Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy and self-expression, while collectivism prioritizes group goals and social harmony. Explore how these cultural values shape relationships and communication styles in this article.
Table of Comparison
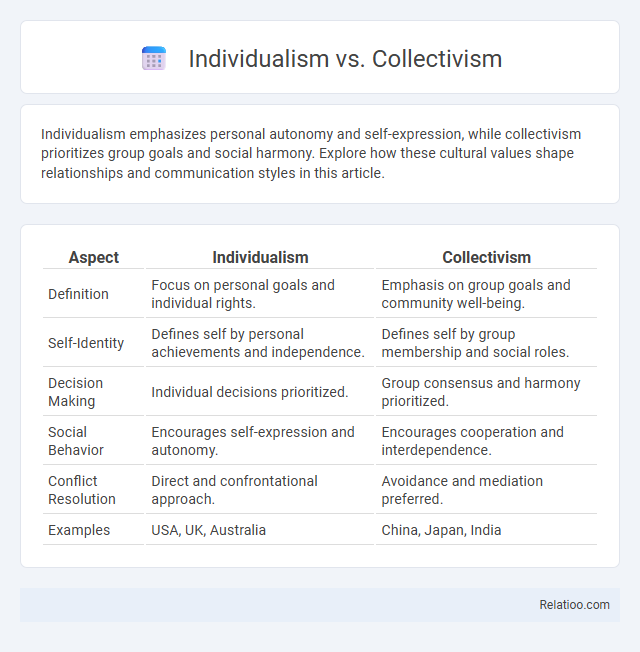
| Aspect | Individualism | Collectivism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focus on personal goals and individual rights. | Emphasis on group goals and community well-being. |
| Self-Identity | Defines self by personal achievements and independence. | Defines self by group membership and social roles. |
| Decision Making | Individual decisions prioritized. | Group consensus and harmony prioritized. |
| Social Behavior | Encourages self-expression and autonomy. | Encourages cooperation and interdependence. |
| Conflict Resolution | Direct and confrontational approach. | Avoidance and mediation preferred. |
| Examples | USA, UK, Australia | China, Japan, India |
Understanding Individualism and Collectivism
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy, self-expression, and individual rights, promoting independence and personal achievement as key societal values. Collectivism prioritizes group goals, social harmony, and interdependence, valuing cooperation and community welfare over individual desires. Understanding the balance between individualism and collectivism reveals how cultural frameworks shape identity, social behavior, and decision-making processes in diverse societies.
Historical Origins of Individualist and Collectivist Cultures
Individualism traces its historical origins to Enlightenment Europe, emphasizing personal freedom, self-reliance, and individual rights rooted in philosophical movements like liberalism and humanism. Collectivism emerged prominently in ancient agricultural societies and Eastern philosophies such as Confucianism, promoting group harmony, social responsibility, and interconnectedness over individual desires. Individuality, while related to individualism, focuses more on personal uniqueness and self-expression that has evolved across cultures through artistic movements and psychological theories highlighting identity formation.
Key Characteristics of Individualist Societies
Individualist societies prioritize personal freedom, self-reliance, and individual achievements, emphasizing the importance of personal goals over group objectives. People in these cultures typically value autonomy, privacy, and individual rights, encouraging independent decision-making and creativity. Social relationships are often voluntary and flexible, with a strong focus on personal responsibility and distinct identity.
Defining Traits of Collectivist Societies
Collectivist societies emphasize group harmony, social cohesion, and interdependence, where individuals prioritize community goals over personal ambitions. Your identity in such cultures is often defined by relationships, roles, and obligations within the group, fostering strong social support networks. Decision-making and responsibilities are commonly shared, promoting collaboration and collective well-being rather than individual success.
The Impact on Personal Identity and Social Roles
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy and self-expression, shaping Your identity through unique traits and individual goals, while collectivism prioritizes group harmony and shared values, influencing social roles within community contexts. Individuality fosters authenticity by encouraging distinctiveness and personal creativity beyond societal expectations, balancing both personal identity and social integration. The interplay among these concepts impacts how individuals define themselves and navigate their responsibilities in social environments.
Decision-Making: Individual Needs vs Group Priorities
Decision-making in individualism emphasizes personal needs, autonomy, and self-interest, prioritizing individual choice and responsibility. Collectivism values group priorities, social harmony, and consensus, often requiring individuals to sacrifice personal preferences for community goals. Individuality integrates unique personal traits within decision processes, balancing self-expression with consideration for collective welfare.
Influence on Workplace Dynamics and Leadership
Individualism prioritizes personal achievement and autonomy, influencing workplace dynamics by fostering competition and self-reliance, while collectivism emphasizes group harmony and collaboration, promoting teamwork and shared goals. Individuality highlights personal expression and unique contributions, encouraging innovation and diverse leadership styles. Understanding these cultural dimensions helps you tailor leadership approaches to enhance motivation, communication, and productivity within diverse teams.
Education Systems: Independent Learning vs Group Collaboration
Education systems emphasizing individualism prioritize independent learning, fostering critical thinking and self-motivation, which enhances personalized educational outcomes. In contrast, collectivist-oriented education emphasizes group collaboration, promoting social skills, teamwork, and communal problem-solving essential for collective success. Balancing individuality and collectivism in education encourages adaptive strategies that prepare students for diverse social and professional environments.
Social Relationships and Family Structures
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy and self-reliance, often leading to nuclear family structures where independent decision-making prevails. Collectivism prioritizes group harmony and interdependence, fostering extended family networks and close-knit community ties. Individuality, while related to individualism, centers on unique personal identity expression within social relationships, balancing personal distinctiveness with communal responsibilities.
Individualism vs Collectivism in the Modern Globalized World
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy and individual rights, fostering innovation and self-expression in modern globalized societies. Collectivism prioritizes group goals and social cohesion, promoting community support and shared responsibility amid diverse cultural interactions. Balancing individualism and collectivism shapes social dynamics and economic strategies in an interconnected world.
Infographic: Individualism vs Collectivism
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com