An alliance is a formal agreement between nations or organizations for mutual benefit and long-term cooperation, while a coalition is a temporary collaboration created to achieve a specific goal. Discover the key differences and strategic implications of alliances versus coalitions in this article.
Table of Comparison
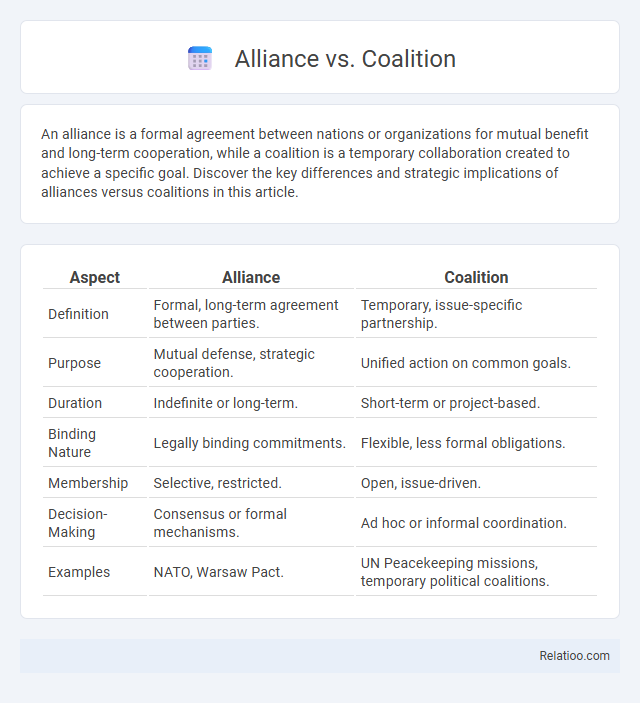
| Aspect | Alliance | Coalition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal, long-term agreement between parties. | Temporary, issue-specific partnership. |
| Purpose | Mutual defense, strategic cooperation. | Unified action on common goals. |
| Duration | Indefinite or long-term. | Short-term or project-based. |
| Binding Nature | Legally binding commitments. | Flexible, less formal obligations. |
| Membership | Selective, restricted. | Open, issue-driven. |
| Decision-Making | Consensus or formal mechanisms. | Ad hoc or informal coordination. |
| Examples | NATO, Warsaw Pact. | UN Peacekeeping missions, temporary political coalitions. |
Understanding Alliances and Coalitions
Understanding alliances involves recognizing formal agreements between two or more entities to achieve common goals, typically characterized by long-term commitments and shared responsibilities. Coalitions are often more flexible, temporary partnerships formed to address specific issues or objectives, allowing participants to maintain individual autonomy while collaborating strategically. Your ability to discern these differences enhances effective decision-making in both diplomatic and organizational contexts.
Key Differences Between Alliances and Coalitions
Alliances are long-term agreements between states or organizations based on formal treaties and shared strategic interests, while coalitions are temporary collaborations formed to address specific, short-term objectives or crises. Alliances often involve mutual defense commitments and institutional frameworks, whereas coalitions emphasize flexibility and rapid assembly without comprehensive legal obligations. The key difference lies in the duration, formality, and scope of cooperation, with alliances fostering sustained partnerships and coalitions enabling ad hoc cooperation.
Historical Examples of Alliances
Historical examples of alliances include the Triple Alliance of World War I, where Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy pledged mutual support against common enemies. The Allied Powers in World War II, comprising the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union, demonstrated the power of strategic collaboration to defeat Axis forces. Understanding these alliances highlights how your nation's strategic partnerships can shape global political and military outcomes.
Prominent Coalition Formations in History
Prominent coalition formations in history include the Allied Powers during World War II, a strategic military alliance that combined the forces of the United States, the Soviet Union, and the United Kingdom to defeat the Axis Powers. The Quadruple Alliance, established after the Napoleonic Wars in 1815, was a significant coalition aimed at maintaining the balance of power in Europe, involving Britain, Austria, Prussia, and Russia. Unlike coalitions formed for temporary objectives, alliances such as the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) represent long-term commitments between member states for collective defense and political cooperation.
Purposes and Objectives: Alliance vs Coalition
An alliance is a formal agreement between countries or organizations aimed at achieving specific long-term strategic objectives, often involving mutual defense or economic cooperation. A coalition is a temporary partnership formed to address short-term goals or crises, emphasizing flexibility and rapid collaboration among diverse actors. Understanding the differences allows you to select the most effective structure for your diplomatic or business objectives.
Structural Dynamics: How Alliances and Coalitions Operate
Alliances operate through formal agreements with defined roles and commitments, often involving comprehensive treaties and shared long-term objectives. Coalitions feature more flexible and temporary collaborations, where diverse entities unite for a specific goal without binding obligations, enabling rapid coordination and adaptability. Understanding these structural dynamics helps your organization navigate cooperation, optimizing resource sharing and decision-making within varied political or strategic environments.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Alliances
Alliances provide strategic advantages such as shared resources, enhanced security, and increased political influence, but can suffer from issues like conflicting objectives, dependency risks, and coordination challenges. Advantages include improved collective defense, pooled expertise, and stronger bargaining power in international relations. Disadvantages involve potential loss of autonomy, uneven burden-sharing, and difficulties maintaining long-term commitment among members.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Coalitions
Coalitions bring together diverse groups to achieve common goals, leveraging varied resources and expertise for greater impact. Their flexibility allows for dynamic partnerships, but differences in priorities and trust issues often lead to internal conflicts and unstable commitments. Unlike formal alliances, coalitions may struggle with coordination and decision-making due to a lack of centralized authority.
Factors Influencing the Choice: Alliance or Coalition
The choice between forming an alliance or a coalition primarily depends on factors such as shared objectives, level of trust, and the scope of collaboration required among parties. Alliances often involve long-term commitments with clear, mutual benefits and tighter integration, whereas coalitions are typically more temporary and issue-specific, allowing for flexible participation. Political alignment, resource availability, and strategic goals also heavily influence whether entities opt for the structured cooperation of an alliance or the broader, often more fluid nature of a coalition.
Future Trends in Alliances and Coalitions
Future trends in alliances and coalitions emphasize increased digital integration and data sharing to enhance strategic decision-making and operational efficiency. You can expect collaborative networks to expand beyond traditional geopolitical boundaries, incorporating artificial intelligence and blockchain for improved trust and transparency. These advancements will redefine how entities align resources and goals, making partnerships more adaptive and resilient in a rapidly changing global landscape.
Infographic: Alliance vs Coalition
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com