Analyzing the financial benefits and long-term impact of renting versus buying a home reveals critical insights for making informed housing decisions. Discover which option suits your lifestyle and investment goals by exploring this article.
Table of Comparison
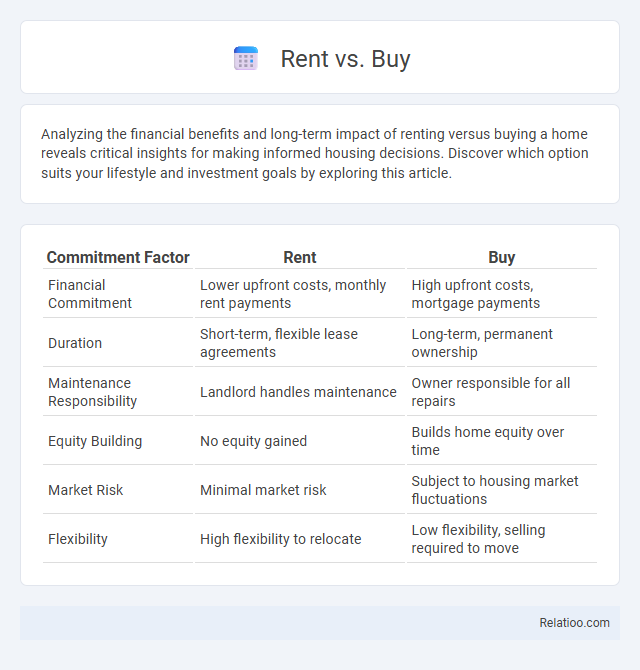
| Commitment Factor | Rent | Buy |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Commitment | Lower upfront costs, monthly rent payments | High upfront costs, mortgage payments |
| Duration | Short-term, flexible lease agreements | Long-term, permanent ownership |
| Maintenance Responsibility | Landlord handles maintenance | Owner responsible for all repairs |
| Equity Building | No equity gained | Builds home equity over time |
| Market Risk | Minimal market risk | Subject to housing market fluctuations |
| Flexibility | High flexibility to relocate | Low flexibility, selling required to move |
Understanding Rent vs Buy: Key Differences
Understanding rent vs buy involves comparing financial commitments, flexibility, and long-term investment benefits. Renting offers lower upfront costs and maintenance responsibilities, ideal for short-term living or uncertain locations. Buying requires significant initial investment, including down payments and property taxes, but builds equity and potential property appreciation over time.
Financial Implications of Renting vs Buying
Renting a home typically requires lower upfront costs, limited maintenance expenses, and flexibility, making it financially viable for short-term stays or uncertain markets. Buying a property involves higher initial investments, including down payments and closing costs, but offers long-term financial benefits such as equity accumulation, tax deductions on mortgage interest, and potential property value appreciation. Homeownership also entails ongoing costs like property taxes, insurance, and maintenance, which should be factored into the financial analysis when comparing renting versus buying.
Upfront Costs: Rental Deposits vs Down Payments
Upfront costs for renting typically include a security deposit equal to one or two months' rent, which is refundable at lease end if no damages occur. Buying a home demands a significantly larger down payment, often 5% to 20% of the property's purchase price, which directly impacts mortgage terms and monthly payments. Renters face lower initial financial barriers, while buyers must prepare for substantial upfront capital but potentially build equity over time.
Long-Term Investment Potential
Renting offers flexibility but provides no equity growth, making it less advantageous for long-term wealth accumulation. Buying a home, on the other hand, builds equity over time and can appreciate in value, serving as a significant long-term investment for your financial future. Your choice between rent and buy should weigh the potential for property value appreciation and equity buildup against short-term costs and lifestyle preferences.
Flexibility and Lifestyle Considerations
Renting offers maximum flexibility, allowing individuals to relocate easily without the burden of property maintenance, ideal for those with uncertain job locations or lifestyle changes. Buying a home provides stability and the potential for property appreciation, appealing to those seeking long-term roots and customization of their living space. Homeownership demands greater financial commitment and less mobility, making it a significant consideration for lifestyle planning and future goals.
Maintenance Responsibilities: Who Pays?
Renters typically pay no more than their monthly rent for maintenance, as landlords are responsible for repairs and upkeep under most lease agreements. Homeowners assume full financial responsibility for all maintenance costs, including unexpected repairs, routine servicing, and home improvements. Buyers considering purchasing a home must factor in ongoing maintenance expenses, which can significantly impact the total cost of ownership compared to renting.
Market Trends Impacting Renting and Buying
Recent market trends reveal rising home prices and increasing mortgage rates drive many consumers toward renting, while limited rental inventory and steady rent growth pressure renters to consider buying. Urbanization and remote work flexibility shape regional housing demands, influencing affordability and availability in both buying and renting markets. Economic uncertainty and shifting demographic preferences continue to impact decision-making, with millennials and Gen Z balancing short-term renting benefits against long-term homeownership investment.
Tax Benefits of Homeownership vs Renting
Homeownership offers significant tax benefits including mortgage interest deductions and property tax deductions, which can reduce taxable income substantially compared to renting. Renters do not receive these tax advantages, making homeownership financially advantageous, especially over the long term. Tax benefits often translate into lower effective housing costs, enhancing the overall value of buying a home versus renting.
Hidden Costs: What Renters and Buyers Should Know
Hidden costs significantly impact the financial equation in the rent vs buy decision, with renters facing unexpected fees such as security deposits, lease termination penalties, and rent increases, while buyers must consider property taxes, maintenance, homeowners insurance, and closing costs. Renters may underestimate the long-term expense of frequent moves and lack of equity building, whereas buyers should be aware of ongoing costs like HOA fees, repairs, and potential devaluation. Understanding these hidden expenses enables both renters and buyers to make more informed decisions about their housing investment and budget planning.
Making the Right Choice: Factors to Consider
Evaluating whether to rent or buy a home hinges on factors such as financial stability, market conditions, and long-term goals. Key considerations include comparing monthly costs, equity building potential, and flexibility requirements. Homebuyers should analyze interest rates, property taxes, maintenance expenses, and local real estate trends to make an informed decision.
Infographic: Rent vs Buy
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com