Commitment in relationships involves dedication and long-term effort, while contentment reflects satisfaction with the present state. Explore the key differences and insights between commitment and contentment in this article.
Table of Comparison
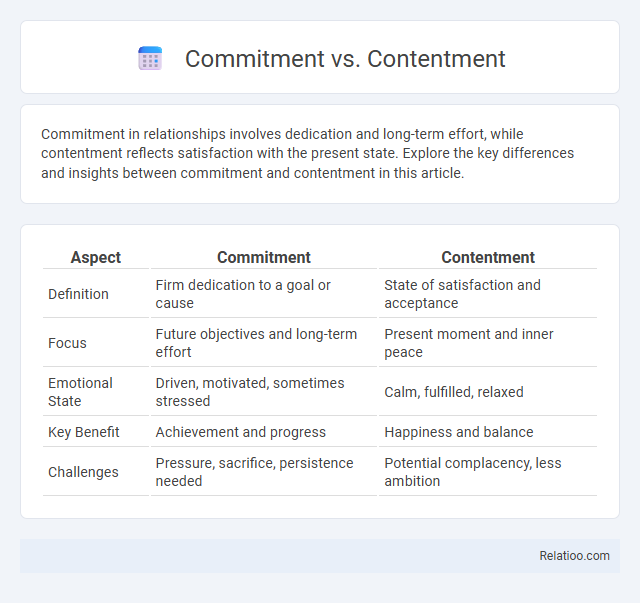
| Aspect | Commitment | Contentment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Firm dedication to a goal or cause | State of satisfaction and acceptance |
| Focus | Future objectives and long-term effort | Present moment and inner peace |
| Emotional State | Driven, motivated, sometimes stressed | Calm, fulfilled, relaxed |
| Key Benefit | Achievement and progress | Happiness and balance |
| Challenges | Pressure, sacrifice, persistence needed | Potential complacency, less ambition |
Understanding Commitment: Definition and Importance
Commitment refers to a steadfast dedication to a cause, relationship, or goal, often requiring consistent effort and sacrifices. Understanding commitment involves recognizing its role in fostering trust, reliability, and long-term success in personal and professional contexts. Its importance lies in driving perseverance, accountability, and meaningful achievements beyond temporary satisfaction or passive contentment.
Defining Contentment: Meaning and Significance
Contentment represents a state of satisfaction and acceptance with one's current circumstances, emphasizing inner peace over external achievements. This emotional equilibrium fosters resilience and positive mental health by reducing stress and fostering gratitude. Defining contentment involves recognizing it as a proactive mindset that balances desires with appreciation, crucial for sustainable happiness and well-being.
The Psychology Behind Commitment
Commitment in psychology involves a deliberate decision to invest time, effort, and emotional energy into a person, goal, or relationship, driven by intrinsic motivation and long-term values. Contentment reflects a state of satisfaction and acceptance with current circumstances, promoting emotional stability without the pressure of ongoing striving. You can achieve balanced well-being by understanding the interplay between commitment's proactive drive and contentment's restful acceptance.
The Science of Contentment
The science of contentment reveals that your brain releases dopamine and serotonin when you achieve a state of satisfaction, highlighting the neurological basis of happiness. Commitment involves sustained effort toward long-term goals, which triggers goal-directed dopamine pathways, whereas contentment stems from acceptance and gratitude, promoting parasympathetic nervous system activation and emotional balance. Understanding these distinctions helps you cultivate lasting well-being by balancing ambition with mindful appreciation.
Key Differences Between Commitment and Contentment
Commitment involves a deliberate dedication to a goal or relationship, often requiring ongoing effort and sacrifice, while contentment is a state of satisfaction and peace with one's current circumstances without the need for change. Key differences lie in commitment's future-oriented nature and active engagement versus contentment's present-focused acceptance and emotional fulfillment. Commitment drives growth and progress, whereas contentment emphasizes stability and inner calm.
How Commitment Influences Personal Growth
Commitment drives your personal growth by fostering discipline, resilience, and goal-oriented behavior that contentment alone may not inspire. While contentment reflects satisfaction with the present, commitment pushes you to challenge boundaries and develop new skills. This proactive mindset enhances self-awareness and long-term fulfillment beyond immediate happiness.
Contentment’s Role in Emotional Well-being
Contentment plays a crucial role in emotional well-being by fostering a sense of inner peace and satisfaction with your current circumstances, reducing stress and anxiety. Unlike commitment, which drives long-term goals, contentment centers on appreciating the present moment and embracing gratitude, which supports mental health resilience. Prioritizing contentment helps balance ambition and happiness, enhancing overall life satisfaction and emotional stability.
Finding Balance: Commitment Without Losing Contentment
Achieving a balance between commitment and contentment requires recognizing when dedication to goals starts to erode your inner peace. You can maintain motivation and focus while still appreciating the present moments that bring satisfaction and happiness. Prioritizing self-awareness helps prevent burnout by ensuring your commitment aligns with your personal values and overall well-being.
Practical Tips to Nurture Both Commitment and Contentment
Nurturing both commitment and contentment requires balancing dedication with appreciation in your daily life. Set clear, achievable goals to strengthen commitment while practicing gratitude and mindfulness to cultivate contentment in the present moment. Regularly reflecting on your progress helps maintain motivation and satisfaction, ensuring sustained personal and professional growth.
Commitment vs Contentment: Which Leads to Lasting Happiness?
Commitment involves dedicating oneself to meaningful goals and relationships, fostering a sense of purpose that contributes to lasting happiness. Contentment reflects a state of satisfaction and acceptance, promoting peace but potentially limiting growth and fulfillment without proactive engagement. Research indicates that while contentment provides immediate emotional stability, commitment cultivates enduring happiness by encouraging personal development and resilience.
Infographic: Commitment vs Contentment
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com