Guilt-tripping manipulates emotions by inducing guilt to control behavior, while gaslighting distorts reality to make someone doubt their perception and sanity. Learn how to identify these toxic tactics and protect your emotional well-being in this article.
Table of Comparison
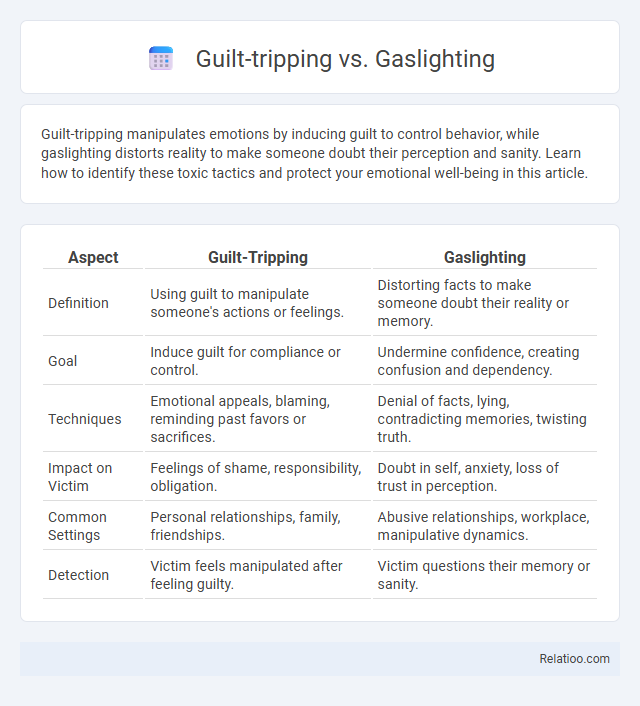
| Aspect | Guilt-Tripping | Gaslighting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Using guilt to manipulate someone's actions or feelings. | Distorting facts to make someone doubt their reality or memory. |
| Goal | Induce guilt for compliance or control. | Undermine confidence, creating confusion and dependency. |
| Techniques | Emotional appeals, blaming, reminding past favors or sacrifices. | Denial of facts, lying, contradicting memories, twisting truth. |
| Impact on Victim | Feelings of shame, responsibility, obligation. | Doubt in self, anxiety, loss of trust in perception. |
| Common Settings | Personal relationships, family, friendships. | Abusive relationships, workplace, manipulative dynamics. |
| Detection | Victim feels manipulated after feeling guilty. | Victim questions their memory or sanity. |
Understanding Guilt-Tripping: Definition and Examples
Guilt-tripping involves manipulating someone's emotions by inducing feelings of guilt to influence their behavior, often through statements like "If you loved me, you would..." or "I did so much for you, and this is how you repay me." Unlike gaslighting, which distorts reality to make someone doubt their perceptions, guilt-tripping targets emotional responsibility to control actions. Examples include a parent telling a child they are selfish for not visiting frequently or a partner implying neglect by not prioritizing their needs, highlighting how psychological pressure shapes decisions.
What Is Gaslighting? Key Characteristics
Gaslighting is a form of psychological manipulation aimed at making a person doubt their perceptions, memories, or sanity, often occurring in abusive relationships. Key characteristics include persistent denial of facts, distortion of reality, and eroding the victim's trust in their own mind. Unlike guilt-tripping, which induces shame to control behavior, gaslighting systematically undermines the victim's sense of reality for deeper control.
Guilt-Tripping vs Gaslighting: Core Differences
Guilt-tripping manipulates your emotions by making you feel responsible for someone else's distress, often to influence your actions or decisions. Gaslighting distorts reality by causing you to question your memory, perception, or sanity, effectively undermining your confidence and autonomy. Understanding these core differences helps you recognize emotional abuse patterns and protect your mental well-being.
Psychological Impact of Guilt-Tripping
Guilt-tripping manipulates your emotions by inducing unnecessary guilt to control behavior, leading to increased anxiety and diminished self-esteem. Unlike gaslighting, which distorts reality to make you question your perceptions, guilt-tripping centers on exploiting your sense of responsibility and empathy. The psychological impact of guilt-tripping can result in chronic stress, self-doubt, and impaired decision-making that erodes your mental well-being over time.
How Gaslighting Affects Mental Health
Gaslighting profoundly impacts mental health by eroding your sense of reality and self-confidence, leading to chronic anxiety, depression, and confusion. Unlike guilt-tripping, which induces shame to manipulate emotions, gaslighting systematically distorts your perception, causing you to doubt your memories and judgment. This psychological manipulation creates a pervasive sense of helplessness and vulnerability, negatively affecting emotional stability and well-being.
Recognizing Signs of Guilt-Tripping in Relationships
Recognizing signs of guilt-tripping in relationships involves identifying behaviors where one partner manipulates your emotions to induce guilt and control your actions, often through subtle blame or passive-aggressive comments. Unlike gaslighting, which distorts your perception of reality, guilt-tripping targets your conscience and self-worth by making you feel responsible for their unhappiness or problems. Understanding these distinctions empowers you to set healthier boundaries and communicate more effectively in your relationships.
Identifying Gaslighting Tactics in Communication
Gaslighting tactics in communication often involve manipulating facts, denying previous statements, and questioning the victim's memory to create confusion and doubt. Unlike guilt-tripping, which appeals to emotions by inducing remorse or obligation, gaslighting aims to undermine the victim's perception of reality and sanity. Key indicators include persistent lying, contradiction of evidence, and minimizing the victim's feelings to control or dominate the conversation.
Why People Resort to Guilt-Tripping or Gaslighting
People resort to guilt-tripping or gaslighting as manipulative tactics to control others and gain power in relationships. Guilt-tripping exploits your sense of responsibility and empathy by making you feel undeserved guilt, while gaslighting distorts your perception of reality, causing self-doubt and confusion. Both behaviors stem from insecurity, fear of abandonment, or a desire to avoid accountability.
Breaking Free: Coping Strategies for Victims
Victims of guilt-tripping and gaslighting can regain control by recognizing manipulative patterns, such as distorted reality in gaslighting or emotional burden in guilt-tripping. Developing assertive communication skills and setting clear personal boundaries are crucial in preventing psychological abuse. Seeking support from trusted friends, therapists, or support groups enhances emotional resilience and facilitates effective coping strategies for breaking free from manipulation.
Seeking Help: When to Consult a Professional
Guilt-tripping and gaslighting involve manipulative psychological tactics that distort reality and evoke undue guilt, making professional intervention crucial when these behaviors cause significant emotional distress or confusion. Consulting a mental health professional, such as a psychologist or therapist, is essential if persistent feelings of anxiety, self-doubt, or depression arise from relational interactions dominated by these manipulations. Early intervention through counseling or therapy improves coping mechanisms, clarifies personal boundaries, and promotes mental well-being, preventing long-term psychological damage.
Infographic: Guilt-tripping vs Gaslighting
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com