Honor killing is a violent act driven by perceived family disgrace, often rooted in patriarchal cultural norms, while cultural murder encompasses broader societal practices that systematically suppress individual freedom in the name of tradition. Explore the distinctions and implications of these practices in this article.
Table of Comparison
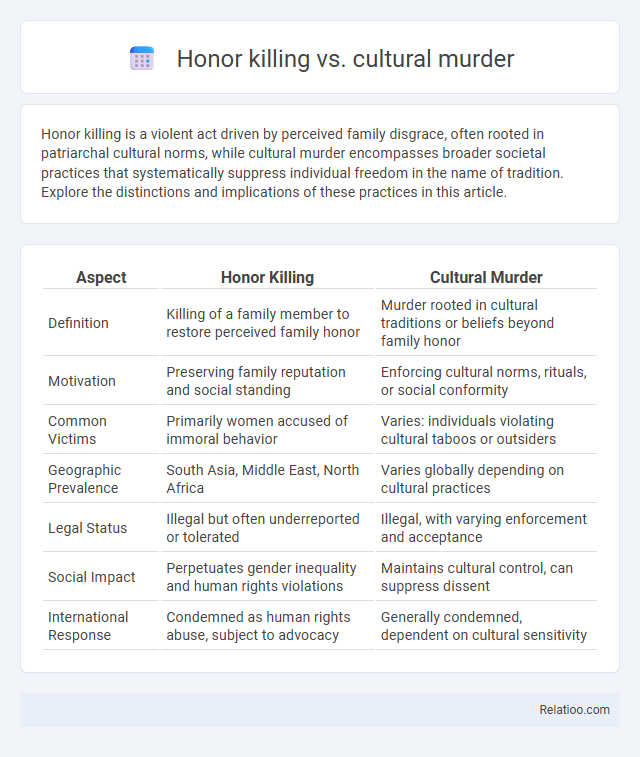
| Aspect | Honor Killing | Cultural Murder |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Killing of a family member to restore perceived family honor | Murder rooted in cultural traditions or beliefs beyond family honor |
| Motivation | Preserving family reputation and social standing | Enforcing cultural norms, rituals, or social conformity |
| Common Victims | Primarily women accused of immoral behavior | Varies: individuals violating cultural taboos or outsiders |
| Geographic Prevalence | South Asia, Middle East, North Africa | Varies globally depending on cultural practices |
| Legal Status | Illegal but often underreported or tolerated | Illegal, with varying enforcement and acceptance |
| Social Impact | Perpetuates gender inequality and human rights violations | Maintains cultural control, can suppress dissent |
| International Response | Condemned as human rights abuse, subject to advocacy | Generally condemned, dependent on cultural sensitivity |
Understanding Honor Killing: Definitions and Context
Honor killing involves the murder of a family member, usually a woman, perceived to have brought dishonor upon the family through actions deemed socially or culturally unacceptable. Cultural murder, while similar in intent, is a broader term encompassing any killing justified by cultural or traditional beliefs, often justified to maintain social order or norms. Understanding the distinctions requires examining the motivations, legal contexts, and societal acceptance of these acts within different communities.
Cultural Murder: Meaning and Distinctions
Cultural murder refers to the systematic destruction of a community's cultural identity, often through practices that erase language, traditions, or heritage, distinguishing it from honor killing, which involves the violent punishment of individuals for supposedly bringing shame to their family. Unlike honor killing, which targets individuals, cultural murder attacks the collective fabric of a society, aiming to obliterate entire cultural groups or their ways of life. Understanding cultural murder helps you recognize the broader social and political implications beyond personal or familial violence.
Historical Roots of Honor Killings
Honor killings have deep historical roots tied to patriarchal societies where family reputation dictated social order, often leading to lethal punishment for perceived moral transgressions. Cultural murder shares similarities but involves a broader spectrum of socially sanctioned violence, not solely limited to family honor codes. Your understanding of these terms deepens when recognizing that honor killings specifically emerge from honor-based cultures where collective reputation outweighs individual rights.
Cultural Murders Across Societies
Cultural murders refer to killings justified by societal norms and traditions, often rooted in collective beliefs that override individual rights. Unlike honor killings, which target perceived family dishonor typically related to women's behavior, cultural murders span broader contexts, including caste-based violence, ritualistic practices, or political purges. Your understanding of these distinctions can help challenge harmful customs and promote human rights across diverse societies.
Motivations Behind Honor Killings
Honor killings stem from deeply ingrained cultural and social norms that prioritize family reputation and social status over individual rights, often targeting women accused of dishonoring their family. Cultural murder extends beyond individual families, involving community-sanctioned violence to enforce collective cultural codes and suppress dissenting behavior. The motivations behind honor killings involve preserving perceived moral order, controlling gender roles, and reinforcing patriarchal authority through extreme measures.
Social Dynamics in Cultural Murders
Social dynamics in cultural murders reveal deeply entrenched community norms that justify violence to uphold traditional honor codes, often reinforcing patriarchal control and social conformity. Honor killings specifically target individuals, usually women, perceived to have brought shame, whereas cultural murders may extend to broader acts sanctioned by collective beliefs or rituals. These acts reflect complex intersections of social pressure, identity, and power, making prevention efforts challenging within tightly knit communities.
Legal Perspectives: Honor Killing vs. Cultural Murder
Legal perspectives distinguish honor killing as a criminal offense punishable under national and international laws, emphasizing its blatant violation of human rights and gender equality. Cultural murder, while not a formal legal term, refers to acts justified by cultural practices but still subject to prosecution when infringing on individual rights, often leading to complex legal debates about cultural relativism versus universal human rights. Understanding the legal frameworks helps you recognize that despite cultural arguments, both honor killing and cultural murder face increasing legal condemnation and stricter enforcement worldwide.
Gender, Power, and Patriarchy
Honor killing, cultural murder, and honor-based violence share roots in patriarchal systems that enforce rigid gender roles and power imbalances, often targeting women to maintain male dominance and social control. These practices reflect deeply ingrained gender inequality, where women's autonomy challenges family or community honor, leading to violence as a means of preserving patriarchal authority. Understanding these acts requires examining the intersection of gender oppression, cultural norms, and power structures that perpetuate systemic violence against women.
Global Responses and Prevention Strategies
Global responses to honor killing, cultural murder, and honor-related violence emphasize legislative reforms, victim protection, and awareness campaigns targeting deep-rooted social norms. Prevention strategies include implementing stringent laws with enforcement mechanisms, promoting gender equality through education, and supporting grassroots movements that challenge patriarchal traditions in countries across South Asia, the Middle East, and North Africa. International organizations collaborate with local governments to enhance survivor support systems and develop culturally sensitive interventions addressing honor-based violence worldwide.
Moving Forward: Advocacy and Change
Moving forward, advocacy against honor killing and cultural murder emphasizes protecting your human rights through education, legal reforms, and community engagement. Promoting awareness about the devastating impact of these practices fosters societal change and strengthens victim support systems. Empowering survivors and challenging harmful traditions are crucial steps in dismantling these culturally ingrained acts of violence.
Infographic: Honor killing vs Cultural murder
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com