Selective perception influences how individuals interpret their partner's behavior, while selective attention determines which relationship cues are noticed and prioritized. Discover how these cognitive processes shape your connection with loved ones in this article.
Table of Comparison
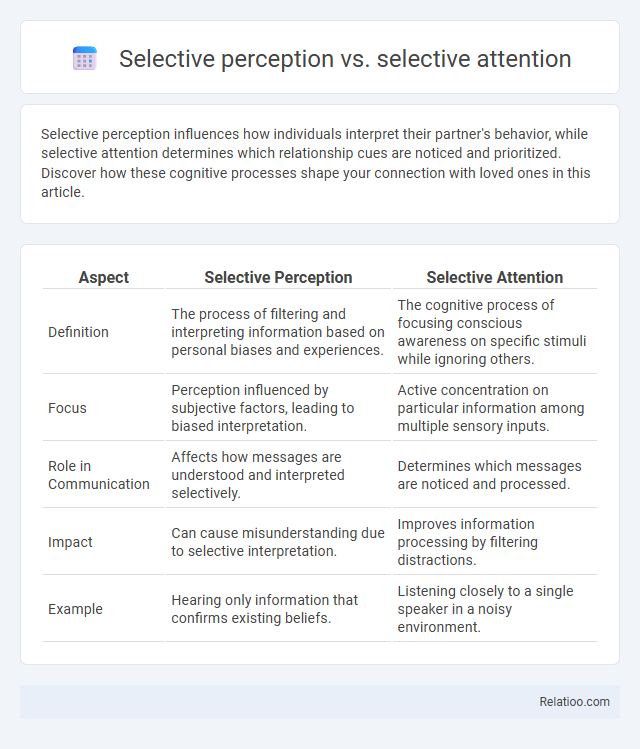
| Aspect | Selective Perception | Selective Attention |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The process of filtering and interpreting information based on personal biases and experiences. | The cognitive process of focusing conscious awareness on specific stimuli while ignoring others. |
| Focus | Perception influenced by subjective factors, leading to biased interpretation. | Active concentration on particular information among multiple sensory inputs. |
| Role in Communication | Affects how messages are understood and interpreted selectively. | Determines which messages are noticed and processed. |
| Impact | Can cause misunderstanding due to selective interpretation. | Improves information processing by filtering distractions. |
| Example | Hearing only information that confirms existing beliefs. | Listening closely to a single speaker in a noisy environment. |
Understanding Selective Perception: Definition and Mechanisms
Selective perception refers to the cognitive process where Your mind filters and interprets sensory information based on personal biases, experiences, and expectations, shaping how stimuli are understood. Unlike selective attention, which directs Your focus to specific stimuli while ignoring others, selective perception involves the interpretation and meaning assigned to those focused stimuli. Understanding selective perception mechanisms involves recognizing how perceptual filters, schemas, and emotional states influence what and how You perceive in complex environments.
What Is Selective Attention? A Cognitive Overview
Selective attention is a cognitive process that enables your brain to focus on specific stimuli while filtering out irrelevant information from the environment. It differs from selective perception, which involves interpreting ambiguous sensory input based on expectations or prior knowledge, and general perception, which is the overall process of organizing and interpreting sensory data. Understanding selective attention helps improve your ability to concentrate in dynamic settings by prioritizing pertinent information for conscious awareness.
Key Differences Between Selective Perception and Selective Attention
Selective perception involves interpreting sensory information based on existing beliefs, causing you to filter and distort stimuli, while selective attention refers to the cognitive process of focusing on specific stimuli and ignoring others. Key differences highlight that selective perception is about how you mentally organize and give meaning to information, whereas selective attention concerns the actual focus and concentration on certain inputs amid distractions. Both processes influence your overall perception but operate at different stages of sensory processing and cognitive evaluation.
How Selective Perception Shapes Our Reality
Selective perception filters sensory information based on prior experiences, beliefs, and expectations, significantly shaping our subjective reality by emphasizing certain stimuli while ignoring others. Unlike selective attention, which directs focus to specific environmental elements, selective perception interprets and biases the meaning of those elements, reinforcing existing cognitive frameworks. This cognitive bias influences decision-making, social interactions, and memory, ultimately constructing a personalized version of reality that diverges from objective truth.
The Role of Selective Attention in Daily Life
Selective attention plays a crucial role in daily life by filtering relevant sensory information from the vast array of stimuli, enabling individuals to focus on important tasks and make informed decisions. It differs from selective perception, which involves interpreting and assigning meaning to stimuli based on experience and biases, while general perception encompasses the overall process of sensing and understanding the environment. Efficient selective attention enhances productivity, safety, and communication by prioritizing critical inputs and minimizing distractions.
Psychological Theories Explaining Selective Processes
Selective perception involves filtering sensory information based on expectations, beliefs, or prior experiences, shaping what you consciously notice. Selective attention is the cognitive process of focusing mental resources on specific stimuli while ignoring others, critical in managing information overload. Perception, encompassing both, refers to the interpretation of sensory input into meaningful experiences, influenced by psychological theories like the Filter Model and Gestalt principles that explain how selective processes prioritize relevant environmental cues.
Real-World Examples of Selective Perception and Attention
Selective perception filters information based on your existing beliefs, leading to biased interpretations such as a political supporter only noticing favorable news about their candidate. Selective attention involves focusing on specific stimuli while ignoring others, like a driver concentrating on traffic signals but missing billboard ads. Understanding these mechanisms helps improve decision-making by recognizing how your mind prioritizes sensory input in real-world situations.
Factors Influencing Selective Perception vs Selective Attention
Selective perception is influenced by factors such as past experiences, beliefs, and emotional state, which shape how individuals interpret stimuli, while selective attention depends heavily on the salience, intensity, and relevance of stimuli to the individual's current goals. Cognitive load and environmental distractions also affect selective attention by limiting the capacity to focus on multiple inputs simultaneously. Both processes are guided by neural mechanisms but differ in that selective perception filters meaning based on internal biases, whereas selective attention filters sensory input based on external features and task demands.
Implications for Communication and Media Consumption
Selective perception filters incoming information according to existing beliefs, shaping how messages are interpreted and often reinforcing biases in media consumption. Selective attention determines which stimuli are consciously noticed, impacting the focus on particular media content while ignoring others, thereby influencing the effectiveness of communication strategies. Together, these cognitive processes affect audience engagement, message retention, and the potential for misunderstanding or echo chamber formation in digital and traditional media environments.
Strategies to Enhance Awareness and Counteract Biases
Selective perception filters information based on existing beliefs, while selective attention directs focus to specific stimuli, and perception interprets sensory input overall. To enhance awareness and counteract biases, you can practice mindfulness techniques, actively seek diverse perspectives, and engage in critical self-reflection to challenge automatic assumptions. Incorporating feedback mechanisms and training in cognitive flexibility further reduces the impact of selective distortions on your decision-making.
Infographic: Selective Perception vs Selective Attention
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com