Emotional Intelligence (EI) enhances relationship quality by improving empathy, communication, and emotional regulation, while Cognitive Intelligence (CI) supports problem-solving and decision-making within interactions. Explore this article to understand how balancing EI and CI fosters stronger, healthier relationships.
Table of Comparison
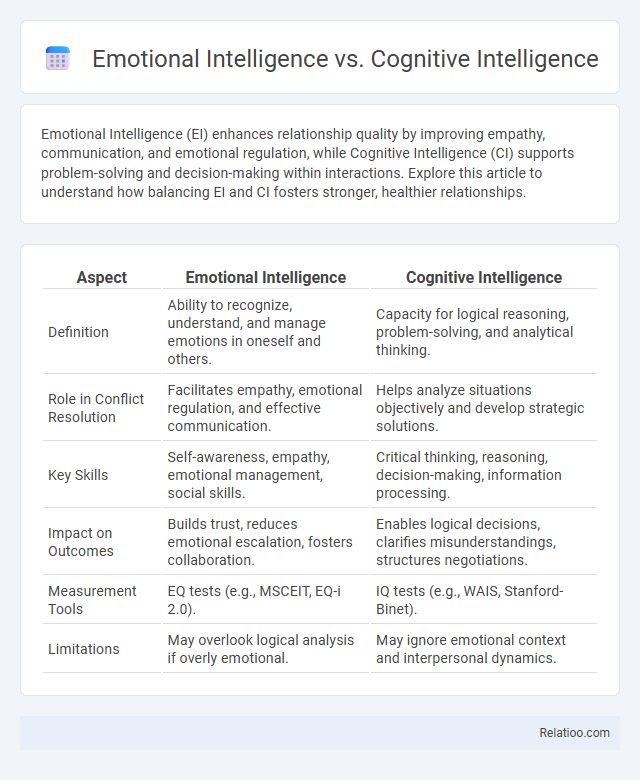
| Aspect | Emotional Intelligence | Cognitive Intelligence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to recognize, understand, and manage emotions in oneself and others. | Capacity for logical reasoning, problem-solving, and analytical thinking. |
| Role in Conflict Resolution | Facilitates empathy, emotional regulation, and effective communication. | Helps analyze situations objectively and develop strategic solutions. |
| Key Skills | Self-awareness, empathy, emotional management, social skills. | Critical thinking, reasoning, decision-making, information processing. |
| Impact on Outcomes | Builds trust, reduces emotional escalation, fosters collaboration. | Enables logical decisions, clarifies misunderstandings, structures negotiations. |
| Measurement Tools | EQ tests (e.g., MSCEIT, EQ-i 2.0). | IQ tests (e.g., WAIS, Stanford-Binet). |
| Limitations | May overlook logical analysis if overly emotional. | May ignore emotional context and interpersonal dynamics. |
Understanding Emotional Intelligence
Understanding emotional intelligence involves recognizing and managing one's own emotions while effectively perceiving and influencing the emotions of others. Unlike cognitive intelligence, which emphasizes analytical problem-solving and logical reasoning, emotional intelligence prioritizes empathy, self-regulation, and social skills. Sensitivity contributes to emotional intelligence by enhancing awareness and responsiveness to subtle emotional cues in interpersonal interactions.
Defining Cognitive Intelligence
Cognitive intelligence refers to your ability to process information, reason logically, and solve complex problems using analytical thinking and memory. Emotional intelligence involves recognizing, understanding, and managing your emotions and the emotions of others, which enhances interpersonal relationships. Sensitivity relates to how acutely you perceive emotional cues and environmental stimuli, influencing empathy and social awareness.
Key Differences Between Emotional and Cognitive Intelligence
Emotional intelligence involves the ability to recognize, understand, and manage emotions in oneself and others, whereas cognitive intelligence refers to intellectual abilities such as logic, reasoning, and problem-solving. Key differences include emotional intelligence's focus on empathy, social skills, and emotional regulation, while cognitive intelligence emphasizes analytical thinking and memory retention. Sensitivity, often linked to emotional intelligence, denotes heightened awareness and responsiveness to environmental and interpersonal stimuli but lacks the structured processing characteristic of cognitive intelligence.
Components of Emotional Intelligence
Emotional Intelligence encompasses self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills, enabling individuals to manage their emotions and understand others effectively. Unlike Cognitive Intelligence, which focuses on logical reasoning, memory, and problem-solving, Emotional Intelligence emphasizes interpersonal communication and emotional management. Sensitivity relates to the responsiveness to emotional stimuli but lacks the structured components found in Emotional Intelligence that promote adaptive social interactions.
Elements of Cognitive Intelligence
Cognitive Intelligence primarily encompasses elements such as memory, problem-solving skills, logical reasoning, and analytical thinking, enabling individuals to process and evaluate information effectively. Unlike Emotional Intelligence, which centers on self-awareness, empathy, and emotional regulation, cognitive intelligence focuses on intellectual capabilities and knowledge acquisition. Sensitivity involves responsiveness to external stimuli and emotional cues, differing fundamentally from the cognitive processes driving intellectual understanding and decision-making.
The Role of Emotional Intelligence in Relationships
Emotional intelligence plays a crucial role in relationships by enabling you to recognize, understand, and manage both your own emotions and those of others, leading to better communication and conflict resolution. Unlike cognitive intelligence, which focuses on logical reasoning and problem-solving, emotional intelligence emphasizes empathy and social skills essential for building trust and intimacy. Sensitivity complements emotional intelligence by enhancing your awareness of emotional cues, but emotional intelligence provides the tools needed to respond effectively and maintain healthy relationships.
Cognitive Intelligence and Problem-Solving
Cognitive intelligence primarily drives problem-solving by enabling logical reasoning, analytical thinking, and the ability to process complex information efficiently. Unlike emotional intelligence, which manages emotions and social interactions, cognitive intelligence focuses on intellectual tasks such as critical thinking and decision-making. Sensitivity, often related to perception and empathy, complements cognitive skills by providing context but does not directly enhance problem-solving capabilities inherent to cognitive intelligence.
Impact on Personal and Professional Success
Emotional intelligence enhances personal and professional success by improving self-awareness, empathy, and interpersonal relationships, leading to better teamwork and conflict resolution. Cognitive intelligence contributes to success through problem-solving abilities, analytical thinking, and knowledge application, essential for decision-making and technical tasks. Sensitivity, often linked to emotional intelligence, aids in recognizing and responding to others' emotions, fostering trust and effective communication in diverse work environments.
Developing Emotional and Cognitive Intelligence
Developing Emotional Intelligence enhances your ability to recognize, understand, and manage emotions effectively, fostering better interpersonal relationships and decision-making. Cognitive Intelligence involves analytical thinking, problem-solving skills, and knowledge acquisition, crucial for learning and adapting in complex environments. Balancing Emotional and Cognitive Intelligence leads to improved self-awareness, empathy, and rational judgment, empowering you to navigate social interactions and challenges with greater ease.
Which Is More Important: Emotional or Cognitive Intelligence?
Emotional intelligence, involving self-awareness, empathy, and emotional regulation, often proves more critical for effective leadership, relationship building, and stress management than cognitive intelligence, which emphasizes analytical thinking and problem-solving skills. Sensitivity enhances emotional intelligence by deepening interpersonal understanding and responsiveness, yet cognitive intelligence remains essential for technical expertise and decision-making. Balancing emotional and cognitive intelligence fosters optimal personal and professional success, with emotional intelligence generally having a greater impact on social interactions and adaptability.
Infographic: Emotional Intelligence vs Cognitive Intelligence
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com