges all forms of gender-based hierarchy without endorsing female supremacy. Understanding these distinctions clarifies that matriarchy is a social system concept, while feminism is a movement seeking equal rights and opportunities across genders.
Real-World Examples of Matriarchal Societies
Real-world examples of matriarchal societies include the Mosuo people in China, known for their matrilineal inheritance and female-centered family structures, and the Minangkabau in Indonesia, the world's largest matrilineal society where property and lineage pass through the female line. Feminism advocates for gender equality across all societal structures, challenging patriarchal norms but not necessarily promoting matriarchy as a replacement. Matriarchy, distinct from feminism, refers to societal systems where women hold primary power in roles of political leadership, moral authority, and control over property, offering unique perspectives on gender roles beyond the binary of feminist theory.
Feminist Achievements and Milestones Globally
Feminist achievements have significantly advanced gender equality worldwide, including landmark milestones such as women's suffrage, legalized reproductive rights, and the rise of female political leaders. International movements like #MeToo and global policy frameworks, such as the UN's Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW), have strengthened advocacy for women's rights. Your understanding of feminism's impact highlights the ongoing challenge to traditional matriarchal and patriarchal structures, shaping societies toward inclusivity and equity.
The Intersection of Matriarchy and Feminism
The intersection of matriarchy and feminism highlights the shared goal of challenging patriarchal norms while emphasizing different approaches to female empowerment and societal organization. Matriarchy advocates for female-centered governance and social structures, often rooted in historical and cultural contexts where women hold primary authority, whereas feminism broadly seeks gender equality and dismantling systemic oppression. Understanding this intersection provides insight into how feminist movements can incorporate matriarchal principles to enhance strategies for equity and social justice.
Future Perspectives: Evolving Gender Paradigms
Future perspectives on evolving gender paradigms emphasize the transformation of traditional matriarchy and feminism into more inclusive frameworks prioritizing gender equality and fluidity. Emerging societal models highlight collaboration between diverse gender identities, dismantling hierarchical power structures and fostering equitable participation across social, political, and economic spheres. Advances in gender theory and intersectional activism continue to redefine norms, promoting adaptive, resilient communities centered on mutual respect and empowerment.
Infographic: Matriarchy vs Feminism
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com