Enmeshment involves blurred boundaries leading to an over-involvement in others' emotions, while codependency is characterized by excessive reliance on another for approval and identity. Discover the key differences and how to navigate these dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
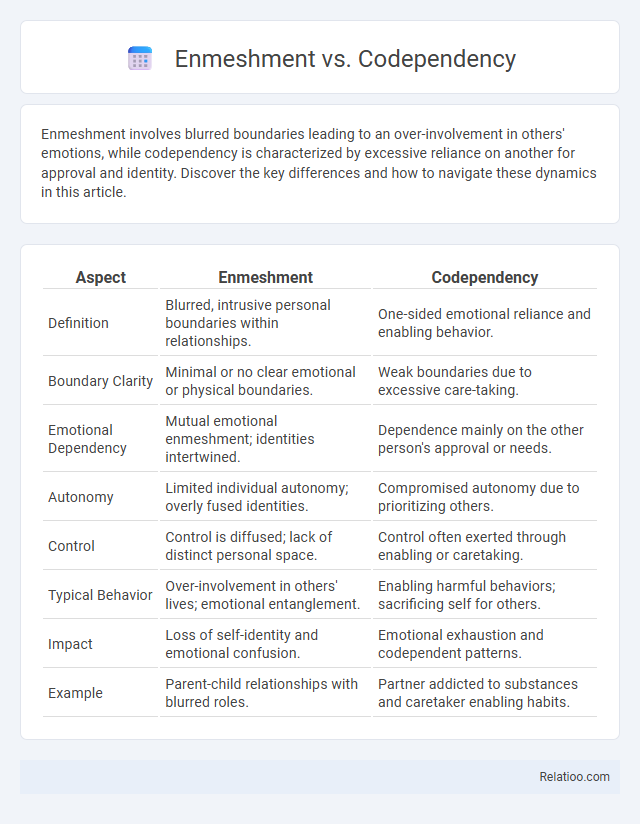
| Aspect | Enmeshment | Codependency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Blurred, intrusive personal boundaries within relationships. | One-sided emotional reliance and enabling behavior. |
| Boundary Clarity | Minimal or no clear emotional or physical boundaries. | Weak boundaries due to excessive care-taking. |
| Emotional Dependency | Mutual emotional enmeshment; identities intertwined. | Dependence mainly on the other person's approval or needs. |
| Autonomy | Limited individual autonomy; overly fused identities. | Compromised autonomy due to prioritizing others. |
| Control | Control is diffused; lack of distinct personal space. | Control often exerted through enabling or caretaking. |
| Typical Behavior | Over-involvement in others' lives; emotional entanglement. | Enabling harmful behaviors; sacrificing self for others. |
| Impact | Loss of self-identity and emotional confusion. | Emotional exhaustion and codependent patterns. |
| Example | Parent-child relationships with blurred roles. | Partner addicted to substances and caretaker enabling habits. |
Understanding Enmeshment: Definition and Key Traits
Enmeshment refers to a relationship dynamic where personal boundaries are blurred, causing individuals to lose their sense of autonomy and self-identity. Key traits include excessive emotional involvement, lack of privacy, and difficulty distinguishing one's own feelings from others. This differs from codependency, which involves enabling dysfunctional behavior, whereas enmeshment emphasizes boundary dissolution and identity fusion.
What Is Codependency? Core Characteristics
Codependency is a dysfunctional behavioral pattern where Your identity and self-worth become excessively tied to another person's needs and emotions, often sacrificing Your own well-being. Core characteristics include a strong desire to please others, difficulty setting boundaries, and an unhealthy reliance on approval and validation. Unlike enmeshment, which involves blurred family boundaries, codependency specifically centers on enabling harmful behaviors and maintaining unhealthy attachment dynamics.
Origins: How Enmeshment and Codependency Develop
Enmeshment often stems from overinvolved family dynamics where boundaries between members are blurred, causing individuals to lose their sense of self. Codependency typically develops in relationships characterized by imbalance, where you prioritize others' needs at the expense of your own emotional health. Both originate from early attachment experiences but differ in how personal identity and emotional dependency are shaped within the family system.
Emotional Boundaries: Enmeshment vs Codependency
Emotional boundaries are significantly blurred in both enmeshment and codependency, but enmeshment involves a mutual loss of self where individual identities are intertwined within family dynamics. In contrast, codependency centers on one person excessively relying on another for emotional support and validation, often enabling destructive behaviors. Understanding how your personal emotional boundaries are affected can help differentiate these patterns and promote healthier relationships.
Signs You May Be Enmeshed
Signs you may be enmeshed include difficulty setting personal boundaries, feeling responsible for others' emotions, and a blurred sense of self-identity. In enmeshment, individuals often experience excessive emotional involvement and dependency within family or close relationships, differing from codependency by lacking clear individual roles. Recognizing these patterns is crucial to fostering healthy autonomy and emotional independence.
Recognizing Codependent Behaviors
Recognizing codependent behaviors involves identifying patterns such as excessive people-pleasing, a strong need for approval, and difficulty setting healthy boundaries. These behaviors often overlap with enmeshment, where personal identities and emotions become intertwined with others, leading to blurred boundaries and a loss of autonomy. Understanding these distinctions helps in addressing unhealthy relational dynamics and fostering emotional independence.
Psychological Impacts: Enmeshment Compared to Codependency
Enmeshment creates blurred boundaries and an over-involvement in each other's emotional lives, leading to identity confusion and difficulty in establishing autonomy. Codependency involves a dysfunctional reliance on others for self-worth, often resulting in enabling behaviors and emotional exhaustion. Psychological impacts of enmeshment typically include low self-esteem and anxiety due to the loss of personal boundaries, while codependency often manifests as chronic people-pleasing and an impaired sense of self separate from others.
Enmeshment vs Codependency in Relationships
Enmeshment and codependency both involve unhealthy relationship dynamics but differ significantly in emotional boundaries; enmeshment occurs when personal boundaries are blurred, leading to an over-involvement in each other's emotions and identities, while codependency centers on an excessive reliance on another for approval and self-worth. Understanding these distinctions helps you recognize patterns where your emotional independence is compromised, especially in intimate or family relationships. Addressing these issues requires setting clear boundaries and fostering individual autonomy to create healthier, more balanced connections.
Healing and Setting Healthy Boundaries
Healing from enmeshment and codependency requires recognizing blurred personal boundaries and fostering individual autonomy. Establishing healthy boundaries involves consistent self-awareness, clear communication, and prioritizing one's emotional needs without guilt. Therapeutic approaches like cognitive-behavioral therapy and boundary-setting exercises facilitate recovery by reinforcing self-identity and resilience.
Seeking Help: Therapy and Recovery Strategies
Therapy for enmeshment and codependency often involves setting healthy boundaries and developing individual identity, which is essential for your emotional recovery. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and family therapy are effective strategies to address the underlying dynamics and improve interpersonal relationships. Professional support guides you through establishing autonomy while fostering healthier connections, facilitating long-term healing and resilience.
Infographic: Enmeshment vs Codependency
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com