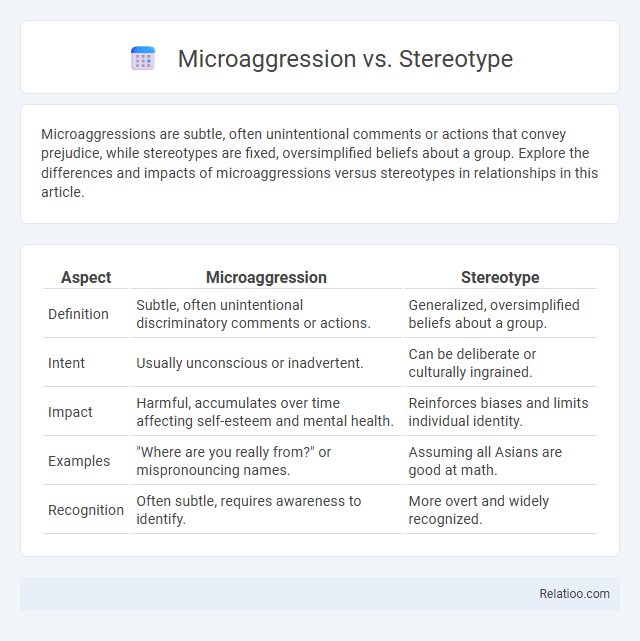
Microaggressions are subtle, often unintentional comments or actions that convey prejudice, while stereotypes are fixed, oversimplified beliefs about a group. Explore the differences and impacts of microaggressions versus stereotypes in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Microaggression | Stereotype |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Subtle, often unintentional discriminatory comments or actions. | Generalized, oversimplified beliefs about a group. |
| Intent | Usually unconscious or inadvertent. | Can be deliberate or culturally ingrained. |
| Impact | Harmful, accumulates over time affecting self-esteem and mental health. | Reinforces biases and limits individual identity. |
| Examples | "Where are you really from?" or mispronouncing names. | Assuming all Asians are good at math. |
| Recognition | Often subtle, requires awareness to identify. | More overt and widely recognized. |
Understanding Microaggressions: Definition and Origins
Microaggressions are subtle, often unintentional actions or comments that convey prejudiced attitudes toward marginalized groups, differing from overt stereotypes that are broad, fixed beliefs about a group. Originating from everyday interactions, microaggressions perpetuate systemic biases by reinforcing negative assumptions and social hierarchies in indirect ways. Understanding microaggressions requires recognizing their impact on psychological well-being and the cumulative effect they have on marginalized individuals, distinguishing them from explicit stereotypes and larger societal prejudices.
What Are Stereotypes? Exploring Their Nature
Stereotypes are generalized beliefs or assumptions about a group of people based on characteristics such as race, gender, or age, often oversimplifying and ignoring individual differences. These cognitive shortcuts influence perception and behavior, shaping social interactions and reinforcing societal biases. Unlike microaggressions which are subtle, often unintentional actions or comments that convey derogatory messages, stereotypes serve as underlying frameworks that can perpetuate prejudiced attitudes.
Key Differences Between Microaggressions and Stereotypes
Microaggressions are subtle, often unintentional, discriminatory comments or actions directed at marginalized groups, reflecting underlying biases. Stereotypes are generalized beliefs or assumptions about a group, which may or may not be expressed through microaggressions. Key differences lie in expression and impact: stereotypes are broad, fixed ideas, whereas microaggressions are specific, often covert behaviors that perpetuate those stereotypes and cause psychological harm.
Common Examples of Microaggressions in Daily Life
Common examples of microaggressions in daily life include subtle comments or actions that convey implicit biases, such as assuming someone's intelligence based on their ethnicity, questioning a person's belonging due to their accent, or complimenting someone by implying surprise at their competence. These small yet pervasive behaviors differ from stereotypes, which are generalized and fixed beliefs about a group, and overt discrimination characterized by explicit prejudice. Recognizing microaggressions helps address the nuanced ways bias manifests in social interactions and workplace environments.
How Stereotypes Influence Social Perceptions
Stereotypes shape social perceptions by creating generalized beliefs about groups, which can lead you to interpret behaviors through biased lenses. These oversimplified ideas affect interactions, often reinforcing microaggressions--subtle, indirect hostile behaviors that stem from these assumptions. Understanding the distinction between stereotypes and microaggressions helps in identifying and reducing their impact on social dynamics.
The Impact of Microaggressions on Mental Health
Microaggressions are subtle, often unintentional, slights that convey negative or derogatory messages to individuals based on their identity, contrasting with overt stereotypes which are broad, fixed beliefs about groups. The continuous exposure to microaggressions triggers stress responses linked to anxiety, depression, and lowered self-esteem, significantly affecting Your mental health. Understanding the nuanced distinctions among microaggressions, stereotypes, and overt discrimination is crucial for fostering inclusive environments and mitigating their psychological impact.
Stereotype Threat: Consequences and Effects
Stereotype threat occurs when individuals fear confirming negative stereotypes about their social group, leading to increased anxiety and reduced performance in academic and professional settings. This psychological burden can cause diminished working memory, lower motivation, and a decrease in task engagement, ultimately reinforcing the very stereotypes it stems from. Understanding stereotype threat is crucial for developing interventions that promote equity and mitigate performance gaps linked to social identity.
Microaggressions in the Workplace and Education
Microaggressions in the workplace and education are subtle, often unintentional, behaviors or comments that communicate bias or discrimination toward marginalized groups, impacting psychological well-being and performance. Unlike overt stereotypes, which are generalized beliefs about a group, microaggressions manifest through everyday interactions that undermine inclusion and diversity efforts. Addressing microaggressions through awareness training and policy reforms is essential for creating equitable environments that support all individuals' growth and success.
Strategies to Address Microaggressions and Stereotypes
Addressing microaggressions and stereotypes requires active awareness and intentional communication in your daily interactions. Strategies include fostering open dialogue to challenge biased assumptions, implementing diversity training programs, and encouraging empathy through perspective-taking exercises. Creating safe spaces where individuals feel valued helps disrupt harmful patterns and promotes inclusive environments.
Promoting Awareness: Fostering Inclusive Environments
Promoting awareness of microaggressions, stereotypes, and biases is essential for fostering inclusive environments where diversity is valued and respected. Understanding the subtle nature of microaggressions and how stereotypes perpetuate systemic inequality empowers individuals and organizations to implement targeted training and policies. Creating spaces that actively address these issues enhances psychological safety, supports equity, and drives cultural competence across communities.
Infographic: Microaggression vs Stereotype
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com