Solar power offers consistent energy production in sunny regions, while wind power provides higher efficiency in areas with strong, steady winds. Explore this article to learn more about the advantages and applications of solar and wind energy.
Table of Comparison
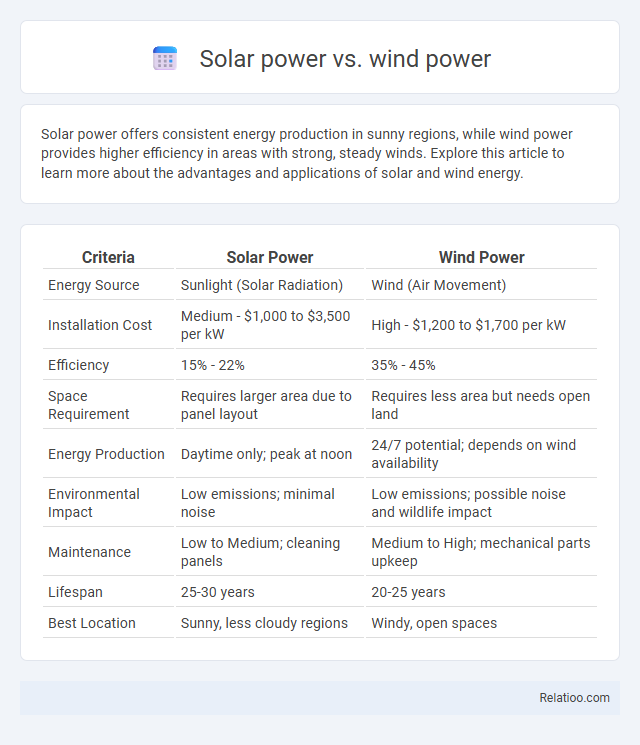
| Criteria | Solar Power | Wind Power |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Sunlight (Solar Radiation) | Wind (Air Movement) |
| Installation Cost | Medium - $1,000 to $3,500 per kW | High - $1,200 to $1,700 per kW |
| Efficiency | 15% - 22% | 35% - 45% |
| Space Requirement | Requires larger area due to panel layout | Requires less area but needs open land |
| Energy Production | Daytime only; peak at noon | 24/7 potential; depends on wind availability |
| Environmental Impact | Low emissions; minimal noise | Low emissions; possible noise and wildlife impact |
| Maintenance | Low to Medium; cleaning panels | Medium to High; mechanical parts upkeep |
| Lifespan | 25-30 years | 20-25 years |
| Best Location | Sunny, less cloudy regions | Windy, open spaces |
Introduction to Renewable Energy Sources
Solar power harnesses energy from sunlight using photovoltaic cells, providing a clean and abundant renewable resource ideal for diverse geographic areas. Wind power captures kinetic energy from air movement through turbines, offering a scalable and efficient solution predominantly in regions with consistent wind patterns. Both solar and wind energy contribute significantly to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and reliance on fossil fuels in the global transition toward sustainable energy systems.
Overview of Solar Power Technology
Solar power technology harnesses sunlight through photovoltaic cells or solar thermal systems to generate electricity with minimal environmental impact. Your energy needs can be met efficiently by solar panels, which convert solar radiation directly into clean power without emitting greenhouse gases. Recent advancements in solar technology have increased efficiency and decreased costs, positioning solar energy as a leading sustainable alternative to wind and traditional fossil-fuel sources.
Overview of Wind Power Technology
Wind power technology harnesses kinetic energy from wind through advanced turbines, converting it into electricity with increasing efficiency due to innovations in blade design and turbine materials. Modern wind farms utilize variable-speed generators and smart grid integration to optimize energy output and stability. Compared to solar and conventional energy sources, wind power offers a renewable, scalable, and low-emission alternative that significantly contributes to reducing carbon footprints.
Installation and Infrastructure Requirements
Solar power requires rooftop panels or large ground arrays with minimal moving parts, making installation straightforward and scalable for residential and commercial use. Wind power demands more complex infrastructure, including tall turbines, sturdy foundations, and ample open space, which often limits installation to rural or offshore locations. Your choice depends on site-specific factors like available land, local climate, and grid connectivity to ensure efficient integration and energy output.
Energy Efficiency and Output Comparison
Solar power systems convert sunlight into electricity with efficiency rates typically between 15-22%, whereas modern wind turbines achieve higher efficiency, often around 35-45%, due to aerodynamic blade designs and consistent wind speeds. In terms of energy output, wind power can generate more electricity per installed capacity, especially in areas with strong, steady winds, while solar power's output is constrained by daylight hours and weather conditions. Evaluating overall energy efficiency and output reveals wind energy's superior capacity factor, often exceeding 40%, compared to solar's average of 15-25%, making wind power more effective for large-scale energy production in optimal locations.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Solar power generates electricity with zero emissions during operation, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution compared to fossil fuels. Wind power also produces clean energy with minimal environmental footprint, but its impact includes land use and potential effects on bird and bat populations. Both solar and wind energy are highly sustainable, relying on abundant natural resources that are replenished continuously, unlike finite fossil fuels.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-term Expenses
Solar power typically requires higher initial investment for panels and installation but offers lower long-term maintenance costs and predictable energy savings. Wind power involves significant upfront costs for turbines and infrastructure, with variable maintenance expenses influenced by location and mechanical wear. Your choice should consider not only upfront expenses but also durability, efficiency, and regional resource availability to optimize long-term financial benefits.
Geographic Suitability and Resource Availability
Solar power is highly effective in regions with abundant sunlight, such as deserts and tropical areas, where irradiance levels exceed 5 kWh/m2/day. Wind power performs best in coastal and open plain regions, where average wind speeds surpass 6-7 m/s at turbine hub heights, making areas like the Great Plains and northern Europe ideal. Energy planning must consider these geographic factors to optimize resource availability, ensuring that solar installations are placed in sun-rich locations while wind farms capitalize on consistently high wind speeds for maximum efficiency.
Scalability and Integration Challenges
Solar power offers high scalability with modular panels easily expanded to meet increasing energy demands, but it faces integration challenges due to intermittent sunlight and energy storage requirements. Wind power scales efficiently in large open areas or offshore but encounters grid integration issues from variable wind patterns and site-specific constraints. Your best energy strategy balances the scalability of both solar and wind with advanced grid management solutions to ensure stable and continuous power supply.
Future Trends in Solar and Wind Power
Future trends in solar and wind power emphasize rapid advancements in efficiency and storage technologies, making renewable energy more reliable and cost-effective. Solar power benefits from improving photovoltaic materials and large-scale deployment of solar farms, while wind power sees growth through taller turbines and offshore wind projects enhancing capacity. Your energy strategy should consider these innovations to capitalize on sustainable, scalable clean power sources in the coming decades.
Infographic: Solar power vs Wind power
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com