Power-based approaches prioritize control and authority in relationships, often leading to imbalance and conflict, while interest-based approaches emphasize mutual needs and collaboration to foster trust and cooperation. Discover detailed strategies to navigate these dynamics effectively in this article.
Table of Comparison
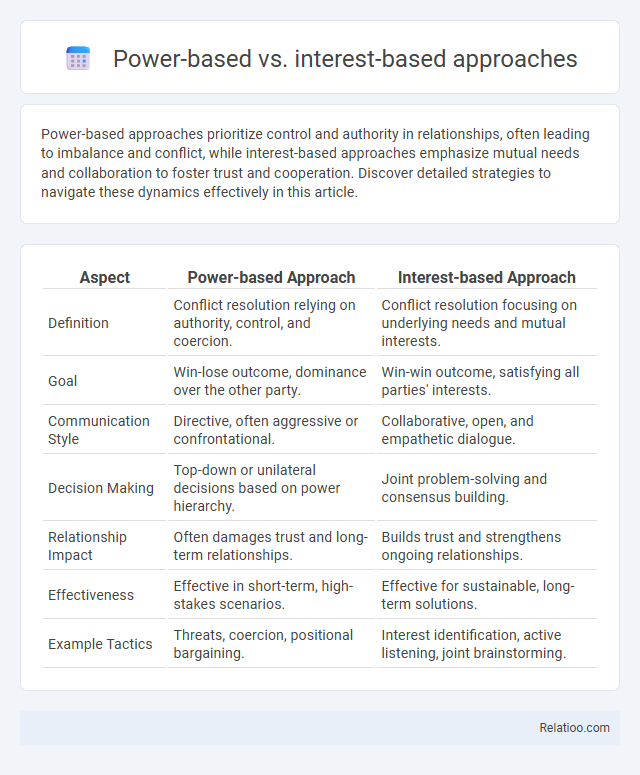
| Aspect | Power-based Approach | Interest-based Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Conflict resolution relying on authority, control, and coercion. | Conflict resolution focusing on underlying needs and mutual interests. |
| Goal | Win-lose outcome, dominance over the other party. | Win-win outcome, satisfying all parties' interests. |
| Communication Style | Directive, often aggressive or confrontational. | Collaborative, open, and empathetic dialogue. |
| Decision Making | Top-down or unilateral decisions based on power hierarchy. | Joint problem-solving and consensus building. |
| Relationship Impact | Often damages trust and long-term relationships. | Builds trust and strengthens ongoing relationships. |
| Effectiveness | Effective in short-term, high-stakes scenarios. | Effective for sustainable, long-term solutions. |
| Example Tactics | Threats, coercion, positional bargaining. | Interest identification, active listening, joint brainstorming. |
Understanding Power-Based Approaches
Power-based approaches emphasize control, authority, and enforcement to achieve desired outcomes, relying on hierarchical structures and resource leverage to influence behavior. Understanding power-based methods involves recognizing how individuals or groups use dominance and coercion to maintain stability and order within organizations or social systems. Your ability to navigate these dynamics can enhance conflict resolution and decision-making effectiveness.
Defining Interest-Based Approaches
Interest-based approaches prioritize understanding the underlying needs, desires, and motivations of all parties to foster collaborative problem-solving and mutual benefit. Your communication becomes more effective as these approaches emphasize empathy and active listening, creating solutions that address core concerns rather than superficial demands. Unlike power-based methods, interest-based techniques enhance stability by building trust and long-term relationships grounded in shared interests.
Key Differences Between Power and Interest-Based Methods
Power-based approaches prioritize authority and control, using hierarchical influence to achieve outcomes, while interest-based methods emphasize understanding stakeholders' needs and fostering collaboration. Stability in power-based methods often relies on maintaining strict command structures, whereas interest-based approaches achieve stability through consensus and mutual benefit. Key differences include the reliance on coercion in power-based tactics versus negotiation and shared goals in interest-based strategies.
Advantages of Power-Based Negotiation
Power-based negotiation leverages your authority and resources to influence outcomes quickly, often resulting in decisive agreements that favor your position. This approach provides clear control over the negotiation process, minimizing uncertainty and reducing the time spent on reaching a resolution. Power-based strategies can be advantageous in high-stakes or competitive environments where maintaining dominance is crucial for achieving strategic objectives.
Advantages of Interest-Based Negotiation
Interest-based negotiation enhances collaboration by prioritizing the underlying needs and concerns of all parties rather than relying on power dynamics, leading to more sustainable and mutually beneficial agreements. This approach reduces conflict and builds trust, promoting long-term stability in relationships and negotiations. You benefit from creative solutions that address core interests, ensuring agreements are resilient and adaptable to future challenges.
Common Scenarios for Power-Based Solutions
Power-based approaches prioritize authority and control to enforce decisions, commonly seen in hierarchical organizations and conflict resolution where clear dominance is necessary. Interest-based methods emphasize collaboration and mutual benefit, suitable for negotiations and partnerships with shared goals. Power-based solutions are stable in scenarios requiring swift enforcement, compliance, or hierarchical order, especially in crisis management, regulatory enforcement, and competitive corporate settings.
When to Employ Interest-Based Strategies
Interest-based strategies are most effective when parties seek collaborative solutions that address underlying needs and promote long-term relationships. You should employ interest-based approaches in situations where mutual gain and ongoing cooperation outweigh the need for immediate power assertion. Stability is enhanced by focusing on shared interests, fostering trust and reducing conflict recurrence.
Challenges and Risks of Power-Based Approaches
Power-based approaches often face challenges such as resistance, lack of cooperation, and potential escalation of conflicts due to their coercive nature. These methods risk undermining long-term stability by fostering resentment and reducing trust among stakeholders. Interest-based approaches, by contrast, promote collaboration and sustainable solutions through understanding and addressing the underlying needs and motivations of parties involved.
Building Consensus with Interest-Based Techniques
Power-based approaches rely on authority and control, often creating resistance and instability in negotiations. Interest-based techniques prioritize understanding underlying needs and fostering collaboration, which enhances trust and leads to more sustainable, consensus-driven outcomes. Building consensus through interest-based methods strengthens relationships and promotes long-term stability in conflict resolution.
Choosing the Right Approach for Effective Conflict Resolution
Power-based approaches leverage authority and control to enforce decisions rapidly, often leading to immediate compliance but risking long-term resentment and instability. Interest-based approaches prioritize understanding underlying needs and motivations, fostering collaborative solutions that enhance mutual satisfaction and sustainable stability. Selecting the appropriate conflict resolution method depends on the context, with interest-based strategies generally promoting enduring harmony, while power-based tactics may be necessary in situations requiring swift resolution.
Infographic: Power-based vs Interest-based approaches
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com