Disappointment arises from unmet expectations, while anger is a reactive emotion triggered by perceived injustice or harm. Explore the nuanced differences between these emotions and their impact on relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
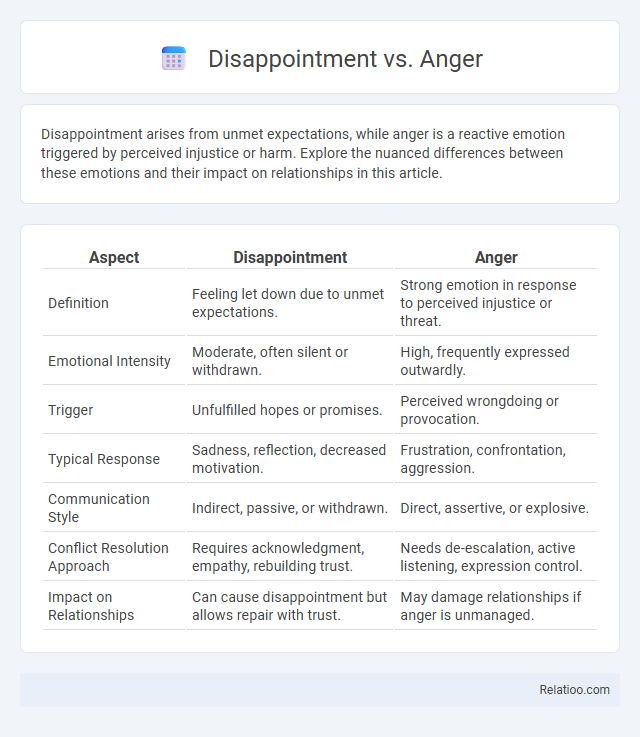
| Aspect | Disappointment | Anger |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Feeling let down due to unmet expectations. | Strong emotion in response to perceived injustice or threat. |
| Emotional Intensity | Moderate, often silent or withdrawn. | High, frequently expressed outwardly. |
| Trigger | Unfulfilled hopes or promises. | Perceived wrongdoing or provocation. |
| Typical Response | Sadness, reflection, decreased motivation. | Frustration, confrontation, aggression. |
| Communication Style | Indirect, passive, or withdrawn. | Direct, assertive, or explosive. |
| Conflict Resolution Approach | Requires acknowledgment, empathy, rebuilding trust. | Needs de-escalation, active listening, expression control. |
| Impact on Relationships | Can cause disappointment but allows repair with trust. | May damage relationships if anger is unmanaged. |
Understanding Disappointment and Anger
Disappointment arises when expectations are unmet, leaving you feeling let down or discouraged, while anger is a more intense emotional reaction often triggered by perceived injustice or harm. Understanding disappointment involves recognizing its connection to unmet hopes, whereas anger involves a readiness to confront or react to an offense. By distinguishing these emotions, you can manage your responses more effectively and improve emotional resilience.
Key Differences Between Disappointment and Anger
Disappointment arises from unmet expectations and a sense of sadness or letdown, while anger stems from perceived injustice or frustration, triggering a stronger emotional and physiological response. Disappointment tends to be passive, involving reflection and regret, whereas anger is often active, provoking confrontation or action. Understanding these distinctions is essential for effective emotional regulation and communication.
Psychological Origins of Disappointment
Disappointment arises from unmet expectations and experiences a disruption in one's anticipated outcomes, rooted in cognitive processing of reality versus desire. Anger typically originates from perceived threats or injustices, triggering a physiological fight-or-flight response, whereas disappointment involves a more reflective emotional state linked to loss or unmet hopes. Understanding the psychological origins of disappointment involves recognizing how cognitive appraisal and emotional regulation shape the distress associated with unfulfilled aspirations.
The Root Causes of Anger
Anger's root causes often stem from unmet expectations, perceived injustices, or feelings of vulnerability, distinguishing it from disappointment, which is primarily linked to unmet hopes or outcomes. While disappointment is a response to specific setbacks affecting your goals or desires, anger involves a deeper emotional reaction tied to personal boundaries and self-protection mechanisms. Understanding these fundamental differences helps you manage emotional responses effectively and improve interpersonal communication.
Emotional and Physical Manifestations
Disappointment often triggers feelings of sadness and withdrawal, accompanied by a decrease in energy and sometimes mild physical symptoms like a heavy chest or fatigue. Anger triggers heightened arousal, with increased heart rate, muscle tension, and a surge of adrenaline, often resulting in irritability or aggressive behavior. While both emotions impact mental states, anger typically induces more intense physical reactions compared to the subdued physical manifestations of disappointment.
How Disappointment Influences Behavior
Disappointment influences behavior by lowering motivation and increasing feelings of sadness, often leading to withdrawal or reduced effort in future tasks. Unlike anger, which can provoke aggressive responses and immediate action, disappointment typically results in more reflective and subdued reactions, affecting your long-term attitude and decision-making. Managing disappointment effectively helps maintain emotional balance and fosters resilience in the face of setbacks.
Anger’s Impact on Relationships
Anger can significantly damage your relationships by creating communication barriers and fostering resentment between individuals. Unlike disappointment, which is often introspective and temporary, anger tends to provoke immediate, intense reactions that strain emotional bonds. Managing anger constructively is essential to maintaining trust and open dialogue with loved ones.
Managing Disappointment Effectively
Managing disappointment effectively involves acknowledging feelings without letting them escalate into anger, which can damage relationships and cloud judgment. Techniques such as cognitive reframing, mindfulness, and setting realistic expectations help in processing disappointment constructively. Emotional regulation strategies enhance resilience, allowing individuals to learn from setbacks and maintain psychological well-being.
Healthy Strategies for Coping with Anger
Healthy strategies for coping with anger include recognizing your emotional triggers, practicing deep breathing exercises, and engaging in physical activities like walking or yoga to release tension. You can also benefit from expressing your feelings constructively through journaling or talking to a trusted friend or therapist, which helps prevent pent-up frustration and misdirected anger. Developing these habits enhances emotional regulation and supports long-term mental well-being.
Choosing Constructive Responses to Difficult Emotions
Disappointment often arises from unmet expectations, while anger stems from perceived injustice or threat, both requiring mindful emotional regulation to foster resilience. Choosing constructive responses involves recognizing these feelings, practicing empathy, and channeling energy into problem-solving rather than blame or rumination. Cognitive-behavioral strategies and mindfulness techniques effectively transform these difficult emotions into opportunities for personal growth and improved relationships.
Infographic: Disappointment vs Anger
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com