False agreement occurs when one party mistakenly perceives mutual understanding, while disagreement arises from clear conflicting views or feelings. Explore this article to learn how to identify and navigate false agreement versus disagreement in relationships.
Table of Comparison
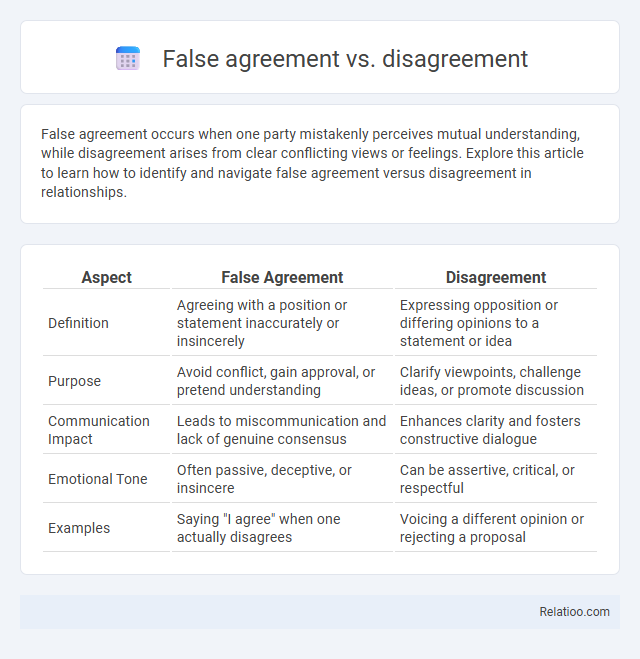
| Aspect | False Agreement | Disagreement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Agreeing with a position or statement inaccurately or insincerely | Expressing opposition or differing opinions to a statement or idea |
| Purpose | Avoid conflict, gain approval, or pretend understanding | Clarify viewpoints, challenge ideas, or promote discussion |
| Communication Impact | Leads to miscommunication and lack of genuine consensus | Enhances clarity and fosters constructive dialogue |
| Emotional Tone | Often passive, deceptive, or insincere | Can be assertive, critical, or respectful |
| Examples | Saying "I agree" when one actually disagrees | Voicing a different opinion or rejecting a proposal |
Understanding False Agreement: Definition and Examples
False agreement occurs when a verb or adjective mistakenly agrees with a word that is not its true grammatical subject, leading to errors in number or gender. For example, in the sentence "The list of items are on the table," the verb "are" falsely agrees with the plural "items" instead of the singular "list." Understanding false agreement helps identify and correct these grammatical inconsistencies to ensure subject-verb harmony and accurate sentence structure.
Disagreement: Types and Common Scenarios
Disagreement occurs when two or more parties hold conflicting views or opinions, often arising in workplace discussions, negotiations, or personal relationships. Types of disagreement include factual disagreement, where parties dispute objective information; value disagreement, involving differing beliefs or ethics; and policy disagreement, focused on best courses of action. Your ability to recognize these common scenarios enhances conflict resolution and effective communication strategies.
Key Differences Between False Agreement and Genuine Disagreement
False agreement occurs when parties appear to agree on a statement but actually hold different underlying meanings or interpretations, leading to miscommunication. Genuine disagreement involves explicit differences in opinion or belief, where parties openly express contrasting views based on distinct premises or evidence. The key difference lies in false agreement masking true dissent beneath surface consensus, while genuine disagreement reflects overt conflict of ideas.
Psychological Reasons Behind False Agreement
False agreement occurs when Your mind inaccurately assumes others share your beliefs, often stemming from cognitive biases such as the false consensus effect. Psychological reasons include the desire for social validation, reducing cognitive dissonance, and overestimating agreement to maintain a coherent worldview. Disagreement arises when individuals genuinely hold differing opinions, contrasting with false agreement where consensus is incorrectly perceived.
The Role of Conflict Avoidance in False Agreement
False agreement often arises when individuals prioritize conflict avoidance over expressing genuine opinions, resulting in misleading consensus in communication. Unlike disagreement, which reflects honest differences in viewpoints, false agreement masks true dissent, complicating decision-making processes and leading to suboptimal outcomes in group dynamics. Understanding the role of conflict avoidance helps identify underlying causes of false agreement and improves strategies for fostering authentic dialogue and effective collaboration.
Consequences of False Agreement in Communication
False agreement occurs when one party mistakenly believes the other agrees, leading to misunderstandings and misaligned expectations in communication. Disagreement, by contrast, involves a clear expression of opposing views, which can foster dialogue and resolution. The consequences of false agreement in communication include reduced trust, impaired decision-making, and unresolved conflicts that impact teamwork and productivity.
Benefits and Challenges of Open Disagreement
Open disagreement fosters transparency and encourages diverse perspectives, enhancing problem-solving and innovation by preventing groupthink. Challenges include the risk of escalating conflicts and potential communication breakdowns if disagreements are not managed constructively. False agreement, contrastingly, may maintain superficial harmony but suppresses authentic input, leading to poor decision-making and diminished trust within teams.
How to Identify False Agreement in Group Settings
False agreement in group settings occurs when individuals appear to concur with a consensus but internally disagree, often to avoid conflict or social rejection. To identify false agreement, observe nonverbal cues like hesitation, lack of eye contact, or inconsistent body language that contradict verbal affirmations. Your ability to encourage open dialogue and create a safe environment for differing opinions helps reveal genuine agreement versus false compliance.
Strategies to Encourage Healthy Disagreement
Encouraging healthy disagreement involves creating a safe environment where different opinions are respected and valued, allowing Your team to express diverse perspectives without fear of judgment. Strategies include active listening, asking open-ended questions, and reframing conflicts as opportunities for learning rather than personal attacks. Emphasizing clear communication and focusing on common goals helps distinguish genuine disagreements from false agreement, promoting constructive dialogue and informed decision-making.
Cultivating Authentic Dialogue: Moving Beyond False Agreement
Cultivating authentic dialogue requires recognizing the limitations of false agreement, where participants superficially concur to avoid conflict, undermining genuine understanding. True dialogue embraces disagreement as a constructive force, encouraging diverse perspectives to foster deeper insight and collaborative problem-solving. Moving beyond false agreement involves creating safe spaces for honest expression, promoting active listening, and valuing differences to achieve meaningful and transformative communication outcomes.
Infographic: False agreement vs Disagreement
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com