Validation ensures a product meets the user's needs and requirements, while verification confirms the product is built correctly according to specifications. Explore this article to understand how validation and verification impact successful relationship management.
Table of Comparison
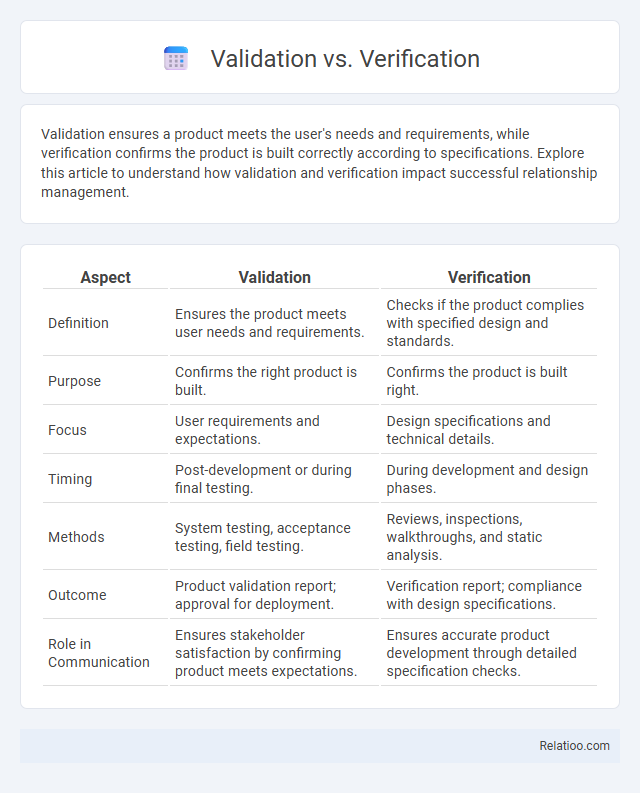
| Aspect | Validation | Verification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ensures the product meets user needs and requirements. | Checks if the product complies with specified design and standards. |
| Purpose | Confirms the right product is built. | Confirms the product is built right. |
| Focus | User requirements and expectations. | Design specifications and technical details. |
| Timing | Post-development or during final testing. | During development and design phases. |
| Methods | System testing, acceptance testing, field testing. | Reviews, inspections, walkthroughs, and static analysis. |
| Outcome | Product validation report; approval for deployment. | Verification report; compliance with design specifications. |
| Role in Communication | Ensures stakeholder satisfaction by confirming product meets expectations. | Ensures accurate product development through detailed specification checks. |
Understanding Validation and Verification
Validation ensures a product meets the needs and expectations of end-users by confirming it fulfills its intended purpose in real-world conditions. Verification involves checking that a product complies with specifications and design requirements through systematic reviews, inspections, and testing during development. Understanding that validation emphasizes user satisfaction while verification focuses on accuracy and adherence to standards is crucial for effective quality assurance.
Key Definitions: Validation vs Verification
Validation ensures that Your product or system meets the intended use and fulfills the actual needs of the end-user, focusing on "Are we building the right product?" Verification confirms that the product complies with specified requirements and design specifications, addressing "Are we building the product right?" Both processes are essential in quality assurance but target different stages of the development lifecycle for comprehensive quality control.
The Purpose of Verification in Development
Verification in development ensures that your product meets specified requirements through systematic checks and reviews, emphasizing accuracy and completeness. This process identifies defects early, reducing costly changes later in the development lifecycle. Verification focuses on building the product right by validating design and functionality against technical specifications.
The Role of Validation in Quality Assurance
Validation ensures that a product meets the needs and requirements of the end user, confirming it fulfills its intended purpose in real-world conditions. Verification focuses on whether the product is built correctly according to specifications, emphasizing design accuracy and development processes. In quality assurance, validation plays a critical role by providing evidence that the final product performs effectively and reliably before release, thereby preventing defects and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Major Differences Between Validation and Verification
Verification ensures the product is built according to specifications, focusing on process and design accuracy through reviews, inspections, and tests. Validation confirms the final product meets user needs and requirements in real-world conditions, emphasizing usability and performance. Major differences lie in their objectives: verification checks correctness during development, while validation assesses the product's effectiveness after completion.
Common Methods for Verification
Verification involves systematic methods such as inspections, reviews, and testing to ensure a product meets specified requirements before release. Common verification techniques include static analysis, unit testing, integration testing, and system testing, which help identify defects early in the development lifecycle. Your project's success depends on efficient verification to confirm that development outputs align with design specifications and functional requirements.
Popular Techniques for Validation
Verification ensures your product meets all specified requirements through reviews, inspections, and walk-throughs, while validation confirms the product fulfills its intended use via practical testing methods like user acceptance testing (UAT) and system testing. Popular techniques for validation focus on evaluating the final product in real-world scenarios, including alpha and beta testing, regression testing, and performance testing, to guarantee the software operates correctly for the end user. Employing these validation techniques helps you deliver reliable, high-quality software aligned with user needs and expectations.
Importance of Validation and Verification in Industry
Validation ensures that a product meets the needs and requirements of the end-user, while verification confirms that it complies with specified design and technical standards. In industries such as pharmaceuticals, aerospace, and software development, rigorous validation and verification processes are critical to ensure safety, reliability, and regulatory compliance. Emphasizing both practices reduces risks, improves product quality, and strengthens customer trust, driving overall industry success.
Challenges in Implementing Validation and Verification
Validation ensures the product meets user needs, while verification confirms it complies with specifications. Challenges in implementing validation and verification include incomplete requirements, limited testing resources, and integrating testing throughout development cycles. Your project success depends on effectively addressing these challenges to achieve accurate and reliable quality assurance.
Best Practices for Ensuring Validation and Verification
Best practices for ensuring validation and verification involve establishing clear, measurable requirements and systematically comparing deliverables against these criteria to confirm accuracy and functionality. Implementing thorough documentation, peer reviews, and automated testing tools enhances reliability and traceability throughout the development lifecycle. Continuous feedback loops with stakeholders and iterative testing phases improve product quality, aligning outcomes with intended use and regulatory standards.
Infographic: Validation vs Verification
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com