Positive feedback reinforces desirable behaviors by encouraging repetition, while negative feedback highlights mistakes to promote correction and improvement. Discover the impact of both feedback types on relationship dynamics in this article.
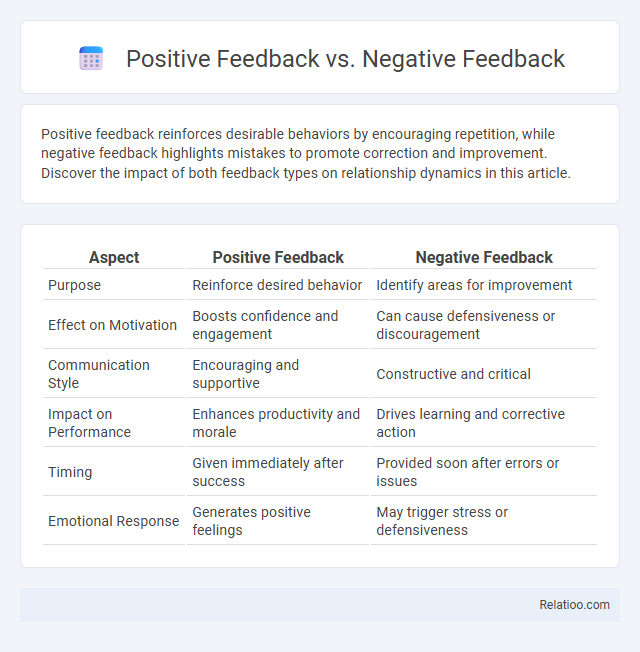
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Positive Feedback | Negative Feedback |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reinforce desired behavior | Identify areas for improvement |
| Effect on Motivation | Boosts confidence and engagement | Can cause defensiveness or discouragement |
| Communication Style | Encouraging and supportive | Constructive and critical |
| Impact on Performance | Enhances productivity and morale | Drives learning and corrective action |
| Timing | Given immediately after success | Provided soon after errors or issues |
| Emotional Response | Generates positive feelings | May trigger stress or defensiveness |
Introduction to Feedback: Positive vs Negative
Feedback consists of information about performance or behavior used to make improvements. Positive feedback reinforces desired actions by highlighting successes or strengths, promoting confidence and continued effort. Negative feedback identifies errors or areas needing correction, guiding adjustments to enhance future outcomes.
Defining Positive Feedback
Positive feedback amplifies changes in a system, reinforcing the original stimulus and driving further deviation from equilibrium. Unlike negative feedback, which counteracts and stabilizes a system by reducing fluctuations, positive feedback accelerates processes and can lead to exponential growth or runaway effects. Understanding how positive feedback functions is essential for managing your systems effectively, ensuring desired outcomes are enhanced rather than destabilized.
Defining Negative Feedback
Negative feedback regulates systems by counteracting changes to maintain stability and homeostasis, commonly seen in biological and engineering contexts. Positive feedback amplifies deviations, driving processes toward completion or escalation, while feedback, in general, refers to the response signals that enable dynamic system adjustments. Understanding negative feedback is crucial for optimizing Your control mechanisms, as it minimizes fluctuations and promotes equilibrium.
Psychological Impact of Positive Feedback
Positive feedback in psychology enhances motivation and self-esteem by reinforcing desired behaviors, leading to increased confidence and improved performance. Negative feedback, while useful for correcting errors, can sometimes lower self-esteem and induce stress if not delivered constructively. Overall, effective feedback balances positive reinforcement with constructive criticism to foster growth and psychological well-being.
Psychological Impact of Negative Feedback
Negative feedback in psychological contexts often triggers stress responses, lowering motivation and self-esteem, which can impede personal growth and learning. Positive feedback enhances neural pathways associated with reward and motivation, fostering confidence and reinforcing desirable behaviors. You can balance both by using feedback constructively to encourage improvement without damaging your self-worth.
Benefits of Positive Feedback in the Workplace
Positive feedback enhances employee motivation by recognizing achievements, which boosts morale and productivity across the workplace. It fosters a growth-oriented environment where team members feel valued and encouraged to improve performance continuously. Positive feedback also strengthens communication, leading to better collaboration and higher overall job satisfaction.
Benefits of Negative Feedback for Growth
Negative feedback is crucial for personal and professional growth as it highlights areas for improvement, enabling targeted development and skill enhancement. Unlike positive feedback, which reinforces existing strengths, negative feedback encourages critical thinking and problem-solving, fostering resilience and adaptability. Consistent negative feedback leads to measurable progress by promoting self-awareness and motivating individuals to overcome challenges effectively.
Common Mistakes in Giving Feedback
Common mistakes in giving feedback include confusing positive feedback with mere praise, which can reduce its effectiveness by lacking specific, actionable insights. Negative feedback is often perceived as personal criticism when it is not delivered with clarity, empathy, and constructive suggestions, leading to defensiveness rather than improvement. Effective feedback combines clear, balanced observations and concrete examples to guide future behavior without diminishing motivation or morale.
Strategies for Balancing Positive and Negative Feedback
Balancing positive and negative feedback involves strategically emphasizing constructive criticism while maintaining encouragement to foster growth and motivation. Effective feedback strategies include using the "sandwich" approach--pairing negative feedback with positive remarks--ensuring clarity and actionable insights to promote continuous improvement. Measuring feedback impact through employee engagement and performance metrics helps refine the balance for optimal development outcomes.
Conclusion: Choosing Effective Feedback Methods
Effective feedback methods hinge on context, goals, and individual needs, making positive feedback essential for motivation and confidence, while negative feedback drives improvement and correction. Balanced feedback integrates both types, fostering growth, clarity, and sustained performance enhancement. Selecting the right feedback approach optimizes learning outcomes and workplace productivity by tailoring communication to specific situations.
Infographic: Positive Feedback vs Negative Feedback
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com