Denial blocks emotional growth by refusing to acknowledge reality, while acceptance fosters healing through embracing truth and feelings. Discover effective strategies to move from denial to acceptance in this article.
Table of Comparison
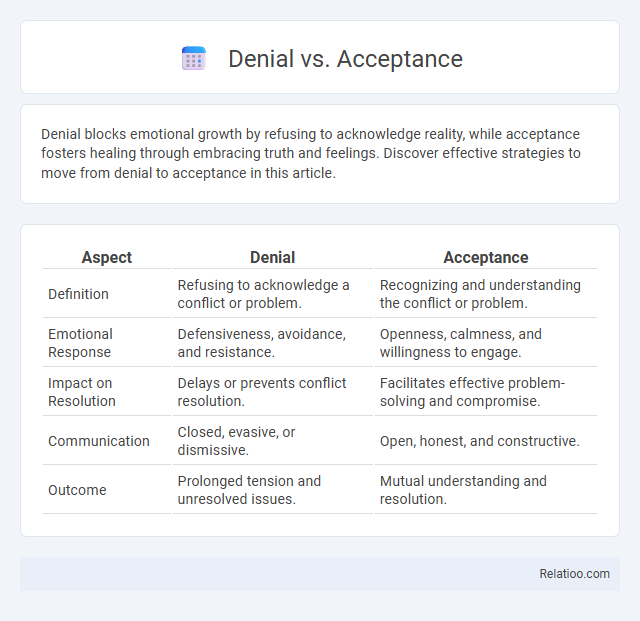
| Aspect | Denial | Acceptance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Refusing to acknowledge a conflict or problem. | Recognizing and understanding the conflict or problem. |
| Emotional Response | Defensiveness, avoidance, and resistance. | Openness, calmness, and willingness to engage. |
| Impact on Resolution | Delays or prevents conflict resolution. | Facilitates effective problem-solving and compromise. |
| Communication | Closed, evasive, or dismissive. | Open, honest, and constructive. |
| Outcome | Prolonged tension and unresolved issues. | Mutual understanding and resolution. |
Understanding Denial and Acceptance
Denial is a psychological defense mechanism where you refuse to acknowledge reality or facts, often to protect yourself from distressing emotions. Acceptance involves recognizing and embracing the truth of a situation, allowing for emotional processing and growth. Understanding denial and acceptance enables you to move from avoidance toward constructive coping strategies, improving mental resilience.
The Psychology Behind Denial
Denial is a psychological defense mechanism that allows Your mind to block or refuse to acknowledge reality, protecting you from emotional pain or stress. This mechanism often occurs unconsciously, helping individuals avoid facing difficult truths or feelings that they are not yet ready to confront. Understanding the psychology behind denial reveals its role in safeguarding mental health while potentially impeding personal growth and acceptance.
The Stages Leading to Acceptance
The stages leading to acceptance typically begin with denial, a protective mechanism that buffers the initial shock of reality by refusing to acknowledge the truth. This is often followed by various emotional phases such as anger, bargaining, and depression, which reflect the struggle to cope with the unchangeable situation. Gradually, individuals move toward acceptance, where they acknowledge the reality, regain emotional balance, and begin to adapt to new circumstances effectively.
Denial: Causes and Consequences
Denial acts as a psychological defense mechanism where Your mind refuses to acknowledge painful realities, often triggered by trauma, stress, or anxiety to protect emotional stability. This avoidance can lead to increased mental strain, delayed problem-solving, and hindered personal growth, potentially prolonging distress or worsening underlying issues. Understanding denial's causes and consequences enables proactive steps toward healthier acceptance and emotional resilience.
Benefits of Embracing Acceptance
Embracing acceptance cultivates emotional resilience by allowing individuals to acknowledge reality without resistance, reducing stress and anxiety linked to denial. Acceptance fosters mindfulness, promoting mental clarity and healthier coping mechanisms compared to escapism, which often leads to avoidance and temporary relief. Practicing acceptance enhances overall well-being by encouraging growth, self-awareness, and adaptive problem-solving in challenging situations.
Denial vs Acceptance in Relationships
Denial in relationships often involves ignoring problems and refusing to acknowledge issues that affect emotional intimacy and trust, while acceptance requires facing challenges openly and embracing reality to foster growth and understanding. You build healthier connections by recognizing your partner's flaws and emotions without judgment, creating a foundation for genuine communication and conflict resolution. Choosing acceptance over denial minimizes emotional distance and encourages resilience in navigating relationship complexities.
Coping Strategies for Moving Beyond Denial
Denial, acceptance, and escapism represent distinct coping strategies that influence how individuals process difficult emotions and situations. Moving beyond denial requires cultivating self-awareness and embracing acceptance to foster emotional healing and resilience, rather than relying on escapism to avoid reality. Your ability to confront challenges directly promotes personal growth and long-term well-being through healthy coping mechanisms.
Acceptance as a Tool for Personal Growth
Acceptance serves as a powerful tool for personal growth by enabling you to acknowledge your current emotions and circumstances without judgment, fostering emotional resilience. Unlike denial, which blocks awareness, or escapism, which avoids reality, acceptance encourages mindfulness and self-compassion, promoting mental clarity. Embracing acceptance helps transform challenges into opportunities for development and strengthens your ability to adapt to change.
Overcoming Barriers to Acceptance
Overcoming barriers to acceptance involves recognizing denial as a defense mechanism that shields individuals from confronting painful realities. Embracing acceptance requires cultivating emotional resilience and mindfulness, enabling a shift from avoidance to acknowledgment of experiences. Escapism, while offering temporary relief, obstructs genuine processing and growth, making conscious acceptance essential for healing and personal development.
Integrating Denial and Acceptance for Emotional Wellness
Integrating denial and acceptance is crucial for emotional wellness, allowing individuals to acknowledge difficult emotions without being overwhelmed. By balancing denial as a temporary coping mechanism and acceptance as a long-term strategy, people can gradually process trauma and stress. This approach fosters resilience and prevents escapism, promoting healthier mental health outcomes.
Infographic: Denial vs Acceptance
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com