Facilitation fosters collaborative communication and consensus-building in relationships, while adjudication involves making decisions to resolve conflicts authoritatively. Explore this article to understand the key differences and applications of facilitation versus adjudication.
Table of Comparison
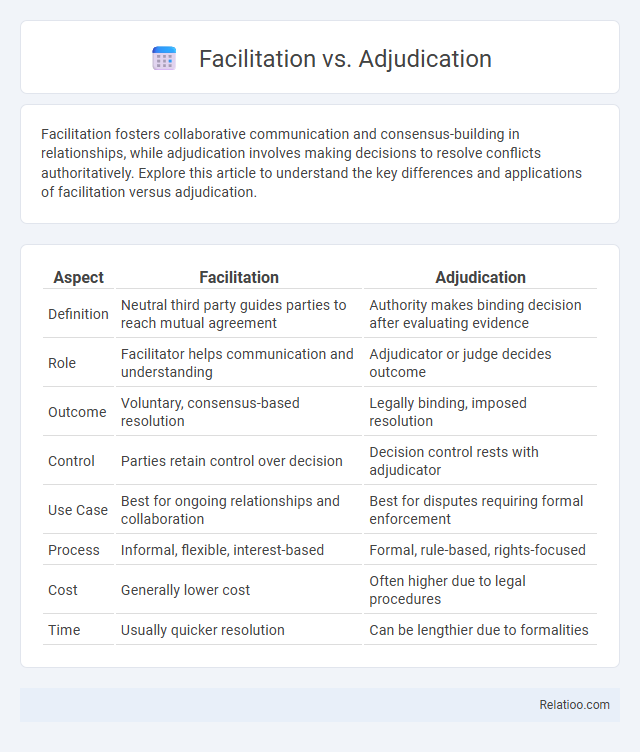
| Aspect | Facilitation | Adjudication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Neutral third party guides parties to reach mutual agreement | Authority makes binding decision after evaluating evidence |
| Role | Facilitator helps communication and understanding | Adjudicator or judge decides outcome |
| Outcome | Voluntary, consensus-based resolution | Legally binding, imposed resolution |
| Control | Parties retain control over decision | Decision control rests with adjudicator |
| Use Case | Best for ongoing relationships and collaboration | Best for disputes requiring formal enforcement |
| Process | Informal, flexible, interest-based | Formal, rule-based, rights-focused |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Often higher due to legal procedures |
| Time | Usually quicker resolution | Can be lengthier due to formalities |
Introduction to Facilitation and Adjudication
Facilitation involves guiding parties toward collaborative problem-solving by fostering open communication and mutual understanding without imposing decisions. Adjudication is a formal process where an impartial adjudicator evaluates evidence and arguments to render a binding decision. Unlike facilitation, adjudication emphasizes authoritative resolution, making it essential in legal and dispute contexts.
Defining Facilitation: Key Concepts
Facilitation involves guiding a group or individuals through a process to achieve mutual understanding and consensus without imposing decisions. It emphasizes active listening, open communication, and creating a collaborative environment to resolve conflicts or plan actions. Unlike adjudication or judgment, facilitation is neutral and process-oriented, focusing on empowerment rather than authoritative decision-making.
Understanding Adjudication: Essential Elements
Adjudication involves a formal process where an impartial adjudicator examines evidence and legal arguments to resolve disputes, making binding decisions enforceable by law. Essential elements include the presence of a competent authority, the right to be heard for all parties, and adherence to procedural fairness ensuring decisions are just and unbiased. Unlike facilitation, which encourages voluntary agreement, adjudication imposes a resolution when parties cannot settle disputes independently.
Primary Objectives of Facilitation
Facilitation primarily aims to guide Your group toward effective communication and collaborative decision-making by fostering a neutral environment that encourages participation and understanding. Unlike adjudication or judgment, which involve authoritative decisions and conflict resolution through imposed rulings, facilitation focuses on helping participants identify common goals and develop mutually acceptable solutions. The core objective is to empower Your team to navigate discussions productively, ensuring inclusive engagement and consensus-building without external imposition.
Core Purposes of Adjudication
The core purpose of adjudication is to provide a legally binding resolution to disputes by evaluating evidence and applying relevant laws, ensuring finality and enforceability. Unlike facilitation, which aims to promote cooperative dialogue without imposing decisions, adjudication involves a formal process where an impartial judge or tribunal renders a definitive ruling. Your understanding of adjudication highlights its critical role in maintaining rule of law and protecting rights through authoritative judgment.
Facilitation vs Adjudication: Process Comparison
Facilitation involves a collaborative process where a neutral third party helps disputing parties communicate effectively to reach a mutually acceptable agreement, emphasizing open dialogue and consensus-building. Adjudication is a more formal procedure where an impartial decision-maker evaluates evidence and arguments to impose a binding resolution based on legal or contractual frameworks. Unlike adjudication, facilitation prioritizes cooperative problem-solving without imposing solutions, making it suitable for maintaining relationships and promoting voluntary compliance.
Key Benefits of Facilitation
Facilitation enhances communication and collaboration by guiding parties toward mutually agreeable solutions, reducing conflict and promoting sustainable outcomes. It empowers participants to actively engage in problem-solving, fostering ownership and commitment to decisions without the need for imposed rulings. Facilitation's key benefits include increased flexibility, time efficiency, and cost-effectiveness compared to adjudication and judgment processes.
Major Advantages of Adjudication
Adjudication offers the major advantage of providing a legally binding decision that ensures enforceability and finality in dispute resolution. It delivers a structured process where an impartial adjudicator or judge evaluates evidence and applies relevant laws to resolve conflicts objectively. This method reduces ambiguity and promotes certainty by producing authoritative rulings that can be upheld or appealed within formal judicial systems.
Choosing Between Facilitation and Adjudication
Choosing between facilitation and adjudication depends on the desired level of control and formality in dispute resolution. Facilitation emphasizes collaborative problem-solving through open communication, making it ideal for preserving relationships and achieving mutually beneficial outcomes. Adjudication involves a formal process where a neutral third party imposes a binding decision, suitable for conflicts requiring definitive resolution and legal authority.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Conflict Resolution Approach
Choosing the appropriate conflict resolution approach depends on the complexity and nature of the dispute, with facilitation promoting collaborative dialogue and mutual understanding, adjudication providing a structured, neutral decision by a third party, and judgment ensuring legally binding outcomes. Your decision should consider factors such as the desired level of control over the outcome, time sensitivity, confidentiality, and the relationship between parties involved. By aligning the resolution method with these criteria, you can effectively address conflicts while preserving relationships and ensuring fair, enforceable solutions.
Infographic: Facilitation vs Adjudication
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com