Grid-tied solar systems rely on the utility grid to provide power when solar production is low, offering cost savings and net metering benefits. Off-grid solar systems operate independently, ensuring energy self-sufficiency but requiring battery storage and higher initial investment. Discover the key differences and decide which system suits your energy needs in this article.
Table of Comparison
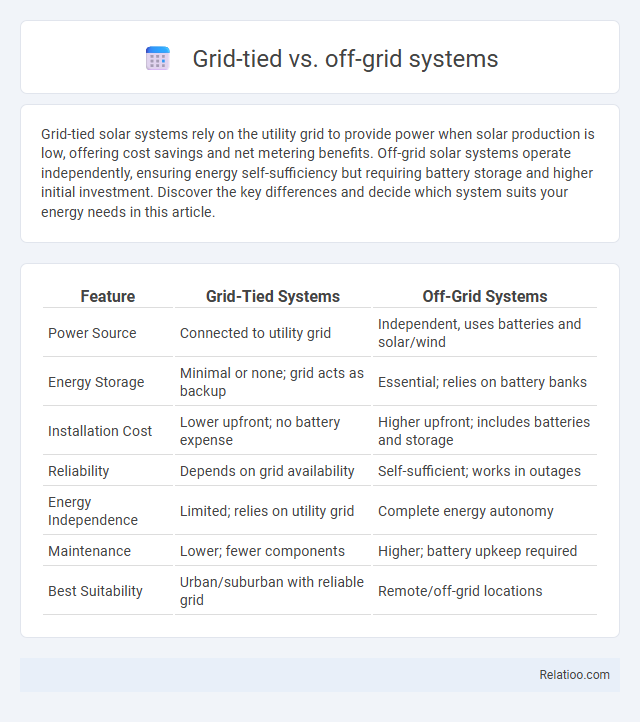
| Feature | Grid-Tied Systems | Off-Grid Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Connected to utility grid | Independent, uses batteries and solar/wind |
| Energy Storage | Minimal or none; grid acts as backup | Essential; relies on battery banks |
| Installation Cost | Lower upfront; no battery expense | Higher upfront; includes batteries and storage |
| Reliability | Depends on grid availability | Self-sufficient; works in outages |
| Energy Independence | Limited; relies on utility grid | Complete energy autonomy |
| Maintenance | Lower; fewer components | Higher; battery upkeep required |
| Best Suitability | Urban/suburban with reliable grid | Remote/off-grid locations |
Introduction to Solar Energy Systems
Solar energy systems convert sunlight into electricity, offering sustainable power solutions for both grid-tied and off-grid applications. Grid-tied systems connect directly to the utility grid, allowing you to use solar energy while relying on the grid for backup and earning credits through net metering. Off-grid systems operate independently, storing excess energy in batteries to ensure power availability in remote areas without access to the electrical grid.
What is a Grid-Tied System?
A grid-tied system connects solar panels or other renewable energy sources directly to the public electricity grid, allowing users to draw power from the grid when their production is low and feed excess energy back for credit. This setup enhances energy efficiency, reduces electricity bills, and supports grid stability by balancing supply and demand. Grid-tied systems typically lack battery storage, relying on the grid as backup, making them ideal for areas with reliable utility connections.
What is an Off-Grid System?
An off-grid system is a standalone energy solution that operates independently from the traditional utility grid, relying on renewable energy sources such as solar panels, wind turbines, or batteries for power generation and storage. This system is ideal for remote locations where grid connection is unavailable or unreliable, providing energy autonomy and sustainability. Key components include inverters, charge controllers, and energy storage systems that ensure continuous power supply without external grid support.
Key Components of Each System
Grid-tied systems rely on solar panels, inverters, and net meters to feed excess energy back to the utility grid, optimizing energy efficiency and reducing electricity costs. Off-grid systems include solar panels, battery banks, charge controllers, and inverters to ensure independent power generation and storage without utility dependence. Understanding these key components helps you determine the best energy solution tailored to your power needs and location.
Installation and Infrastructure Requirements
Grid-tied systems require professional installation with connection to the existing electrical grid, necessitating infrastructure such as inverters, meters, and compliance with utility regulations. Off-grid systems demand extensive infrastructure investment, including battery storage, charge controllers, and backup generators, to maintain energy independence without grid access. Your choice impacts installation complexity, regulatory approvals, and ongoing maintenance depending on whether you prioritize seamless integration or complete energy self-sufficiency.
Cost Comparison: Grid-Tied vs Off-Grid
Grid-tied solar systems generally have lower initial costs compared to off-grid systems due to the absence of expensive battery storage and backup components. Off-grid systems require substantial investment in batteries and inverters to ensure energy availability, increasing overall expenses by 30-50%. Your choice between grid-tied and off-grid impacts long-term energy savings, reliability, and upfront financial commitment.
Energy Independence and Reliability
Grid-tied and off-grid energy systems offer distinct advantages in achieving energy independence and reliability. Off-grid systems provide complete energy autonomy by operating independently from utility grids, ensuring uninterrupted power supply but requiring battery storage and maintenance. Grid-tied systems enhance reliability by allowing energy exchange with the grid, reducing storage needs while offering backup power during outages, ultimately giving you flexible control over your energy sources.
Scalability and Future Expansion
Grid-tied systems offer seamless scalability by allowing you to increase energy capacity with minimal infrastructure changes and integrate stored or excess energy into the local utility grid. Off-grid systems require more careful planning for future expansion since scalability depends heavily on battery storage size, inverter capacity, and standalone generation units such as solar panels or wind turbines. Choosing the right system impacts your energy independence and long-term adaptability to growing power needs.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Grid-tied systems typically have a lower environmental impact due to their ability to use existing infrastructure and reduce reliance on fossil fuels by feeding excess energy back into the grid. Off-grid systems, while providing energy independence, require battery storage and often additional backup power, which can increase environmental concerns related to battery production and disposal. Assessing your energy needs and comparing the life-cycle emissions of both systems is crucial for a comprehensive environmental impact assessment.
Choosing the Right System for Your Needs
Grid-tied systems offer reliable access to electricity by connecting directly to the local power grid, making them cost-effective and ideal for areas with stable utility services. Off-grid systems provide energy independence through solar panels, batteries, and generators, perfect for remote locations or for those aiming to reduce reliance on traditional utilities. Evaluating your energy consumption, location, budget, and goals is crucial to choosing the right system tailored to your needs.
Infographic: Grid-tied vs Off-grid systems
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com