Passive communication involves avoiding expressing feelings or opinions openly, leading to unaddressed issues and misunderstandings. Passive-aggressive communication disguises anger or resentment through indirect actions or sarcasm, creating confusion and tension in relationships; discover more about these patterns and how to improve communication in this article.
Table of Comparison
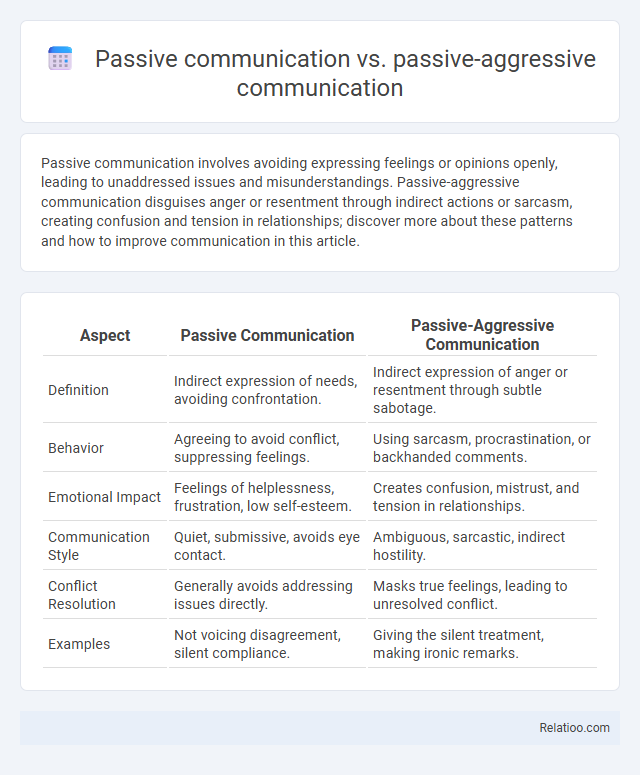
| Aspect | Passive Communication | Passive-Aggressive Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Indirect expression of needs, avoiding confrontation. | Indirect expression of anger or resentment through subtle sabotage. |
| Behavior | Agreeing to avoid conflict, suppressing feelings. | Using sarcasm, procrastination, or backhanded comments. |
| Emotional Impact | Feelings of helplessness, frustration, low self-esteem. | Creates confusion, mistrust, and tension in relationships. |
| Communication Style | Quiet, submissive, avoids eye contact. | Ambiguous, sarcastic, indirect hostility. |
| Conflict Resolution | Generally avoids addressing issues directly. | Masks true feelings, leading to unresolved conflict. |
| Examples | Not voicing disagreement, silent compliance. | Giving the silent treatment, making ironic remarks. |
Understanding Passive Communication
Passive communication involves avoiding direct expression of feelings and needs, often leading to suppressed emotions and unmet personal boundaries. In contrast, passive-aggressive communication masks resentment through indirect behaviors, such as sarcasm or subtle sabotage, rather than clear dialogue. Understanding passive communication is crucial for recognizing when avoidance hinders effective interaction and for developing assertive skills that promote healthier, more transparent relationships.
Defining Passive-Aggressive Communication
Passive-aggressive communication is characterized by indirect expressions of hostility or resentment, often through subtle behaviors such as sarcasm, procrastination, or intentional inefficiency, contrasting with the straightforward nature of passive communication where individuals avoid expressing their feelings openly. Unlike passive communication that typically stems from fear or avoidance of conflict, passive-aggressive communication involves underlying anger or dissatisfaction that is masked rather than addressed directly. Understanding this distinction helps Your interactions by enabling you to identify hidden tensions and respond more effectively to ambiguous or contradictory messages.
Key Differences Between Passive and Passive-Aggressive Behaviors
Passive communication involves avoiding confrontation and expressing needs indirectly, often leading to suppressed feelings and unassertiveness. Passive-aggressive communication displays hidden resentment and indirect resistance, such as sarcasm or procrastination, masking true emotions behind seemingly passive behavior. Key differences lie in intent and expression: passive communication seeks to avoid conflict while passive-aggressive communication covertly expresses anger or dissatisfaction.
Core Characteristics of Passive Communicators
Passive communication is characterized by an avoidance of expressing opinions or feelings, often resulting in difficulty asserting personal rights and a tendency to yield to others' demands. Passive-aggressive communication combines indirect resistance and hidden resentment, where passive communicators may express dissatisfaction through subtle behaviors rather than direct confrontation. Core characteristics of passive communicators include low self-confidence, fear of conflict, and a pervasive pattern of prioritizing others' needs over their own, which can lead to unmet personal needs and suppressed emotions.
Typical Traits of Passive-Aggressive Communicators
Passive communication often involves avoiding direct expression of thoughts or feelings, leading to misunderstandings and unmet needs. Passive-aggressive communication is characterized by indirect resistance, sarcasm, and subtle sabotage, reflecting hidden hostility despite an outwardly agreeable demeanor. Your interactions with passive-aggressive communicators may reveal typical traits like stubbornness, chronic procrastination, backhanded compliments, and a tendency to sulk or give the silent treatment.
Common Examples in Daily Interactions
Passive communication often involves avoiding expressing your feelings or opinions, such as agreeing to plans you dislike without protest. Passive-aggressive communication includes indirect expressions of hostility, like giving sarcastic remarks or giving the silent treatment to convey displeasure. Passive communication in daily interactions appears when you refrain from asserting yourself, such as allowing others to interrupt you repeatedly without speaking up.
Psychological Impact on Relationships
Passive communication often leads to misunderstandings and emotional distance in relationships by suppressing true feelings. Passive-aggressive communication causes confusion and distrust, as indirect hostility undermines open dialogue and creates emotional tension. You can improve relationship health by recognizing these patterns and fostering honest, assertive communication to build trust and emotional connection.
Consequences in Workplace and Personal Life
Passive communication often leads to misunderstandings and unresolved conflicts in workplace and personal life, reducing team productivity and emotional satisfaction. Passive-aggressive communication creates hidden resentment and distrust, escalating tensions and damaging relationships over time. Combining assertiveness with empathy is crucial to fostering clearer dialogue, enhancing collaboration, and maintaining healthier interpersonal dynamics.
How to Recognize Passive and Passive-Aggressive Patterns
Recognizing passive communication involves noting indirect expressions of needs or feelings, often characterized by avoidance, hesitation, or submissive language. Passive-aggressive communication combines passive behavior with underlying hostility, marked by sarcasm, procrastination, or subtle sabotage. Identifying these patterns requires attention to inconsistencies between words and actions, nonverbal cues, and the presence of unspoken resentment or avoidance in interactions.
Strategies for Healthier Communication Styles
Passive communication often leads to unmet needs and suppressed emotions, while passive-aggressive communication disguises hostility with indirect behaviors, creating confusion and conflict. To foster healthier communication, you should practice assertiveness by expressing your needs clearly and respectfully, setting boundaries without guilt, and using "I" statements to reduce misunderstandings. Developing emotional awareness and active listening skills can transform interactions from passive or passive-aggressive patterns into constructive dialogues that promote mutual respect and understanding.
Infographic: Passive communication vs Passive-aggressive communication
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com