Natural gas heating offers lower operational costs and faster heat delivery compared to electric heating, which provides cleaner energy and easier installation. Explore this article to understand the benefits and drawbacks of natural gas versus electric heating for your home.
Table of Comparison
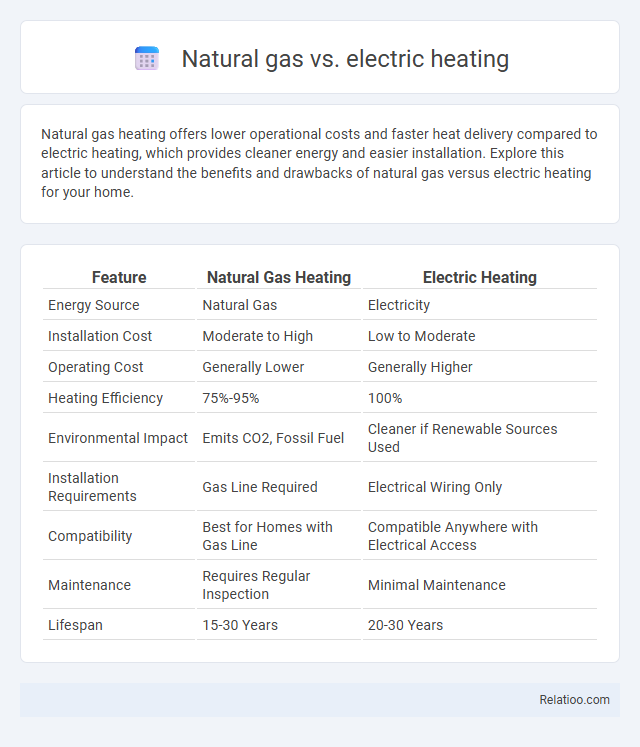
| Feature | Natural Gas Heating | Electric Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Natural Gas | Electricity |
| Installation Cost | Moderate to High | Low to Moderate |
| Operating Cost | Generally Lower | Generally Higher |
| Heating Efficiency | 75%-95% | 100% |
| Environmental Impact | Emits CO2, Fossil Fuel | Cleaner if Renewable Sources Used |
| Installation Requirements | Gas Line Required | Electrical Wiring Only |
| Compatibility | Best for Homes with Gas Line | Compatible Anywhere with Electrical Access |
| Maintenance | Requires Regular Inspection | Minimal Maintenance |
| Lifespan | 15-30 Years | 20-30 Years |
Introduction to Natural Gas and Electric Heating
Natural gas heating offers efficient and cost-effective energy by utilizing methane to generate heat directly, making it a popular choice for residential and commercial buildings. Electric heating converts electrical energy into heat through resistance coils or heat pumps, providing precise temperature control and easier installation in diverse settings. Your decision between natural gas and electric heating depends on factors like energy availability, environmental impact, initial installation costs, and long-term efficiency.
How Natural Gas Heating Works
Natural gas heating works by burning methane-rich natural gas to produce heat, which is then distributed throughout your home via a furnace or boiler system connected to a network of ducts or radiators. This method is often more cost-effective than electric heating, as natural gas prices are generally lower and provide a consistent, reliable energy source. Understanding the efficiency of natural gas heating helps you make informed decisions when comparing it to electric heating and other energy options for your property.
How Electric Heating Works
Electric heating converts electrical energy into heat using resistive elements or infrared radiation, providing efficient and direct heat distribution. Natural gas heating burns methane to produce heat, often requiring ventilation and combustion safety measures, while electric systems offer cleaner indoor air with minimal maintenance. Electric heaters utilize thermostats for precise temperature control, contributing to energy-efficient operation and lower emissions compared to fossil fuel-based heating.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Natural gas heating systems typically deliver higher energy efficiency with seasonal efficiency ratings around 80-98%, reducing your overall energy consumption. Electric heating converts nearly 100% of energy to heat at the point of use, but when considering generation and transmission losses, its overall efficiency is lower compared to natural gas. Evaluating the full energy lifecycle highlights that natural gas often provides more cost-effective heating due to lower energy losses and fuel costs.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Ongoing Expenses
Natural gas heating systems typically have lower upfront costs compared to electric heating units but require ongoing expenses for fuel that vary with market prices. Electric heating offers higher installation costs but benefits from lower maintenance and stable energy rates, potentially offsetting initial investments over time. Your choice should consider long-term energy consumption patterns, local utility rates, and efficiency ratings to optimize cost-effectiveness.
Environmental Impact: Emissions and Sustainability
Natural gas heating produces significant carbon dioxide emissions contributing to greenhouse gas effects, while electric heating can leverage renewable energy sources to reduce your carbon footprint substantially. Electric systems powered by wind, solar, or hydroelectric energy offer greater sustainability compared to fossil fuel-dependent natural gas. Choosing electric heating with a focus on clean energy integration supports long-term environmental goals and reduces harmful air pollutants.
Heating Performance and Comfort
Natural gas heating systems typically offer faster heat-up times and consistent warmth, enhancing overall comfort in colder climates. Electric heating, while often more energy-efficient and easier to install, may provide less rapid temperature adjustments, potentially affecting immediate heating performance. Evaluating energy costs and environmental impact, natural gas tends to have lower operational expenses but higher greenhouse gas emissions compared to electric heating powered by renewable energy sources.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Natural gas heating systems typically require professional installation involving gas line connections and ventilation setup, while electric heating units are generally easier and quicker to install with minimal structural modifications. Maintenance for natural gas systems often includes regular inspections for leaks, burner cleaning, and vent checks to ensure safety and efficiency, whereas electric heaters require less frequent upkeep, mainly limited to component checks and occasional cleaning. Considering installation and maintenance costs, electric heating systems usually offer lower upfront and ongoing expenses, making them an appealing option for homeowners prioritizing convenience and lower operational effort.
Safety Factors: Risks and Precautions
Natural gas heating involves risks such as gas leaks and carbon monoxide poisoning, necessitating regular maintenance and installation of detectors to ensure safety. Electric heating eliminates combustion hazards but poses fire risks from faulty wiring or overloaded circuits, warranting certified electrical installations and use of proper appliances. Both systems require adherence to safety standards and precautions, with energy-efficient models reducing overall hazard exposure by limiting operational strain and potential failures.
Choosing the Best Option for Your Home
Natural gas heating offers lower operational costs and faster heat production, making it ideal for colder climates with high energy demands. Electric heating provides cleaner energy options with easier installation and maintenance, especially if your home supports renewable energy integration. Evaluating your home's insulation, local energy prices, and environmental impact helps determine the most efficient and cost-effective heating solution tailored to your needs.
Infographic: Natural gas vs Electric heating
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com