Inclusion in relationships ensures emotional acceptance and active participation, while accessibility focuses on removing barriers to interaction. Explore the distinctions and benefits of both inclusion and accessibility in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
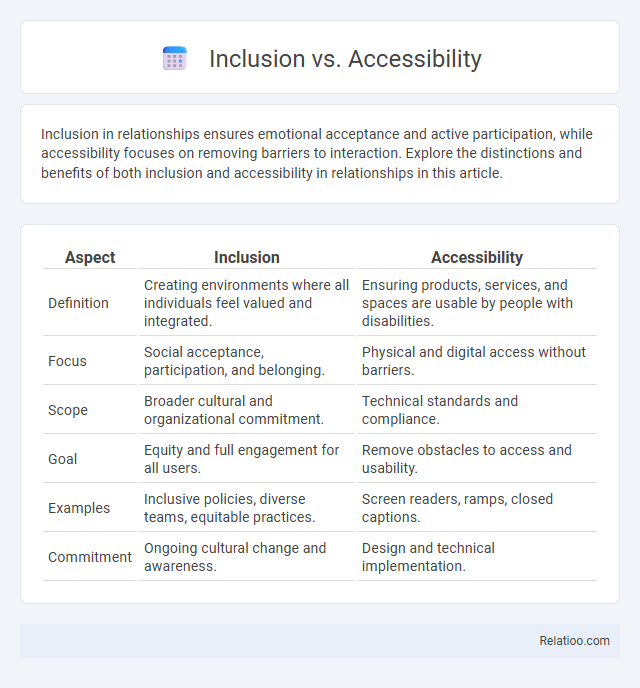
| Aspect | Inclusion | Accessibility |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Creating environments where all individuals feel valued and integrated. | Ensuring products, services, and spaces are usable by people with disabilities. |
| Focus | Social acceptance, participation, and belonging. | Physical and digital access without barriers. |
| Scope | Broader cultural and organizational commitment. | Technical standards and compliance. |
| Goal | Equity and full engagement for all users. | Remove obstacles to access and usability. |
| Examples | Inclusive policies, diverse teams, equitable practices. | Screen readers, ramps, closed captions. |
| Commitment | Ongoing cultural change and awareness. | Design and technical implementation. |
Understanding Inclusion and Accessibility
Inclusion emphasizes creating environments where diverse individuals feel valued and have equal opportunities to participate fully. Accessibility focuses on removing barriers in physical spaces, technology, and communication to ensure everyone, especially people with disabilities, can access services and information. Understanding inclusion and accessibility involves recognizing that while accessibility addresses practical needs, inclusion fosters a culture of acceptance and belonging for all.
Key Differences Between Inclusion and Accessibility
Inclusion ensures that Your environment embraces diverse individuals by offering equal opportunity and active participation, while accessibility concentrates on removing barriers for people with disabilities through specific adaptations or assistive technologies. Inclusion involves a broader cultural and organizational commitment to diversity, equity, and belonging, whereas accessibility is mainly about compliance with standards and legal requirements. Understanding these key differences helps organizations create truly supportive spaces where everyone's unique needs are recognized and met.
The Importance of Inclusive Design
Inclusive design ensures products and environments cater to diverse user needs, enhancing usability for people with different abilities and backgrounds. Accessibility focuses on removing barriers, enabling individuals with disabilities to fully participate, while inclusiveness promotes a sense of belonging and equal opportunity for all. Your commitment to inclusive design not only improves user experience but also fosters social equity and innovation.
Accessibility: Breaking Down Barriers
Accessibility focuses on creating environments, products, and services that are usable by individuals with diverse abilities, removing physical, digital, and attitudinal barriers. This ensures equal access to education, employment, technology, and public spaces, promoting independence and participation for people with disabilities. Implementing accessibility standards such as WCAG and ADA guidelines enhances usability for all users, supporting broader inclusiveness efforts.
Inclusive Practices in Education and Workplaces
Inclusive practices in education and workplaces prioritize creating environments where diverse individuals feel valued and supported, emphasizing tailored strategies that address specific needs rather than mere physical access. Accessibility focuses on removing barriers to ensure equal entry and participation for people with disabilities, incorporating assistive technologies and adaptable infrastructure. Inclusiveness extends beyond accessibility by fostering a culture of respect, representation, and active engagement, promoting equity through policies, training, and collaborative decision-making.
Legal Frameworks for Accessibility and Inclusion
Legal frameworks for accessibility and inclusion establish mandatory standards to ensure equal access and participation for individuals with disabilities across public and private sectors. Accessibility laws, such as the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and the EU's Accessibility Act, require the removal of physical, digital, and communication barriers, creating environments where inclusion can be realized effectively. Inclusiveness policies go beyond compliance by promoting proactive social integration and accommodation, fostering environments that respect diversity and support full participation in educational, employment, and civic spaces.
Common Misconceptions About Inclusion and Accessibility
Inclusion often gets confused with accessibility, but inclusion involves creating environments where everyone feels valued, whereas accessibility focuses specifically on removing barriers for people with disabilities. Common misconceptions include thinking that merely providing physical access or assistive technologies equals true inclusion, overlooking emotional and social aspects that foster belonging. Differentiating these terms is crucial for developing comprehensive strategies that address both tangible accommodations and inclusive attitudes in workplaces and communities.
Benefits of Prioritizing Both Inclusion and Accessibility
Prioritizing both inclusion and accessibility fosters a diverse environment where everyone, regardless of ability or background, can fully participate and contribute. This approach enhances innovation, productivity, and user satisfaction by ensuring equitable access and representation. Organizations that integrate inclusive practices and accessible design experience improved engagement, compliance with legal standards, and a stronger reputation for social responsibility.
Real-World Examples: Inclusion vs Accessibility
Inclusion ensures that diverse individuals actively participate in environments such as workplaces or schools, exemplified by companies implementing mentorship programs for employees with disabilities. Accessibility focuses on removing barriers, like providing wheelchair ramps and screen readers in public buildings or websites to accommodate users with different needs. Real-world practices combine both approaches when universities offer accessible online platforms and foster inclusive curricula that represent diverse cultures and abilities.
Strategies for Integrating Inclusion and Accessibility
Strategies for integrating inclusion and accessibility focus on creating environments where diversity is actively embraced and barriers are removed for all individuals, including those with disabilities. Your organization can implement universal design principles, provide assistive technologies, and foster inclusive policies that ensure equitable participation and representation. Continuous training and feedback loops help maintain a culture that values both accessibility and inclusiveness as foundational elements.
Infographic: Inclusion vs Accessibility
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com