Implicit bias operates unconsciously, influencing behavior without awareness, while explicit bias involves deliberate attitudes and beliefs. Explore this article to understand how both biases shape relationships and impact interactions.
Table of Comparison
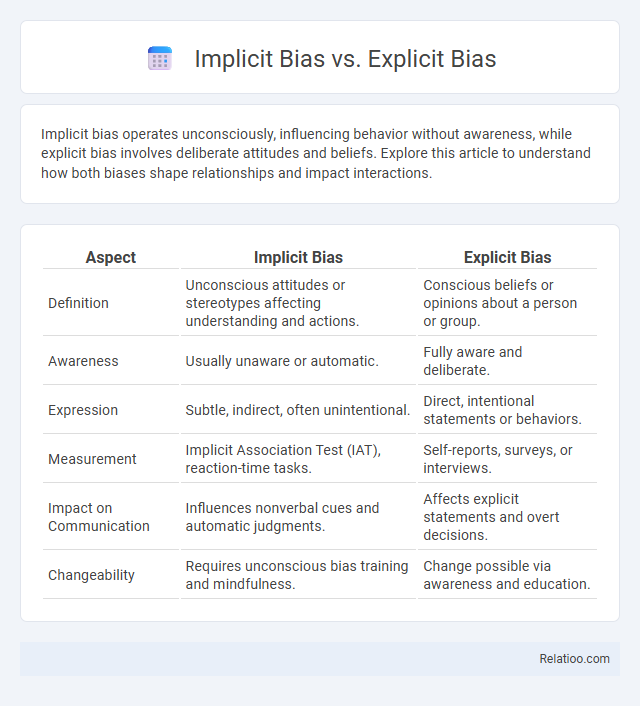
| Aspect | Implicit Bias | Explicit Bias |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unconscious attitudes or stereotypes affecting understanding and actions. | Conscious beliefs or opinions about a person or group. |
| Awareness | Usually unaware or automatic. | Fully aware and deliberate. |
| Expression | Subtle, indirect, often unintentional. | Direct, intentional statements or behaviors. |
| Measurement | Implicit Association Test (IAT), reaction-time tasks. | Self-reports, surveys, or interviews. |
| Impact on Communication | Influences nonverbal cues and automatic judgments. | Affects explicit statements and overt decisions. |
| Changeability | Requires unconscious bias training and mindfulness. | Change possible via awareness and education. |
Understanding Implicit Bias
Implicit bias refers to unconscious attitudes or stereotypes that influence your understanding and actions unknowingly, differing from explicit bias, which involves conscious beliefs and deliberate decisions. Understanding implicit bias is crucial for recognizing how automatic associations affect behavior and decision-making in various contexts, including workplace dynamics, healthcare, and social interactions. Addressing these unconscious biases helps promote fairness and inclusivity by revealing hidden prejudices that traditional awareness may overlook.
Defining Explicit Bias
Explicit bias refers to the conscious attitudes or beliefs that individuals hold about a group, which can influence decisions and behaviors in a deliberate manner. Unlike implicit bias, which operates unconsciously, explicit bias is recognized and often expressed openly, affecting interactions and judgments. Understanding your explicit biases is crucial for fostering fair and equitable environments.
Key Differences Between Implicit and Explicit Bias
Implicit bias refers to unconscious attitudes or stereotypes that influence behavior without awareness, while explicit bias involves conscious and deliberate beliefs or feelings about a group. Key differences include the awareness level and control over these biases: implicit bias operates unconsciously and can affect decisions unintentionally, whereas explicit bias is openly acknowledged and intentionally expressed. Measuring implicit bias often relies on indirect tests like the Implicit Association Test (IAT), while explicit bias is typically assessed through self-reported attitudes or expressed opinions.
Origins and Development of Biases
Bias originates from cognitive processes shaped by social, cultural, and environmental influences during early development. Implicit bias develops unconsciously through repeated exposure to stereotypes and social norms, often without awareness or intentionality, while explicit bias forms through deliberate beliefs and attitudes shaped by personal experiences and ideological values. Both types of bias are reinforced by ongoing interactions within societal structures, creating patterns that influence perception and behavior.
Psychological Mechanisms Behind Each Bias
Implicit bias operates through unconscious cognitive processes that automatically influence your judgments and decisions without awareness, often shaped by societal stereotypes and past experiences. Explicit bias involves conscious attitudes and beliefs that you deliberately endorse and express, reflecting intentional discrimination or preferences. Both biases stem from underlying psychological mechanisms such as automatic categorization, social learning, and motivated reasoning, which collectively shape behavior and perceptions.
Real-World Examples of Implicit and Explicit Bias
Implicit bias operates unconsciously, influencing your decisions without awareness, such as a hiring manager unknowingly favoring candidates from their own alma mater. Explicit bias involves conscious attitudes or beliefs, demonstrated when a landlord openly refuses to rent to certain ethnic groups. Recognizing these distinctions helps address systemic inequalities and promotes fairer treatment in real-world scenarios.
Impacts on Decision-Making and Behavior
Implicit bias operates unconsciously, subtly influencing your decisions and behaviors without your awareness, while explicit bias involves conscious attitudes that directly affect choices. Both forms of bias shape perception and judgment, leading to unfair treatment or missed opportunities by reinforcing stereotypes and limiting objectivity. Understanding the distinctions between implicit bias, explicit bias, and general bias is crucial for improving decision-making processes and fostering more equitable behavior in personal and professional settings.
Measuring and Identifying Biases
Measuring bias involves different techniques for implicit, explicit, and general biases, with implicit bias assessed through indirect tests like the Implicit Association Test (IAT) that reveal unconscious preferences influencing your decisions. Explicit bias measurement relies on self-report surveys and interviews that capture conscious attitudes and beliefs people express openly. Identifying bias requires combining these methods to understand both hidden and acknowledged prejudices affecting behavior and decision-making processes.
Strategies for Reducing Bias
Strategies for reducing bias involve identifying and addressing both implicit bias, which operates unconsciously, and explicit bias, which is deliberate and conscious. You can implement structured decision-making processes, diversity training programs, and promote awareness through self-reflection exercises to minimize the impact of biases in various settings. Consistent evaluation and feedback mechanisms help ensure these strategies effectively reduce bias over time.
The Importance of Awareness in Combating Bias
Implicit bias operates unconsciously, influencing decisions and actions without explicit awareness, while explicit bias involves conscious and deliberate attitudes or beliefs. Recognizing the distinction between implicit and explicit bias is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate prejudiced behaviors and promote inclusivity. Increasing awareness of both forms of bias enhances self-reflection and fosters environments where fairness and equity can be actively pursued.
Infographic: Implicit Bias vs Explicit Bias
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com