Rational appeal in relationships emphasizes logic, facts, and practical benefits, while emotional appeal targets feelings, empathy, and emotional connection. Discover how balancing these approaches strengthens bonds in this article.
Table of Comparison
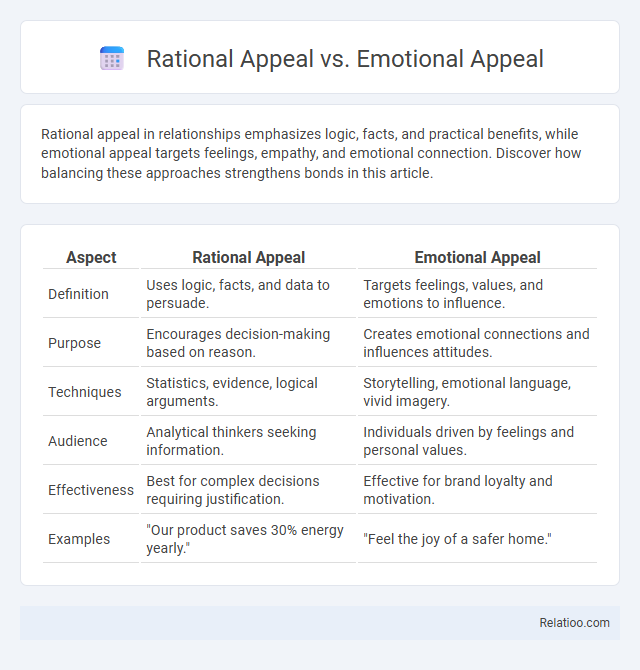
| Aspect | Rational Appeal | Emotional Appeal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses logic, facts, and data to persuade. | Targets feelings, values, and emotions to influence. |
| Purpose | Encourages decision-making based on reason. | Creates emotional connections and influences attitudes. |
| Techniques | Statistics, evidence, logical arguments. | Storytelling, emotional language, vivid imagery. |
| Audience | Analytical thinkers seeking information. | Individuals driven by feelings and personal values. |
| Effectiveness | Best for complex decisions requiring justification. | Effective for brand loyalty and motivation. |
| Examples | "Our product saves 30% energy yearly." | "Feel the joy of a safer home." |
Understanding Rational and Emotional Appeals
Rational appeal relies on logic, facts, and evidence to influence decision-making by appealing to reason, often utilizing statistics, data, and concrete information to support arguments. Emotional appeal targets feelings, values, and emotional responses to connect with the audience on a personal level, often leveraging stories, vivid imagery, and empathetic language to evoke emotions such as fear, happiness, or anger. Understanding the distinct mechanisms of rational and emotional appeals enhances persuasion strategies by aligning communication methods with the audience's cognitive and emotional processing styles.
Key Differences Between Rational and Emotional Appeals
Rational appeal targets logical reasoning by presenting facts, data, and evidence to influence decision-making, emphasizing credibility and clear benefits. Emotional appeal leverages feelings such as fear, happiness, or nostalgia to create a psychological connection, often driving quicker, instinctive responses. Persuasion encompasses both strategies, but the key difference lies in rational appeals relying on objective analysis while emotional appeals evoke subjective experiences.
The Psychology Behind Appeal Strategies
The psychology behind appeal strategies reveals that rational appeal targets the logical reasoning and analytical thinking in Your decision-making process by providing facts, statistics, and evidence. Emotional appeal, in contrast, leverages feelings, values, and emotional triggers to create a personal connection and influence Your attitudes or behavior on a subconscious level. Persuasion combines these elements by strategically balancing logic and emotion to effectively motivate action, shaping perceptions through cognitive and affective pathways in the brain.
When to Use Rational Appeal in Communication
Use Rational Appeal in communication when presenting complex information or data-driven arguments that require logical analysis and clear evidence. Your audience benefits most from this approach when decision-making involves critical thinking, such as in technical fields, business proposals, or educational settings. Employing facts, statistics, and concrete examples strengthens credibility and helps persuade those who value reason over emotion.
When to Leverage Emotional Appeal for Impact
Emotional appeal effectively captures your audience's attention and builds a deep connection by triggering feelings such as empathy, fear, or happiness, which can drive immediate action or brand loyalty. Use emotional appeal when your goal is to create a memorable experience or influence decisions tied to personal values, especially in marketing, storytelling, or social campaigns. Rational appeal works best for decisions requiring logical evaluation, but emotional appeal leverages subconscious motivations to enhance persuasion and long-term engagement.
Advantages of Rational Appeal
Rational appeal leverages logical reasoning and factual evidence to influence decision-making, making it highly effective in building credibility and trust with analytical audiences. It enables clear presentation of benefits, cost-effectiveness, and tangible results, which enhances informed choices and long-term satisfaction. Emphasizing statistical data, expert testimonials, and concrete examples strengthens persuasive communication by appealing directly to intellect and practical needs.
Benefits of Emotional Appeal
Emotional appeal leverages feelings to create a powerful connection with the audience, enhancing message retention and motivating action more effectively than rational appeal alone. This persuasion technique taps into emotions such as fear, happiness, or empathy, driving immediate responses and fostering brand loyalty. Emotional appeal often leads to higher engagement rates and stronger consumer trust by resonating deeply with personal values and experiences.
Common Mistakes in Using Appeals
Common mistakes in using rational appeal include overloading an argument with excessive data, causing audience disengagement, while emotional appeal often fails when it manipulates feelings without credible evidence, leading to skepticism. Confusing persuasion with mere appeal can result in ignoring the necessity of logical structure combined with emotional connection to influence effectively. Successful persuasion integrates both rational and emotional appeals strategically to avoid alienating the audience or appearing insincere.
Integrating Rational and Emotional Appeals for Maximum Effect
Integrating rational and emotional appeals amplifies persuasion by engaging both the logical and affective dimensions of decision-making processes. Effective communication harnesses data-driven evidence and emotional storytelling to create compelling narratives that resonate with diverse audiences. Balancing facts with feelings enhances message retention and drives desired behavioral responses in marketing, advertising, and public relations.
Choosing the Right Appeal for Your Audience
Choosing the right appeal for your audience involves understanding their values and decision-making processes; rational appeal leverages logic, facts, and data to engage analytical thinkers, while emotional appeal taps into feelings like fear, joy, or empathy to connect with those motivated by sentiment. An effective persuasion strategy often combines both appeals, aligning the message with the audience's mindset to maximize impact and drive action. Your success in persuasion hinges on tailoring your appeal to what resonates most deeply with your specific audience's preferences and expectations.
Infographic: Rational Appeal vs Emotional Appeal
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com