Dismissal refers to the employer-initiated termination of an employee's contract for reasons such as misconduct or poor performance, whereas discharge typically implies the formal release of an employee from duty, often upon completion of contract or due to redundancies. Explore the distinctions between dismissal and discharge to better understand your rights and obligations in employment law in this article.
Table of Comparison
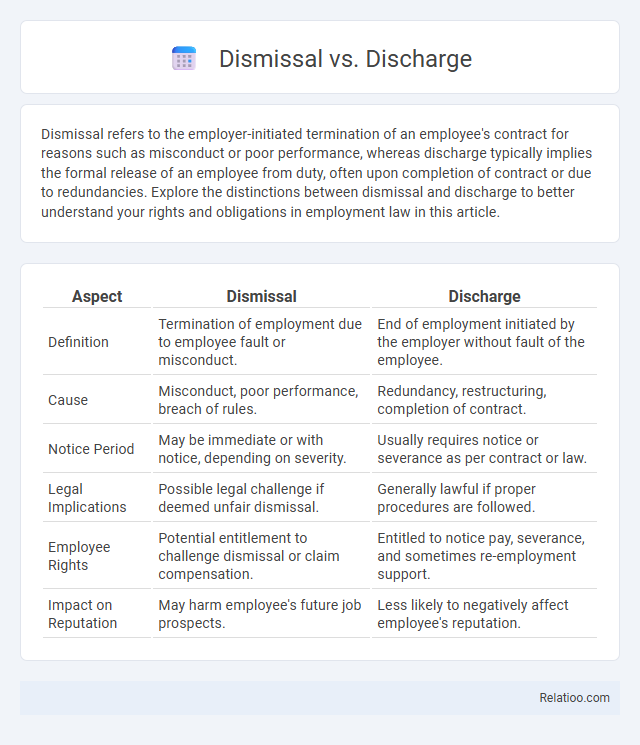
| Aspect | Dismissal | Discharge |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Termination of employment due to employee fault or misconduct. | End of employment initiated by the employer without fault of the employee. |
| Cause | Misconduct, poor performance, breach of rules. | Redundancy, restructuring, completion of contract. |
| Notice Period | May be immediate or with notice, depending on severity. | Usually requires notice or severance as per contract or law. |
| Legal Implications | Possible legal challenge if deemed unfair dismissal. | Generally lawful if proper procedures are followed. |
| Employee Rights | Potential entitlement to challenge dismissal or claim compensation. | Entitled to notice pay, severance, and sometimes re-employment support. |
| Impact on Reputation | May harm employee's future job prospects. | Less likely to negatively affect employee's reputation. |
Understanding Dismissal and Discharge
Understanding dismissal involves recognizing it as the termination of an employee's contract due to performance or conduct issues, often initiated by the employer. Discharge typically refers to the formal release from employment, which may include termination for reasons such as redundancy, resignation, or mutual agreement. Distinguishing between dismissal and discharge is critical for legal clarity, as dismissal usually implies fault, while discharge can be neutral or voluntary.
Key Differences Between Dismissal and Discharge
Dismissal refers to the termination of an employee's contract due to misconduct or performance issues, often implying fault on the employee's part. Discharge is a broader term encompassing any form of employment termination initiated by the employer, including layoffs or redundancy, without necessarily attributing blame. The key difference lies in Dismissal being fault-based and disciplinary, while Discharge can be faultless and organizational in nature.
Legal Definitions of Dismissal and Discharge
Dismissal refers to the termination of an employee's contract by the employer due to misconduct, poor performance, or redundancy, often implying fault or cause. Discharge denotes the formal release of an individual from a duty, obligation, or legal charge, typically without negative connotation, such as a discharge from military service or criminal charges. In legal contexts, dismissal commonly applies to the ending of employment with reasons and potential consequences, while discharge indicates completion or release from responsibilities or accusations.
Grounds for Employee Dismissal
Grounds for employee dismissal typically involve misconduct, poor performance, violation of company policies, or redundancy due to organizational restructuring. Discharge often refers to termination resulting from employee actions such as insubordination or failure to meet job requirements, whereas dismissal specifically emphasizes the employer's decision to terminate employment based on justified reasons. Understanding the precise grounds ensures compliance with labor laws and protects both employer and employee rights.
Common Reasons for Employee Discharge
Common reasons for employee discharge include poor performance, violation of company policies, misconduct, attendance issues, and redundancy due to organizational restructuring. Discharge typically implies a formal termination often linked to specific causes or failures, contrasted with dismissal, which may sometimes be less formal or related to temporary separations. Understanding these distinctions helps employers apply appropriate legal grounds and documentation to ensure compliance with labor laws and protect organizational interests.
Employer Obligations When Dismissing Employees
Employer obligations when dismissing employees require clear communication of the reason for dismissal to ensure legal compliance and avoid wrongful termination claims. Proper documentation and adherence to company policies and labor laws, such as providing notice or severance pay, safeguard both employer and employee rights during dismissal or discharge. You must also conduct a fair investigation and maintain transparency to uphold ethical standards and minimize disputes related to dismissal or discharge.
Employee Rights During Dismissal and Discharge
Employee rights during dismissal and discharge include protection against unlawful termination, entitlement to notice periods or severance pay, and access to grievance procedures ensuring fair treatment. Your rights may vary based on employment contracts and local labor laws, which typically require employers to provide valid reasons for dismissal or discharge to prevent wrongful termination claims. Understanding the distinctions between dismissal, discharge, and termination helps you safeguard your employment rights and pursue legal recourse if those rights are violated.
Impact on Employment Records: Dismissal vs Discharge
Dismissal typically reflects negatively on your employment record, indicating termination for cause such as poor performance or misconduct, which can affect future job prospects. Discharge, often used interchangeably but sometimes referring to termination without fault, may be recorded neutrally or less negatively, especially if it involves layoffs or company restructuring. Understanding the specific terminology used in your employment documents is crucial, as dismissal can carry more severe consequences than discharge in professional histories.
Handling Disputes: Dismissal and Discharge Cases
Handling disputes in dismissal and discharge cases requires a clear understanding of legal distinctions and evidence evaluation. Your ability to demonstrate wrongful termination or contractual breach directly impacts the resolution process and potential remedies. Effective dispute management hinges on accurate documentation, adherence to employment laws, and strategic negotiation to protect your rights.
Best Practices for Employers: Fair Termination Processes
Employers should implement transparent and consistent best practices for dismissal, discharge, and termination to ensure fair treatment and legal compliance. Documenting performance issues, providing clear communication, and offering opportunities to improve help protect your organization from wrongful termination claims. Establishing these fair termination processes fosters trust while minimizing disputes and potential liabilities.
Infographic: Dismissal vs Discharge
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com