Belonging fosters a deep sense of acceptance and identity within a group, while inclusion ensures diverse participation and equitable access. Explore the distinctions and importance of belonging versus inclusion in this article.
Table of Comparison
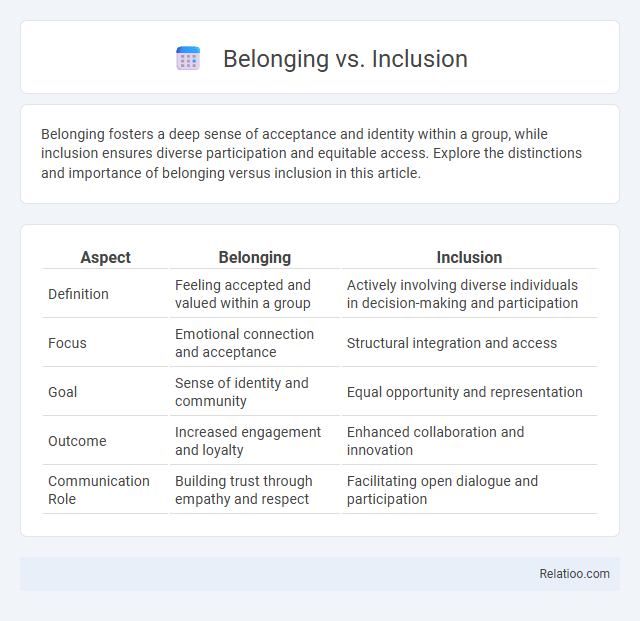
| Aspect | Belonging | Inclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Feeling accepted and valued within a group | Actively involving diverse individuals in decision-making and participation |
| Focus | Emotional connection and acceptance | Structural integration and access |
| Goal | Sense of identity and community | Equal opportunity and representation |
| Outcome | Increased engagement and loyalty | Enhanced collaboration and innovation |
| Communication Role | Building trust through empathy and respect | Facilitating open dialogue and participation |
Understanding the Concepts: Belonging and Inclusion
Belonging and inclusion are distinct yet interconnected concepts crucial for fostering positive environments in workplaces and communities. Inclusion involves actively creating spaces where diverse individuals are welcomed and their differences respected, while belonging goes deeper, reflecting the emotional experience of being accepted and valued as an integral part of the group. Understanding these nuances empowers you to cultivate environments where everyone feels not only included but genuinely connected and supported.
Key Differences Between Belonging and Inclusion
Belonging reflects an emotional experience where You feel truly accepted and valued within a group, while inclusion emphasizes creating environments and policies that ensure diverse individuals have access and participation. Inclusion is often a strategic, organizational effort to remove barriers and promote representation, whereas belonging is a personal sense of connection and psychological safety. Understanding these key differences helps organizations move beyond just diverse numbers to fostering meaningful acceptance and engagement.
The Importance of Inclusion in Modern Workplaces
Inclusion in modern workplaces fosters a culture where diverse perspectives are valued, empowering Your team to contribute fully and authentically. Unlike mere belonging, which centers on fitting in, inclusion ensures equitable access to opportunities and resources for all employees. Prioritizing inclusion drives innovation, employee engagement, and overall organizational success by creating an environment where everyone feels respected and empowered.
Why Belonging Matters Beyond Inclusion
Belonging goes beyond inclusion by fostering a deep sense of acceptance where individuals feel valued for their authentic selves, which drives engagement and well-being in organizations. While inclusion ensures diverse representation and equitable access, belonging creates psychological safety that empowers creativity and collaboration. Research shows that teams with high belonging experience lower turnover rates and improved performance, highlighting its critical role in sustainable organizational success.
Challenges to Achieving True Belonging
True belonging requires more than just inclusion; it demands an environment where You feel genuinely accepted and valued for your unique identity. Challenges include overcoming unconscious biases, dismantling systemic barriers, and fostering authentic connections beyond surface-level diversity efforts. Organizations must prioritize psychological safety and continuous dialogue to move from mere inclusion to meaningful belonging.
Building Inclusive Cultures: Best Practices
Building inclusive cultures requires understanding the distinctions between belonging, inclusion, and diversity to foster environments where everyone feels valued and empowered. Your organization can implement best practices such as active listening, equitable policies, and continuous education to promote psychological safety and authentic engagement among diverse teams. Emphasizing shared values and respect for individual differences drives collaboration, innovation, and long-term success.
Measuring Belonging and Inclusion in Organizations
Measuring belonging in organizations involves assessing employees' sense of acceptance, connection, and psychological safety, often through surveys that evaluate trust, respect, and authentic interpersonal relationships. Inclusion measurement focuses on the equitable treatment, participation, and value of diverse perspectives, using metrics such as representation data, involvement in decision-making, and feedback on workplace policies. Your organization can use combined belonging and inclusion indices alongside qualitative feedback to identify gaps and drive targeted initiatives that enhance engagement and retention.
The Role of Leadership in Fostering Belonging
Leadership that prioritizes belonging creates a culture where employees feel valued, respected, and connected to the organization's mission, enhancing overall engagement and productivity. Unlike inclusion, which focuses on diverse representation, fostering belonging requires leaders to actively nurture trust, open communication, and psychological safety within teams. Effective leaders implement inclusive policies, promote empathy, and model behaviors that encourage authentic participation, ultimately driving innovation and employee retention.
Impact of Belonging and Inclusion on Employee Well-being
Belonging and inclusion significantly enhance employee well-being by creating environments where individuals feel valued and accepted, leading to higher job satisfaction and reduced stress levels. Inclusive workplaces promote psychological safety and engagement, which directly improve mental health and productivity. The impact of belonging fosters a sense of connection that mitigates feelings of isolation, contributing to overall emotional resilience among employees.
Moving from Inclusion to Genuine Belonging
Moving from inclusion to genuine belonging shifts organizational efforts from mere representation and participation to fostering authentic connections where individuals feel deeply valued and accepted. Genuine belonging enhances employee engagement, collaboration, and retention by creating environments where diverse perspectives are embraced and psychological safety is prioritized. This transition requires intentional culture-building strategies, inclusive leadership, and ongoing dialogue that empower individuals to bring their whole selves to work.
Infographic: Belonging vs Inclusion
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com