Formal feedback involves structured, scheduled evaluations often documented for performance tracking, while informal feedback occurs spontaneously in casual interactions to provide immediate guidance or reinforcement. Explore this article to understand the impact of both feedback types on relationship development and effectiveness.
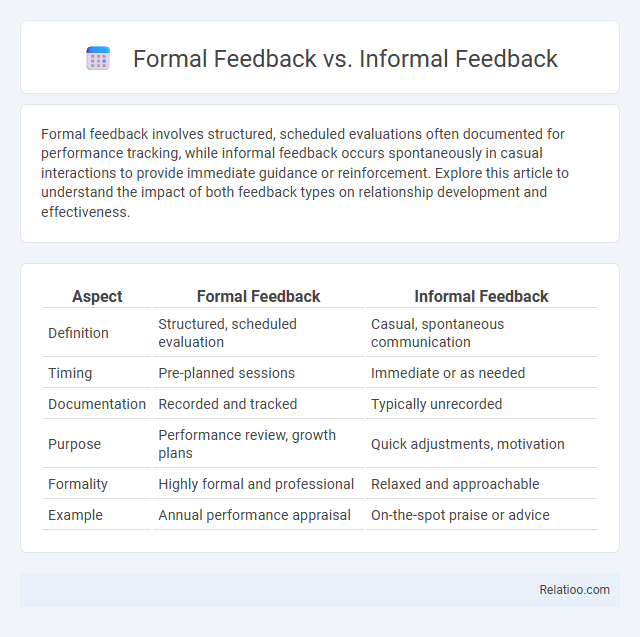
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Formal Feedback | Informal Feedback |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured, scheduled evaluation | Casual, spontaneous communication |
| Timing | Pre-planned sessions | Immediate or as needed |
| Documentation | Recorded and tracked | Typically unrecorded |
| Purpose | Performance review, growth plans | Quick adjustments, motivation |
| Formality | Highly formal and professional | Relaxed and approachable |
| Example | Annual performance appraisal | On-the-spot praise or advice |
Introduction to Formal and Informal Feedback
Formal feedback is structured and typically occurs through scheduled evaluations such as performance reviews or official assessments, providing clear, documented insights into Your progress or performance. Informal feedback happens spontaneously in everyday interactions, offering immediate, casual guidance that helps in real-time improvement without formal documentation. Understanding the distinctions between these feedback types allows You to effectively leverage both methods for continuous development.
Defining Formal Feedback
Formal feedback is a structured and documented process often used in professional or educational settings to evaluate performance based on specific criteria. Your progress is measured against standardized benchmarks, enabling clear, actionable insights for improvement. This contrasts with informal feedback, which is spontaneous and casual, lacking the systematic approach that formal feedback provides.
Defining Informal Feedback
Informal feedback refers to spontaneous, casual comments or reactions that occur naturally during everyday interactions, providing immediate and context-specific responses. Unlike formal feedback, which is structured and documented through scheduled evaluations or meetings, informal feedback is typically conversational and less systematic, helping to reinforce or adjust behavior in real-time. This type of feedback fosters a dynamic communication environment, encouraging continuous improvement and adaptation without the constraints of formal assessment processes.
Key Differences Between Formal and Informal Feedback
Formal feedback involves structured, scheduled evaluations often documented and used for performance reviews, while informal feedback occurs spontaneously through casual conversations, providing immediate insights. You benefit from formal feedback by receiving clear, measurable guidance for improvement, whereas informal feedback fosters continuous development and immediate adjustment. Understanding these differences helps optimize communication strategies for growth and effectiveness in professional environments.
Advantages of Formal Feedback
Formal feedback provides structured, documented evaluations that ensure consistency and clarity in performance assessments. This type of feedback supports measurable goal tracking and can be used as reliable evidence for employee development or organizational decisions. Your ability to receive formal feedback enhances professional growth by fostering clear communication and setting defined expectations.
Advantages of Informal Feedback
Informal feedback offers real-time insights that foster immediate improvements and enhance communication between team members, creating a more dynamic and supportive work environment. It encourages open dialogue and continuous learning without the pressure of formal evaluations, leading to higher employee engagement and motivation. The flexibility of informal feedback allows for personalized, context-specific suggestions that are often more relevant and actionable than formal feedback mechanisms.
When to Use Formal Feedback
Formal feedback is best used during performance reviews, project evaluations, or when documenting progress for accountability and improvement within organizations. It provides structured, objective insights that guide professional development and align with company policies or goals. This type of feedback fosters clear communication and measurable outcomes, especially in situations requiring official records or follow-up actions.
When to Use Informal Feedback
Informal feedback is most effective during ongoing projects or day-to-day tasks when quick adjustments and encouragement are needed to enhance performance and morale. It provides timely, specific insights without the pressure of formal evaluation, helping you address issues promptly and maintain open communication. Use informal feedback to foster continuous development and immediate support before formal reviews take place.
Integrating Both Feedback Types for Maximum Benefit
Integrating formal feedback, which provides structured, detailed evaluations, with informal feedback, characterized by spontaneous, real-time insights, creates a comprehensive understanding of performance and areas for growth. Your ability to balance scheduled performance reviews with everyday conversations ensures continuous development and fosters a culture of open communication. Leveraging both feedback types maximizes clarity, motivation, and actionable outcomes in professional and personal settings.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Feedback Approach
Selecting the appropriate feedback approach hinges on context, purpose, and desired outcomes, with formal feedback providing structured, documented insights crucial for performance appraisals, while informal feedback offers immediate, conversational touchpoints that promote continuous improvement. Effective feedback strategies combine both methods to enhance communication, foster growth, and adapt to organizational culture and individual needs. Emphasizing clarity, relevance, and timeliness ensures that feedback drives meaningful development and engagement.
Infographic: Formal Feedback vs Informal Feedback
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com