Trust forms the emotional foundation in relationships, while reliability demonstrates consistent actions that reinforce that trust. Explore how balancing trust and reliability strengthens connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
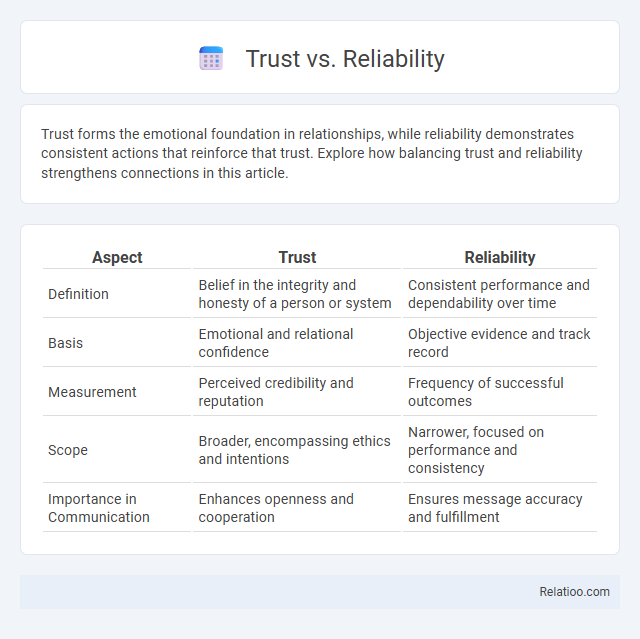
| Aspect | Trust | Reliability |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Belief in the integrity and honesty of a person or system | Consistent performance and dependability over time |
| Basis | Emotional and relational confidence | Objective evidence and track record |
| Measurement | Perceived credibility and reputation | Frequency of successful outcomes |
| Scope | Broader, encompassing ethics and intentions | Narrower, focused on performance and consistency |
| Importance in Communication | Enhances openness and cooperation | Ensures message accuracy and fulfillment |
Defining Trust: Beyond Surface-Level Confidence
Trust extends beyond mere reliability by encompassing emotional confidence and a belief in integrity, not just consistent performance. It involves your willingness to be vulnerable based on positive expectations of another's actions and intentions. Defining trust requires recognizing this deeper connection between dependability and genuine assurance that fosters lasting relationships.
Understanding Reliability: Consistency in Action
Reliability reflects consistent performance across time, ensuring systems or individuals deliver expected outcomes without failure. Trust builds upon reliability by incorporating confidence in the entity's intentions and integrity beyond mere consistency. Understanding reliability emphasizes measurable dependability, which forms the foundation for establishing and maintaining trust.
Core Differences Between Trust and Reliability
Trust involves your belief in someone's integrity and intentions, while reliability refers to their consistency in performing tasks or delivering results. Trust is emotional and subjective, often built over time through experiences, whereas reliability is measurable and objective, based on repeated performance. Understanding these core differences helps you assess relationships and expectations more accurately.
The Psychological Foundations of Trust
Trust is built on the psychological foundations of belief, vulnerability, and expectation, where individuals feel confident that others will act in their best interest despite uncertainty. Reliability is a key component influencing trust, as consistent and dependable behavior reinforces the perception that someone can be counted on. Your ability to assess trustworthiness depends on recognizing these psychological cues and past experiences that shape your willingness to depend on others.
How Reliability Builds—or Breaks—Trust
Reliability serves as the foundation for building trust by consistently meeting expectations and delivering on promises, which reinforces your credibility. When reliability falters, trust erodes quickly because unpredictability creates doubt and uncertainty in relationships or business transactions. Maintaining high reliability ensures that your trustworthiness remains strong, fostering long-term confidence and loyalty.
Measuring Trust vs Measuring Reliability
Measuring trust involves assessing subjective factors such as confidence, reputation, and perceived integrity, often through surveys, feedback, and sentiment analysis. Reliability measurement focuses on objective data, including system uptime, failure rates, and consistent performance metrics to evaluate dependability. Your choice between these depends on whether you prioritize human perception and relationship dynamics or quantifiable operational consistency.
Real-World Scenarios: Trust and Reliability in Practice
In real-world scenarios, trust is the belief in the integrity and intentions of a person or system, while reliability refers to consistent performance and dependability over time. For example, a trusted employee not only delivers results but also demonstrates honesty and ethical behavior, whereas reliability is measured by their consistent task completion and punctuality. Effective decision-making in business or technology often hinges on balancing trustworthiness with proven reliability to ensure both confidence and performance.
Impact of Trust and Reliability on Relationships
Trust forms the foundation of strong relationships by fostering emotional security and mutual respect, while reliability reinforces trust through consistent actions and dependability. The impact of trust and reliability on relationships is profound, as trust encourages openness and vulnerability, whereas reliability ensures predictability and accountability. Together, they create a synergistic bond that enhances cooperation, reduces conflicts, and builds long-term commitment.
Strategies to Foster Both Trust and Reliability
Building trust and reliability requires consistent transparency, clear communication, and delivering on promises to create dependable relationships. Implementing feedback systems and accountability measures reinforces reliability while encouraging open dialogue fosters mutual trust. Regularly evaluating performance and addressing concerns promptly ensures sustained confidence and dependability in partnerships.
Trust and Reliability in the Digital Age
Trust and reliability in the digital age are crucial for building lasting relationships between users and technology platforms. Trust involves users' belief in the integrity and security of digital services, while reliability focuses on consistent and dependable performance of these services under varying conditions. Enhancing cybersecurity measures, transparent data practices, and robust system architectures foster both trust and reliability, creating a secure and seamless digital experience.
Infographic: Trust vs Reliability
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com