Paraphrasing involves restating someone's words using different phrasing while preserving the original meaning, whereas interpretation adds deeper analysis or personal insight beyond the initial message. Discover the key differences and applications of paraphrasing versus interpretation in this article.
Table of Comparison
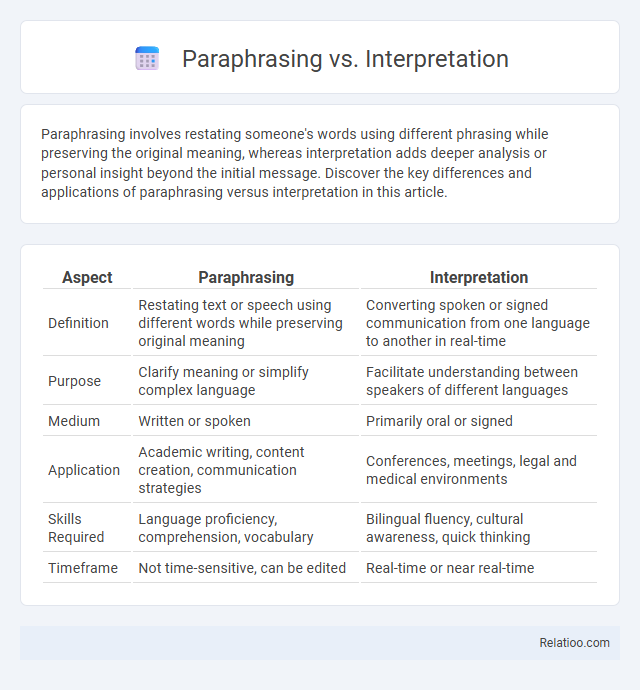
| Aspect | Paraphrasing | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Restating text or speech using different words while preserving original meaning | Converting spoken or signed communication from one language to another in real-time |
| Purpose | Clarify meaning or simplify complex language | Facilitate understanding between speakers of different languages |
| Medium | Written or spoken | Primarily oral or signed |
| Application | Academic writing, content creation, communication strategies | Conferences, meetings, legal and medical environments |
| Skills Required | Language proficiency, comprehension, vocabulary | Bilingual fluency, cultural awareness, quick thinking |
| Timeframe | Not time-sensitive, can be edited | Real-time or near real-time |
Understanding Paraphrasing and Interpretation
Understanding paraphrasing involves rewording a text to convey the original message clearly without adding personal opinions, maintaining the core meaning intact. Interpretation goes beyond mere rewording by analyzing and explaining the underlying significance or intention of the content, often incorporating the interpreter's perspective. Effective comprehension of paraphrasing and interpretation enhances communication clarity and fosters deeper engagement with the material.
Key Differences Between Paraphrasing and Interpretation
Paraphrasing involves restating text or speech using different words while preserving the original meaning, emphasizing clarity and accuracy. Interpretation goes beyond mere rewording by conveying underlying ideas, emotions, or context, often adapting content for different audiences or formats. The key difference lies in paraphrasing maintaining semantic equivalence, whereas interpretation introduces subjective elements and broader understanding.
Purpose and Context: When to Paraphrase vs. Interpret
Paraphrasing involves restating text in different words to clarify meaning while preserving the original intent, commonly used in academic writing and summarization. Interpretation goes beyond restatement by adding analysis or personal understanding, often employed in literature, law, or complex texts to uncover deeper implications. Choosing between paraphrasing and interpretation depends on the purpose: use paraphrasing to maintain factual accuracy and interpretation to explain meaning in context or offer insight.
Techniques for Effective Paraphrasing
Effective paraphrasing techniques include understanding the original text thoroughly, using synonyms and altering sentence structures while preserving the original meaning, and maintaining the tone and context. Interpretation involves explaining or clarifying the meaning behind the text, often adding personal insight, whereas summarization condenses the main ideas into a shorter version without detailed rephrasing. To enhance Your paraphrasing skills, practice active reading, take notes, and ensure Your version accurately reflects the source material without copying verbatim.
Strategies for Accurate Interpretation
Strategies for accurate interpretation involve understanding the context, tone, and cultural nuances behind the original message to convey its true meaning effectively. While paraphrasing focuses on rewording text to enhance clarity and avoid plagiarism, interpretation requires a deeper cognitive process to translate emotions, intentions, and implications beyond literal words. Your ability to distinguish these techniques ensures precise communication and prevents misrepresentation of the source material.
Common Challenges in Paraphrasing and Interpretation
Common challenges in paraphrasing include maintaining the original meaning while changing the wording, avoiding plagiarism, and preserving the tone and context of the source material. Interpretation faces difficulties such as accurately conveying nuanced ideas across languages or contexts, managing cultural differences, and ensuring clarity without oversimplification. Both processes demand strong comprehension skills, attention to detail, and the ability to adapt content for different audiences without losing intended significance.
The Role of Subjectivity in Interpretation
Paraphrasing involves restating text in Your own words to clarify meaning while maintaining the original message, whereas interpretation requires analyzing and explaining deeper significance, often influenced by personal perspectives. The role of subjectivity in interpretation is crucial as it shapes how concepts are understood and conveyed, reflecting the interpreter's beliefs, cultural background, and experiences. Unlike paraphrasing, interpretation embraces ambiguity and nuance, highlighting the dynamic nature of meaning in communication.
Plagiarism Concerns: Paraphrasing vs. Interpretation
Paraphrasing involves restating text in different words while maintaining the original meaning, which requires proper citation to avoid plagiarism. Interpretation goes beyond mere rewording by adding personal insights or explanations, thus reducing direct plagiarism risks but still necessitating acknowledgment of the source. Careful differentiation between paraphrasing and interpretation ensures ethical use of information and adherence to academic integrity standards.
Tools and Resources for Paraphrasing and Interpretation
Paraphrasing tools like QuillBot and Spinbot use AI algorithms to rewrite text while maintaining the original meaning, making them essential for efficient content creation and avoiding plagiarism. Interpretation resources, such as SDL Trados Studio and MemoQ, offer advanced language processing features for accurate translation and contextual understanding, crucial in multilingual communication. Your choice between paraphrasing and interpretation depends on whether you need to rephrase existing content or convey meaning across languages, and leveraging the right tools enhances accuracy and productivity.
Practical Examples: Paraphrasing and Interpretation in Action
Paraphrasing involves restating text using different words while preserving the original meaning, such as summarizing a scientific article in simpler language for easier understanding. Interpretation goes beyond restating by adding personal insight or context, like explaining the significance of a political speech to uncover underlying messages. Practical examples highlight paraphrasing in academic writing to avoid plagiarism, whereas interpretation is commonly used in law or literature to derive deeper meaning from texts.
Infographic: Paraphrasing vs Interpretation
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com