Effective communication hinges on the sender's clarity and the receiver's interpretation to build a strong relationship. Explore key strategies to enhance sender-receiver dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
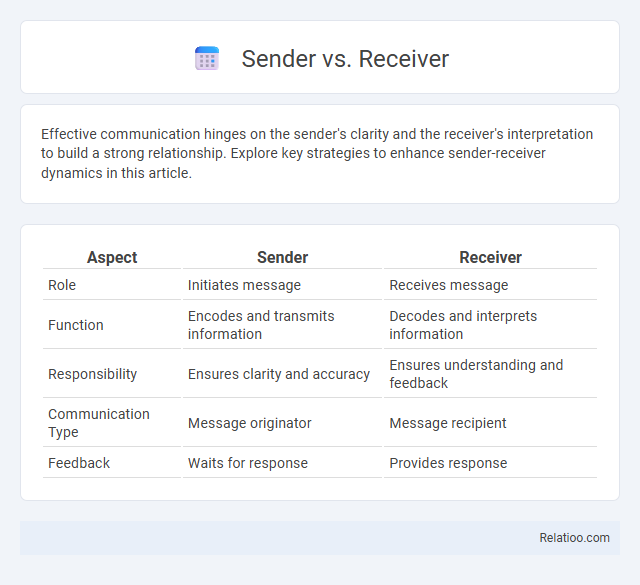
| Aspect | Sender | Receiver |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Initiates message | Receives message |
| Function | Encodes and transmits information | Decodes and interprets information |
| Responsibility | Ensures clarity and accuracy | Ensures understanding and feedback |
| Communication Type | Message originator | Message recipient |
| Feedback | Waits for response | Provides response |
Understanding the Sender vs Receiver Model
The Sender vs Receiver model highlights the dynamic process of communication where the sender encodes and transmits messages while the receiver decodes and interprets them, making mutual understanding essential. Your ability to recognize the role of feedback allows continuous adjustment to clarify messages and resolve misunderstandings effectively. This feedback loop ensures that communication remains interactive, confirming that the intended meaning is accurately received and responded to.
Key Roles: Who is the Sender?
The sender is the originator of the message, responsible for encoding and transmitting information to the receiver through a chosen communication channel. Key roles of the sender include clarity in message formulation, selecting appropriate symbols or language, and ensuring the intent is effectively conveyed. In the communication process, the sender initiates interaction and influences feedback by how well the message is crafted and delivered.
Defining the Role of the Receiver
The receiver decodes and interprets the message sent by the sender, ensuring accurate understanding within the communication process. Your active engagement as the receiver determines how effectively the information is processed and responded to. Feedback loops enable the receiver to confirm comprehension, clarify misunderstandings, and maintain a dynamic exchange of information.
Core Differences Between Sender and Receiver
The core difference between sender and receiver lies in their roles within communication: the sender encodes and transmits the message, while the receiver decodes and interprets it. Effective communication depends on the sender's clarity and the receiver's understanding, ensuring the intended message is accurately conveyed. Feedback loops occur when the receiver responds, enabling the sender to confirm message reception and clarify misunderstandings.
The Communication Process: Step by Step
The communication process involves the sender encoding a message and transmitting it through a chosen channel to the receiver, who decodes and interprets the information based on their understanding. Feedback loops are essential for confirming message clarity, allowing the receiver to respond and the sender to adjust the communication accordingly. Your engagement in this cycle ensures effective information exchange and minimizes misunderstandings.
Common Barriers in Sender-Receiver Communication
Common barriers in sender-receiver communication include noise, which distorts the message during transmission, and semantic misunderstandings where language differences or ambiguous terms confuse Your intent. Emotional interference and lack of feedback disrupt the feedback loop, preventing accurate message evaluation and adjustment. Ineffective communication often stems from these obstacles, reducing message clarity and mutual understanding.
Feedback: Closing the Sender-Receiver Loop
The feedback loop is essential for closing the communication gap between sender and receiver by allowing the receiver to respond, ensuring message clarity and mutual understanding. Effective feedback helps you identify misunderstandings and adjust the message accordingly, enhancing communication accuracy. This continuous exchange improves collaboration and decision-making within personal and professional interactions.
Importance of Clarity for the Sender
Clarity in communication is crucial for the sender to ensure the intended message is accurately transmitted to the receiver, minimizing misunderstandings and enhancing effective information exchange. Clear articulation helps reduce noise and distortion in the feedback loop, allowing your audience to respond appropriately and improve overall interaction. Prioritizing clarity strengthens the sender's role in establishing a successful and efficient communication process.
Active Listening: Essential for the Receiver
Active listening is essential for the receiver to accurately interpret the sender's message and respond effectively, ensuring clear communication within the feedback loop. Maintaining focus on verbal and non-verbal cues enhances understanding and reduces misunderstandings. Your ability to engage in active listening strengthens the communication process and fosters meaningful interaction.
Improving Sender and Receiver Effectiveness
Sender effectiveness improves through clear message encoding, active listening, and adapting communication style to Your audience's needs. Receiver effectiveness relies on accurate decoding, providing feedback, and minimizing distractions to enhance understanding. Strengthening both roles within the feedback loop ensures continuous message clarity, reducing misunderstandings and improving overall communication outcomes.
Infographic: Sender vs Receiver
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com