Anxious attachment is characterized by fear of abandonment and intense emotional dependence, while disorganized attachment involves inconsistent behavior and confusion in relationships due to trauma or neglect. Explore this article to understand how these attachment styles impact relationship dynamics and ways to foster healthier connections.
Table of Comparison
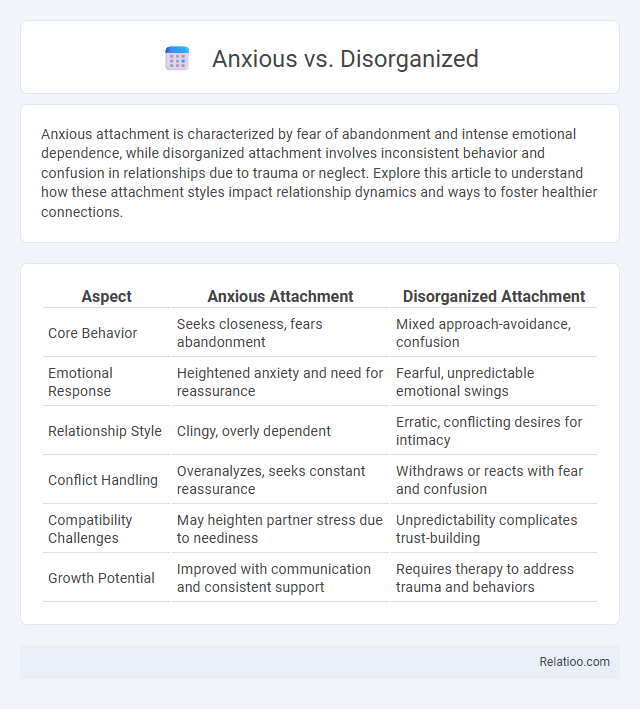
| Aspect | Anxious Attachment | Disorganized Attachment |
|---|---|---|
| Core Behavior | Seeks closeness, fears abandonment | Mixed approach-avoidance, confusion |
| Emotional Response | Heightened anxiety and need for reassurance | Fearful, unpredictable emotional swings |
| Relationship Style | Clingy, overly dependent | Erratic, conflicting desires for intimacy |
| Conflict Handling | Overanalyzes, seeks constant reassurance | Withdraws or reacts with fear and confusion |
| Compatibility Challenges | May heighten partner stress due to neediness | Unpredictability complicates trust-building |
| Growth Potential | Improved with communication and consistent support | Requires therapy to address trauma and behaviors |
Understanding Attachment Styles: Anxious vs Disorganized
Understanding attachment styles helps clarify complex emotional behaviors in relationships. Anxious attachment is characterized by a constant need for reassurance and fear of abandonment, while disorganized attachment combines fear with confusion, often resulting from trauma or inconsistent caregiving. You can improve your relationships by recognizing these patterns and learning strategies to foster secure attachments.
Key Traits of Anxious Attachment
Anxious attachment is characterized by intense fear of abandonment, excessive need for reassurance, and heightened sensitivity to relationship dynamics. Individuals with anxious attachment often exhibit clinginess, emotional volatility, and difficulty trusting their partner's commitment. This attachment style contrasts with disorganized attachment, which involves contradictory behaviors and confusion, and highlights challenges in emotional regulation and consistency in relationships.
Core Characteristics of Disorganized Attachment
Disorganized attachment is characterized by a lack of clear attachment behavior, often exhibiting contradictory responses such as seeking comfort yet displaying fear or avoidance toward caregivers. This style typically arises from inconsistent or frightening caregiving, leading to confusion and difficulty regulating emotions. Individuals with disorganized attachment struggle with trust and may experience heightened anxiety or emotional dysregulation in relationships.
Childhood Origins: How Anxious and Disorganized Styles Develop
Anxious attachment style often originates from inconsistent caregiving during childhood, where Your caregiver's unpredictable responses create heightened fear of abandonment and clinginess. Disorganized attachment develops through exposure to frightening or traumatic experiences in early relationships, leading to confusion and difficulty managing emotions. These early interactions shape neural pathways that influence how You relate to others in adulthood.
Relationship Patterns: Anxious vs Disorganized Behaviors
Anxious attachment style in relationships often manifests through excessive need for reassurance and fear of abandonment, leading to clingy or overly dependent behaviors. Disorganized attachment, however, combines approach-avoidance tendencies characterized by confusion, fear, and inconsistent responses to intimacy, reflecting trauma or unresolved fear. Understanding these differing patterns can help you navigate and address the underlying emotional needs influencing your relationship dynamics.
Emotional Responses and Coping Mechanisms
Anxious attachment style triggers heightened emotional responses characterized by intense fear of abandonment and constant need for reassurance, leading you to seek proximity and validation to cope. Disorganized attachment manifests in mixed, unpredictable emotional reactions, often resulting in confusion and difficulty managing stress, causing fragmented coping strategies like avoidance or aggression. Each attachment style influences how emotional responses are processed and the effectiveness of your coping mechanisms in relationships and stress management.
Impact on Adult Relationships: Friendships and Romance
Anxious attachment leads to heightened sensitivity to rejection and a constant need for reassurance, affecting trust and communication in both friendships and romantic partnerships. Disorganized attachment causes unpredictable behavior and difficulty managing emotions, often resulting in unstable or conflict-ridden relationships. Understanding Your attachment style helps you recognize patterns that impact intimacy, allowing for healthier connections and emotional resilience in adult relationships.
Signs You May Have an Anxious or Disorganized Style
Signs of an anxious attachment style include excessive worry about relationships, fear of abandonment, and constant need for reassurance. Disorganized attachment is characterized by unpredictable or contradictory behavior, difficulty regulating emotions, and a strong fear of rejection coupled with confusion in interpersonal connections. Recognizing these patterns can help individuals understand their relational challenges and work toward healthier emotional responses.
Healing and Growth: Strategies for Change
Anxious attachment styles benefit from consistent communication, emotional validation, and mindfulness practices to reduce fear of abandonment and build self-worth. Disorganized attachment requires trauma-informed therapy focusing on creating safety, integrating conflicting emotions, and developing trust for emotional regulation. Growth in all attachment styles hinges on building secure connections, practicing self-compassion, and learning adaptive coping mechanisms to foster resilience and healthy relationships.
Seeking Help: Professional Support and Resources
Understanding the differences between anxious, disorganized, and other attachment styles is crucial when seeking professional support, as therapists tailor interventions to your specific attachment patterns for effective healing. Resources such as attachment-based therapy, trauma-informed counseling, and support groups provide targeted strategies to manage anxiety and disorganization in relationships. Accessing specialized professionals familiar with attachment theory ensures you receive personalized guidance to improve emotional regulation and relational stability.
Infographic: Anxious vs Disorganized
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com